Abstract
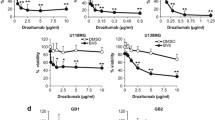
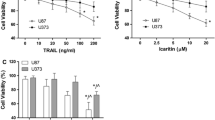
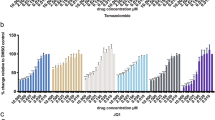
The major aim of this study was to develop novel therapeutic approaches to potentiate and reactivate apoptosis induced by TNF-Related Apoptosis Inducing Ligand (TRAIL) in malignant glioma. Analysis of five glioma cell lines (U87, U251, U373, MZ-54 and MZ-18) indicated that only two of the cell lines were sensitive to apoptosis induced by TRAIL alone. TRAIL resistance was not correlated to expression levels of the death receptors DR4 and DR5 or the decoy receptors DcR1 and DcR2, suggesting that it was mediated by inactivation of TRAIL-induced downstream signalling. Activation of the BH3 only protein Bid and subsequent activation of the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway are known to play a pivotal role in TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Since this process is blocked by overexpression of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members, we analyzed the therapeutic potential of BH3 mimetics in potentiating TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Treatment with TRAIL in combination with the specific Bcl-2 inhibitor HA14-1 and the Bcl-2/Bcl-xL inhibitor BH3I-2′ potently enhanced apoptosis in TRAIL-sensitive U87 cells in a dose-dependent fashion. TRAIL-induced apoptosis was significantly reactivated by HA14-1 and BH3I-2′ in one (U343) and two (MZ-54 and MZ-18) of three investigated TRAIL-insensitive cell lines, respectively. Knockdown of the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family member Mcl-1 by RNA interference had no additional effect on apoptosis induced by TRAIL and HA14-1 in U87 and U343 cells. Our data indicate that Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL play fundamental roles in TRAIL resistance of malignant glioma and suggest that using TRAIL or agonistic TRAIL receptor antibodies in combination with BH3 mimetics may represent a promising approach to reactivate apoptosis in therapy-resistant high grade gliomas.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulfoxide
- DR4:
-
Death receptor 4
- DR5:
-
Death receptor 5
- TRAIL:
-
Tumor necrosis factor related apoptosis inducing ligand
References
Kleihues P, Louis DN, Scheithauer BW, Rorke LB, Reifenberger G, Burger PC, Cavenee WK (2002) The WHO classification of tumors of the nervous system. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 61:215–225; discussion 226–219
Maher EA, Furnari FB, Bachoo RM, Rowitch DH, Louis DN, Cavenee WK, DePinho RA (2001) Malignant glioma: genetics and biology of a grave matter. Genes Dev 15:1311–1333
van den Bent MJ, Hegi ME, Stupp R (2006) Recent developments in the use of chemotherapy in brain tumours. Eur J Cancer 42:582–588
Bogler O, Weller M (2002) Apoptosis in gliomas, and its role in their current and future treatment. Front Biosci 7:e339–e353
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Brenner C (2007) Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization in cell death. Physiol Rev 87:99–163
Shoemaker AR, Oleksijew A, Bauch J, Belli BA, Borre T, Bruncko M, Deckwirth T, Frost DJ, Jarvis K, Joseph MK, Marsh K, McClellan W, Nellans H, Ng S, Nimmer P, O’Connor JM, Oltersdorf T, Qing W, Shen W, Stavropoulos J, Tahir SK, Wang B, Warner R, Zhang H, Fesik SW, Rosenberg SH, Elmore SW (2006) A small-molecule inhibitor of Bcl-XL potentiates the activity of cytotoxic drugs in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res 66:8731–8739
Cory S, Adams JM (2005) Killing cancer cells by flipping the Bcl-2/Bax switch. Cancer Cell 8:5–6
Bouralexis S, Findlay DM, Evdokiou A (2005) Death to the bad guys: targeting cancer via Apo2L/TRAIL. Apoptosis 10:35–51
Srivastava RK (2001) TRAIL/Apo-2L: mechanisms and clinical applications in cancer. Neoplasia 3:535–546
Fulda S, Wick W, Weller M, Debatin KM (2002) Smac agonists sensitize for Apo2L/TRAIL- or anticancer drug-induced apoptosis and induce regression of malignant glioma in vivo. Nat Med 8:808–815
