Abstract
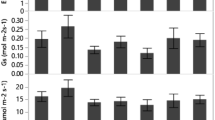
Abies fabri (Mast.) Craib is an endemic and dominant species in typical sub-alpine dark coniferous forests distributed in mountainous regions of the eastern Tibetan Plateau, China. We investigated the ecophysiological responses of A. fabri seedlings to short-term artificially-applied drought, nitrogen addition alone, and the combination of these treatments. Drought was created by excluding natural precipitation with an automatically controlled plastic roof that covered the seedlings. Nitrogen fertilization was applied weekly by spraying over seedlings with ammonium nitrate solution. Experiment results showed that drought caused a reduction in photosynthetic nitrogen use efficiency and leaf mass per area. Nitrogen addition enhanced photosynthetic performance by increasing net photosynthetic rate. In the drought plots, nitrogen addition increased net photosynthetic rate and instantaneous water use efficiency. These results showed that applied nitrogen improved plant water use efficiency and N accumulation in plant organs under drought conditions. Especially under drought conditions more N was concentrated into needles by applied nitrogen as compared with other organs. In conclusion, our results indicated that the combination of nitrogen addition and drought may result in positive effects on A. fabri seedlings in the short-term.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexieva V, Sergiev I, Mapelli S, Karanov E (2001) The effect of drought and ultraviolet radiation growth and stress markers in pea and wheat. Plant Cell Environ 24:1337–1344
Ashraf M, Foolad MR (2007) Role of glycine betaine and proline in improving plant abiotic stress resistance. Environ Exp Bot 59:206–216
Bacelar EA, Moutinho-Pereira JM, Goncalves BC, Ferreira HF, Correia CM (2007) Changes in growth, gas exchange, xylem hydraulic properties and water use efficiency of three olive cultivars under contrasting water availability regimes. Environ Exp Bot 60:183–192
Bobbink R, Hicks K, Galloway J (2010) Global assessment of nitrogen deposition effects on terrestrial plant diversity: a synthesis. Ecol Appl 20:30–59
Chen SP, Bai YF, Zhang LX, Han XG (2005) Comparing physiological responses of two dominant grass species to nitrogen addition in Xilin River Basin of China. Environ Exp Bot 53:65–75
DaMatta FM, Loos RA, Silva EA, Loureiro ME, Ducatti C (2002) Effects of soil water deficit and nitrogen nutrition on water relations and photosynthesis of pot-grown Coffea canephora Pierre. Trees 16:555–558
Evans JR (1989) Photosynthesis and nitrogen relationships in leaves of C3 plants. Oecologia 78:9–19
Field C, Merino J, Mooney HA (1983) Compromises between water-use efficiency and nitrogen-use efficiency in five species of California evergreens. Oecologia 60:384–389
Geßler A, Jung K, Gasche R, Papen H, Heidenfelder A, Borner E, Metzler B, Augustin S, Hildebrand E, Rennenberg H (2005) Climate and forest management influence nitrogen balance of European beech forests: microbial N transformations and inorganic N transformations and inorganic N net uptake capacity of mycorrhizal roots. Eur J For Res 124:95–111
Graciano C, Guiamét JJ, Goya JF (2005) Impact of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilization on drought responses in Eucalyptus grandis seedlings. For Ecol Manag 212:40–49
Guo JY, Yang Y, Wang GX, Yang LD, Sun XY (2010) Ecophysiological responses of Abies fabri seedlings to drought stress and nitrogen addition. Physiol Plant 139:335–347
Li MH, Xiao WF, Shi PL, Wang SG, Zhong YD, Liu XL, Wang XD, Cai XH, Shi ZM (2008) Nitrogen and carbon source-sink relationships in trees at the Himalayan treelines compared with lower elevations. Plant cell Environ 31(10):1377–1387
Lu YW, Duan BL, Zhang XL, Korpelainen H, Berninger F, Li CY (2009) Intraspecific variation in drought response of Populus cathayana grown under ambient and enhanced UV-B radiation. Ann For Sci 66:163
Makino A, Osmond B (1991) Effects of nitrogen nutrition on nitrogen partitioning between chloroplasts and mitochondria in pea and wheat. Plant Physiol 96:355–362
Martin T, Oswald O, Graham IA (2002) Arabidopsis seedling growth, storage lipid mobilization and photosynthetic gene expression are regulated by carbon: nitrogen availability. Plant Physiol 128:472–481
Mo JM, Li DJ, Gundersen P (2008) Seedling growth response of two tropical tree species to nitrogen deposition in southern China. Eur J For Res 127:275–283
Morgan JA (1986) The effects of N nutrition on the water relations and gas exchange characteristics of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Physiol 80:52–58
Nelson DW, Sommers LE (1982) Total carbon, organic carbon and organic matter. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis, Part 2. American Society of Agronomy and Soil Science, Madison, pp 539–579
