Abstract
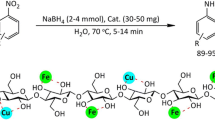
A facile and efficient one-pot method for the synthesis of well-dispersed hollow CuFe2O4 nanoparticles (H-CuFe2O4 NPs) in the presence of cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) as the support was described. Based on the one-pot solvothermal condition control, magnetic H-CuFe2O4 NPs were in-situ grown on the CNC surface uniformly. TEM images indicated good dispersity of H-CuFe2O4 NPs with uniform size of 300 nm. The catalytic activity of H-CuFe2O4/CNC was tested in the catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol (4-NP) in aqueous solution. Compared with most CNC-based ferrite catalysts, H-CuFe2O4/CNC catalyst exhibited an excellent catalytic activity toward the reduction of 4-NP. The catalytic performance of H-CuFe2O4/CNC catalyst was remarkably enhanced with the rate constant of 3.24 s−1 g−1, which was higher than H-CuFe2O4 NPs (0.50 s−1 g−1). The high catalytic activity was attributed to the introduction of CNC and the special hollow mesostructure of H-CuFe2O4 NPs. In addition, the H-CuFe2O4/CNC catalyst promised good conversion efficiency without significant decrease even after 10 cycles, confirming relatively high stability. Because of its environmental sustainability and magnetic separability, H-CuFe2O4/CNC catalyst was shown to indicate that the ferrite nanoparticles supported on CNC were acted as a promising catalyst and exhibited potential applications in numerous ferrite based catalytic reactions.

ᅟ












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen R, Wang Q, Du Y, Xing WH, Xu NP (2009) Effect of initial solution apparent pH on nano-sized nickel catalysts in p-nitrophenol hydrogenation. Chem Eng J 145:371–376
Chen GY, Yu HY, Zhang CH, Zhou Y, Yao JM (2016) A universal route for the simultaneous extraction and functionalization of cellulose nanocrystals from industrial and agricultural celluloses. J Nanopart Res 18:48–62
Chook SW, Yau SX, Chia CH, Chin SX, Zakaria S (2017) Carboxylated-nanoncellulose as a template for the synthesis of silver nanoprism. Appl Surf Sc 422:32–38
Dandia A, Jain AK, Sharma S (2013) CuFe2O4 nanoparticles as a highly efficient and magnetically recoverable catalyst for the synthesis of medicinally privileged spiropyrimidine scaffolds. RSC Adv 3:2924–2934
Divya KP, Miroshnikov M, Dutta D, Vemula PK, Ajayan PM, John G (2016) In situ synthesis of metal nanoparticle embedded hybrid soft nanomaterials. Accounts Chem Res 49:1671–1680
Dong YY, Liu S, Liu YJ, Meng LY, Ma MG (2017) Ag@Fe3O4@cellulose nanocrystals nanocomposites: microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis, antimicrobial properties, and good adsorption of dye solution. J Mater Sci 52:1–12
Feng J, Su L, Ma Y, Ren CL, Guo Q, Chen XG (2013) CuFe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles: a simple and efficient catalyst for the reduction of nitrophenol. Chem Eng J 221:16–24
Gazi S, Ananthakrishnan R (2011) Metal-free-photocatalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol by resin-supported dye under the visible irradiation. Appl Catal B Environ 105:317–325
Goyal A, Bansal S, Singhal S (2014) Facile reduction of nitrophenols: comparative catalytic efficiency of MFe2O4(M = Ni, Cu, Zn) nanoferrites. Int J Hydrogen Energ 39:4895–4908
Guo P, Cui L, Wang Y, Lv M, Wang BY, Zhao XS (2013) Facile synthesis of ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles with tunable magnetic and sensing properties. Langmuir 29:8997–9003
Han Y, Wu X, Zhang X, Zhou ZH, Lu CH (2016) Reductant-free synthesis of silver nanoparticles-doped cellulose microgels for catalyzing and product separation. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4:6322–6331
