Abstract
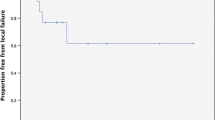
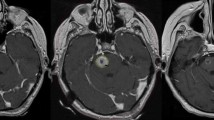
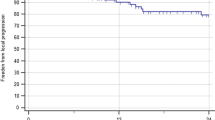
Purpose: To assess clinical and imaging outcomes in patients treated with Gamma Knife stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) for brainstem metastases. Materials and methods: We reviewed all patients with brain metastases treated with SRS at the University of California, San Francisco from 1991–2005 to identify patients who had SRS to a brainstem metastasis. Survival time and freedom from progression (FFP) were calculated from date of SRS using the Kaplan–Meier method. Prognostic factors were evaluated using the log-rank test and Cox proportional hazards model. Results: From 1991 through 2005, 42 consecutive patients with brainstem metastases had SRS to 44 lesions (seven midbrain, 31 pontine, and six medullary) in 42 sessions. Primary diagnoses included 14 cases of lung cancer (one small-cell), 10 melanoma, 12 breast cancer, five renal cell, and one unknown. The median age was 55 years (range, 25–79). The median survival time was 9 months after SRS. Longer survival time was associated with single metastasis, non-melanoma histology, and extracranial disease control. The median target volume was 0.26 ml (0.015–2.8 ml) and the median prescribed dose was 16.0 Gy (10.0–19.8 Gy). Brainstem lesion FFP was 90% at 6 months and 77% at 1 year. Four patients had brainstem complications following treatment. Poor brainstem outcome was associated with melanoma and renal cell histology as well as brainstem lesion volume ≥1 ml. Conclusions: In this series, SRS using a median dose of 16 Gy provided excellent local control with relatively low morbidity in patients with brainstem metastases less than 1 ml or non-melanoma, non-renal cell histology.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Posner JB, Chernik NL (1978) Intracranial metastases from systemic cancer. Adv Neurol 19:579–592
Patchell RA (2003) The management of brain metastases. Cancer Treat Rev 29:533–540
Schouten LJ, Rutten J, Huveneers HA, Twijnstra A (2002) Incidence of brain metastases in a cohort of patients with carcinoma of the breast, colon, kidney, and lung and melanoma. Cancer 94:2698–2705
Barnholtz-Sloan JS, Sloan AE, Davis FG, Vigneau FD, Lai P, Sawaya RE (2004) Incidence proportions of brain metastases in patients diagnosed (1973 to 2001) in the Metropolitan Detroit Cancer Surveillance System. J Clin Oncol 22:2865–2872
Chason JL, Walker FB, Landers JW (1963) Metastatic carcinoma in the central nervous system and dorsal root ganglia. A prospective autopsy study. Cancer 16:781–787
Soffietti R, Ruda R, Mutani R (2002) Management of brain metastases. J Neurol 249:1357–1369
Andrews DW, Scott CB, Sperduto PW, Flanders AE, Gaspar LE, Schell MC, Werner-Wasik M, Demas W, Ryu J, Bahary JP, Souhami L, Rotman M, Mehta MP, Curran WJ Jr. (2004) Whole brain radiation therapy with or without stereotactic radiosurgery boost for patients with one to three brain metastases: phase III results of the RTOG 9508 randomised trial. Lancet 363:1665–1672
Aoyama H, Shirato H, Tago M, Nakagawa K, Toyoda T, Hatano K, Kenjyo M, Oya N, Hirota S, Shioura H, Kunieda E, Inomata T, Hayakawa K, Katoh N, Kobashi G (2006) Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole-brain radiation therapy vs. stereotactic radiosurgery alone for treatment of brain metastases: a randomized controlled trial. Jama 295:2483–2491
Chidel MA, Suh JH, Reddy CA, Chao ST, Lundbeck MF, Barnett GH (2000) Application of recursive partitioning analysis and evaluation of the use of whole brain radiation among patients treated with stereotactic radiosurgery for newly diagnosed brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 47:993–999
Flickinger JC, Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD, Coffey RJ, Goodman ML, Shaw EG, Hudgins WR, Weiner R, Harsh GRt, Sneed PK et al (1994) A multi-institutional experience with stereotactic radiosurgery for solitary brain metastasis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 28:797–802
Goodman KA, Sneed PK, McDermott MW, Shiau CY, Lamborn KR, Chang S, Park E, Wara WM, Larson DA (2001) Relationship between pattern of enhancement and local control of brain metastases after radiosurgery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 50:139–146
Kondziolka D, Patel A, Lunsford LD, Kassam A, Flickinger JC (1999) Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole brain radiotherapy versus radiotherapy alone for patients with multiple brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 45:427–434
Sneed PK, Lamborn KR, Forstner JM, McDermott MW, Chang S, Park E, Gutin PH, Phillips TL, Wara WM, Larson DA (1999) Radiosurgery for brain metastases: is whole brain radiotherapy necessary? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 43:549–558
Fuentes S, Delsanti C, Metellus P, Peragut JC, Grisoli F, Regis J (2006) Brainstem metastases: management using gamma knife radiosurgery. Neurosurgery 58:37–42; discussion 37–42
Huang CF, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD (1999) Stereotactic radiosurgery for brainstem metastases. J Neurosurg 91:563–568
Hussain A, Brown PD, Stafford SL, Pollock BE (2007) Stereotactic radiosurgery for brainstem metastases: Survival, tumor control, and patient outcomes. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 67:521–524
Shuto T, Fujino H, Asada H, Inomori S, Nagano H (2003) Gamma knife radiosurgery for metastatic tumours in the brain stem. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 145:755–760
Yen CP, Sheehan J, Patterson G, Steiner L (2006) Gamma knife surgery for metastatic brainstem tumors. J Neurosurg 105:213–219
Lindquist C (1995) Gamma knife radiosurgery. Semin Radiat Oncol 5:197–202
Wu A, Lindner G, Maitz AH, Kalend AM, Lunsford LD, Flickinger JC, Bloomer WD (1990) Physics of gamma knife approach on convergent beams in stereotactic radiosurgery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 18:941–949
Flickinger JC, Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD, Kassam A, Phuong LK, Liscak R, Pollock B (2000) Development of a model to predict permanent symptomatic postradiosurgery injury for arteriovenous malformation patients. Arteriovenous Malformation Radiosurgery Study Group. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 46:1143–1148
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kased, N., Huang, K., Nakamura, J.L. et al. Gamma Knife radiosurgery for brainstem metastases: the UCSF experience. J Neurooncol 86, 195–205 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-007-9458-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-007-9458-4