Nikiema P, Nzokou P, Rothstein D (2011) Effects of groundcover management on soil properties, tree physiology, foliar chemistry and growth in a newly established Fraser fir (Abies fraseri [Pursh] Poir). New For. doi:10.1007/s11056-011-9274-8 (in press)
Nilsson LO, Wiklund K (1994) Nitrogen uptake in a Norway spruce stand following ammonium sulphate application, fertilization, irrigation, drought and nitrogen-free-fertilization. Plant Soil 164:221–228
Oliet JA, Planelles R, Artero F, Valverde R, Jacobs DF, Segura ML (2011) Field performance of Pinus halepensis planted in Mediterranean arid conditions: relative influence of seedling morphology and mineral nutrition. New For 37(3):313–331
Otoo E, Ishii R, Kumura A (1989) Interaction of nitrogen addition and soil water stress on photosynthesis and transpiration in rice. Jpn J Crop Sci 58(3):424–429
Patterson TB, Guy RD, Dang QL (1997) Whole-plant nitrogen- and water-relations traits, and their associated trade-offs, in adjacent muskeg and upland boreal spruce species. Oecologia 110:160–168
Phoenix GK, Hicks WK, Cinderby S, Kuylenstierna JCI, Stock WD, Dentener FJ, Giller KE, Austin AT, Lefroy RDB, Gimeno BS (2006) Atmospheric nitrogen deposition in world biodiversity hotspots: the need for a greater global perspective in assessing N deposition impacts. Global Change Biol 12:470–476
Qaderi MM, Kurepin LV, Reid DM (2006) Growth and physiological responses of canola (Brassica napus) to three components of global climate change: temperature, carbon dioxide and drought. Physiol Plant 128:710–721
Ramalho JC, Pons TL, Groeneveld HW, Azinheira HG, Nunes MA (2000) Photosynthetic acclimation of high light conditions in mature leaves of Coffea Arabica L.: role of xanthophylls, quenching mechanisms and nitrogen nutrition. Aust J Plant Physiol 27:43–51
Reich PB, Walters MB, Tabone TJ (1989) Response of Ulmus americana seedlings to varying nitrogen and water status. 2. Water- and nitrogen-use efficiency in photosynthesis. Tree Physiol 5:173–184
Saneoka H, Moghaieb REA, Premachandra GS, Fujita K (2004) Nitrogen nutrition and water stress effects on cell membrane stability and leaf water relations in Agrostis palustris Huds. Environ Exp Bot 52:131–138
Sardans J, Peñuuelas J, Estiarte M, Prieto P (2008) Warming and drought alter C and N concentration allocation and accumulation in a Mediterranean shrubland. Global Change Biol 14:2304–2316
Sinclair TR, Pinter PJ, Kimball BA, Adamsen FJ, LaMorte RL, Wall GW, Hunsaker DJ, Adam N, Brooks TJ, Garcia RL, Thompson T, Leavitt S, Matthias A (2000) Leaf nitrogen concentration of wheat subjected to elevated [CO2] and either water or N deficits. Agric Ecosyst Environ 79:53–60
Smolander A, Barnette L, Kitunen V, Lumme I (2005) N and C transformations in long-term N-fertilized forest soils in response to seasonal drought. Appl Soil Ecol 29:225–235
Solomon S, Qin DH, Manning M, Chen Z, Marquis M, Averyt KB, Tignor M, Miler HL (eds) (2007) IPCC, Climate change 2007: the physical scientific basis (contribution of Working Group I to the fourth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Wallace ZP, Lovett GM, Hart JE, Machona B (2007) Effects of nitrogen saturation on tree growth and death in a mixed oak forest. For Ecol Manag 243:210–218
Wu FZ, Bao WK, Li FL, Wu N (2008) Effects of water stress and nitrogen addition on leaf gas exchange and fluorescence parameters of Sophora davidii seedlings. Photosynthetica 46:40–48
Yang YQ, Yao YA, Xu G, Li CY (2005) Growth and physiological responses to drought and elevated ultraviolet-B in two contrasting populations of Hippophae rhamnoides. Physiol Plant 124:431–440
Yang Y, Han C, Liu Q, Lin B, Wang JW (2008) Effect of drought and low light on growth and enzymatic antioxidant system of Picea asperata seedlings. Acta Physiol Plant 30:433–440
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Knowledge Innovative Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (KZCX2-YW-331-2, KZCX2-EW-309-2) and West Light Talents Training Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Y0R2100100, Y0R2130130). We thank Quan Lan, Na Li, Yun Lin, and Guangsheng Liu for providing valuable comments and help. We thank acknowledge all workers of the Alpine Ecosystem Observation and Experiment Station.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Guo, J., Wang, G. et al. Effects of drought and nitrogen addition on photosynthetic characteristics and resource allocation of Abies fabri seedlings in eastern Tibetan Plateau. New Forests 43, 505–518 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11056-011-9295-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11056-011-9295-3