Hu Z, Meng Q, Liu R, Fu SY, Lucia LA (2017) Physical study of the primary and secondary photothermal events in gold/cellulose nanocrystals (AuNP/CNC) nanocomposites embedded in PVA matrices. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5:1601–1609
Ibrahim I, Ali IO, Salama TM, Bahgat AA, Mohamed MM (2016) Synthesis of magnetically recyclable spinel ferrite (MFe2O4, M = Zn, Co, Mn) nanocrystals engineered by sol gel-hydrothermal technology: high catalytic performances for nitroarenes reduction. Appl Catal B Environ 181:389–402
Kaushik M, Li AY, Hudson R, Masnadi M, Li CJ, Moores A (2016) Reversing aggregation: direct synthesis of nanocatalysts from bulk metal. Cellulose nanocrystals as active support to access efficient hydrogenation silver nanocatalysts. Green Chem 18:129–133
Koczkur KM, Mourdikoudis S, Polavarapu L, Skrabalak SE (2015) Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) in nanoparticle synthesis. Dalton T 44:17883–17905
Lai J, Niu W, Luque R, Xu GB (2015) Solvothermal synthesis of metal nanocrystals and their applications. Nano Today 10:240–267
Li Q, Li Y, Li X, Chen SL, Zhang SD, Wang JZ, Hou H (2014) A facile synthesis of superparamagnetic hybrid hollow nanospheres based on monodisperse nickel-zinc ferrite/polyethylene glycol and their electromagnetic, microwave absorbing properties. J Alloys Compd 608:35–43
Li Y, Shen J, Hu Y, Qiu SJ, Min GQ, Song ZT, Sun Z, Li CZ (2015) General flame approach to chainlike MFe2O4 spinel (M = Cu, Ni, Co, Zn) nanoaggregates for reduction of nitroaromatic compounds. Ind Eng Chem Res 54:9750–9757
Li R, Li Z, Wu Q, Li D, Shi J, Chen Y, Yu S, Ding T, Qiao C (2016) One-step synthesis of monodisperse AuNPs@ PANI composite nanospheres as recyclable catalysts for 4-nitrophenol reduction. J Nanopart Res 18:142–153
Li Y, Xu L, Xu B, Mao ZP, Xu H, Zhong Y, Zhang LP, Wang BJ, Sui XF (2017) Cellulose sponge supported palladium nanoparticles as recyclable cross-coupling catalysts. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:17155–17162
Lin X, Ji G, Liu Y, Huang Q, Yang Z, Du Y (2012) Formation mechanism and magnetic properties of hollow Fe3O4 nanospheres synthesized without any surfactant. Cryst Eng Commun 14:8658–8663
Liu S, Yao K, Fu LH, Ma MG (2016) Selective synthesis of Fe3O4, γ-Fe2O3, and α-Fe2O3 using cellulose-based composites as precursors. RSC Adv 6:2135–2140
Ma MG, Zhu JF, Li SM, Jia N, Sun RC (2012) Nanocomposites of cellulose/iron oxide: influence of synthesis conditions on their morphological behavior and thermal stability. Mat Sci Eng C-Mater 32:1511–1517
Nasrollahzadeh M, Atarod M, Sajadi SM (2016a) Green synthesis of the Cu/Fe3O4 nanoparticles using Morinda morindoides leaf aqueous extract: a highly efficient magnetically separable catalyst for the reduction of organic dyes in aqueous medium at room temperature. Appl Surf Sci 364:636–644
Nasrollahzadeh M, Bagherzadeh M, Karimi H (2016b) Preparation, characterization and catalytic activity of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles as a magnetically recoverable catalyst for selective oxidation of benzyl alcohol to benzaldehyde and reduction of organic dyes. J Colloid Interf Sci 465:271–278
Nypelö T, Rodriguez-Abreu C, Rivas J, Dickey MD, Rojas OJ (2014) Magneto-responsive hybrid materials based on cellulose nanocrystals. Cellulose 21:2557–2566
Polat K, Aksu ML, Pekel AT (2002) Electroreduction of nitrobenzene to p-aminophenol using voltammetric and semipilot scale preparative electrolysis techniques. J Appl Electrochem 32:217–223
Ren Y, Li S, Dai B, Huang XH (2014) Microwave absorption properties of cobalt ferrite-modified carbonized bacterial cellulose. Appl Surf Sci 311:1–4
Ren Y, Lin L, Ma J, Yang J, Feng J, Fan ZJ (2015) Sulfate radicals induced from peroxymonosulfate by magnetic ferrospinel MFe2O4 (M = Co, Cu, Mn, and Zn) as heterogeneous catalysts in the water. Appl Catal B Environ 165:572–578