Hao C, Beguinot F, Condorelli G, Trencia A, Van Meir EG, Yong VW, Parney IF, Roa WH, Petruk KC (2001) Induction and intracellular regulation of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) mediated apotosis in human malignant glioma cells. Cancer Res 61:1162–1170
Song JH, Song DK, Pyrzynska B, Petruk KC, Van Meir EG, Hao C (2003) TRAIL triggers apoptosis in human malignant glioma cells through extrinsic and intrinsic pathways. Brain Pathol 13:539–553
Kögel D, Schomburg R, Copanaki E, Prehn JH (2005) Regulation of gene expression by the amyloid precursor protein: inhibition of the JNK/c-Jun pathway. Cell Death Differ 12:1–9
Rieger J, Naumann U, Glaser T, Ashkenazi A, Weller M (1998) APO2 ligand: a novel lethal weapon against malignant glioma? FEBS Lett 427:124–128
Jaganathan J, Petit JH, Lazio BE, Singh SK, Chin LS (2002) Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-mediated apoptosis in established and primary glioma cell lines. Neurosurg Focus 13:ecp1
Li YC, Tzeng CC, Song JH, Tsia FJ, Hsieh LJ, Liao SJ, Tsai CH, Van Meir EG, Hao C, Lin CC (2006) Genomic alterations in human malignant glioma cells associate with the cell resistance to the combination treatment with tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand and chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res 12:2716–2729
Fulda S, Meyer E, Debatin KM (2002) Inhibition of TRAIL-induced apoptosis by Bcl-2 overexpression. Oncogene 21:2283–2294
Jiang Z, Zheng X, Rich KM (2003) Down-regulation of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL expression with bispecific antisense treatment in glioblastoma cell lines induce cell death. J Neurochem 84:273–281
Feng WY, Liu FT, Patwari Y, Agrawal SG, Newland AC, Jia L (2003) BH3-domain mimetic compound BH3I-2′ induces rapid damage to the inner mitochondrial membrane prior to the cytochrome c release from mitochondria. Br J Haematol 121:332–340
Degterev A, Lugovskoy A, Cardone M, Mulley B, Wagner G, Mitchison T, Yuan J (2001) Identification of small-molecule inhibitors of interaction between the BH3 domain and Bcl-xL. Nat Cell Biol 3:173–182
Wang JL, Liu D, Zhang ZJ, Shan S, Han X, Srinivasula SM, Croce CM, Alnemri ES, Huang Z (2000) Structure-based discovery of an organic compound that binds Bcl-2 protein and induces apoptosis of tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:7124–7129
Chen S, Dai Y, Harada H, Dent P, Grant S (2007) Mcl-1 down-regulation potentiates ABT-737 lethality by cooperatively inducing Bak activation and Bax translocation. Cancer Res 67:782–791
van Delft MF, Wei AH, Mason KD, Vandenberg CJ, Chen L, Czabotar PE, Willis SN, Scott CL, Day CL, Cory S, Adams JM, Roberts AW, Huang DC (2006) The BH3 mimetic ABT-737 targets selective Bcl-2 proteins and efficiently induces apoptosis via Bak/Bax if Mcl-1 is neutralized. Cancer Cell 10:389–399
Knight MJ, Riffkin CD, Muscat AM, Ashley DM, Hawkins CJ (2001) Analysis of FasL and TRAIL induced apoptosis pathways in glioma cells. Oncogene 20:5789–5798
Martin S, Toquet C, Oliver L, Cartron PF, Perrin P, Meflah K, Cuillere P, Vallette FM (2001) Expression of bcl-2, bax and bcl-xl in human gliomas: a re-appraisal. J Neurooncol 52:129–139
Yamada H, Tada-Oikawa S, Uchida A, Kawanishi S (1999) TRAIL causes cleavage of bid by caspase-8 and loss of mitochondrial membrane potential resulting in apoptosis in BJAB cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 265:130–133
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Hildegard Schweers and Monika Herr for excellent technical assistance. This study was supported by the Wilhelm Sander Stiftung (grant 2005.067.1) to DK and by Science Foundation Ireland to JHMP.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hetschko, H., Voss, V., Horn, S. et al. Pharmacological inhibition of Bcl-2 family members reactivates TRAIL-induced apoptosis in malignant glioma. J Neurooncol 86, 265–272 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-007-9472-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-007-9472-6