Su L, Qin W, Zhang H, Rahman ZU, Ren CL, Ma SD, Chen SG (2015) The peroxidase/catalase-like activities of MFe2O4(M = Mg, Ni, Cu) MNPs and their application in colorimetric biosensing of glucose. Biosens Bioelectron 63:384–391
Taghavi F, Falamaki C, Shabanov A, Bayrami L, Roumianfar A (2011) Kinetic study of the hydrogenation of p-nitrophenol to p-aminophenol over micro-aggregates of nano-Ni2B catalyst particles. Appl Cataly A-Gen 407:173–180
Tang J, Sisler J, Grishkewich N, Tam KC (2017) Functionalization of cellulose nanocrystals for advanced applications. J Colloid Interf Sci 494:397–409
Tian C, Fu S, Lucia LA (2015) Magnetic Cu0.5Co0.5Fe2O4 ferrite nanoparticles immobilized in situ on the surfaces of cellulose nanocrystals. Cellulose 22:2571–2587
Udupa HVK, Rao MV (1967) The electrolytic reduction of p-nitrophenol to p-aminophenol. Electrochim Acta 12:353–361
Wan C, Lu Y, Jiao Y, Jin CD, Sun QF, Li J (2015) Fabrication of hydrophobic, electrically conductive and flame-resistant carbon aerogels by pyrolysis of regenerated cellulose aerogels. Carbohydr Polym 118:115–118
Wu Y, He Y, Wu T, Chen T, Weng WZ, Wan HL (2007) Influence of some parameters on the synthesis of nanosized NiO material by modified sol-gel method. Mater Lett 61:3174–3178
Wu L, Xiao Q, Li Z, Lei GT, Zhang P, Wang L (2012) CoFe2O4/C composite fibers as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries with stable and high electrochemical performance. Solid State Ionics 215:24–28
Wu X, Lu C, Zhang W, Yuan GP, Xiong R, Zhang X (2013) A novel reagentless approach for synthesizing cellulose nanocrystal-supported palladium nanoparticles with enhanced catalytic performance. J Mater Chem A 1:8645–8652
Xiong R, Lu C, Wang Y, Zhou ZH, Zhang X (2013) Nanofibrillated cellulose as the support and reductant for the facile synthesis of Fe3O4/Ag nanocomposites with catalytic and antibacterial activity. J Mater Chem A 1:14910–14918
Xiong R, Wang Y, Zhang X, Lu CH, Lan L (2014) In-situ growth of gold nanoparticles on magnetic γ-Fe2O3@cellulose nanocomposites: a highly active and recyclable catalyst for reduction of 4-nitrophenol. RSC Adv 4:6454–6462
Xu S, Shen D, Wu P, Xu S, Shen D, Wu P (2013) Fabrication of water-repellent cellulose fiber coated with magnetic nanoparticles under supercritical carbon dioxide. J Nanopart Res 15:1–12
Yan W, Chen C, Wang L, Zhang D, Li AJ, Yao Z, Shi LY (2016) Facile and green synthesis of cellulose nanocrystal-supported gold nanoparticles with superior catalytic activity. Carbohydr Polym 140:66–73
Zeynizadeh B, Mohammadzadeh I, Shokri Z, Hosseini SA (2017) Synthesis and characterization of NiFe2O4@Cu nanoparticles as a magnetically recoverable catalyst for reduction of nitroarenes to arylamines with NaBH4. J Colloid Interf Sci 500:285–293
Zhang W, Quan B, Lee C, Park SK, Li X, Choi E, Diao G, Piao Y (2015a) One-step facile solvothermal synthesis of copper ferrite-graphene composite as a high-performance supercapacitor material. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:2404–2414
Zhang H, Zhao Y, Liu W, Gao ST, Shang NZ, Wang C, Wang Z (2015b) Preparation of magnetically separable Cu6/7Co1/7Fe2O4-graphene catalyst and its application in selective reduction of nitroarenes. Catal Commun 59:161–165
Zhang X, Feng M, Qu R, Liu H, Wang L, Wang Z (2016) Catalytic degradation of diethyl phthalate in aqueous solution by persulfate activated with nano-scaled magnetic CuFe2O4/MWCNTs. Chem Eng J 301:1–11
Zhang D, Zhang G, Wang Q, Zhang L (2017) Dual-functional catalytic materials: magnetically hollow porous Ni-manganese oxides microspheres/cotton cellulose fiber. J Taiwan Inst Chem E 77:311–320
Zhao Y, He G, Dai W, Chen H (2014) High catalytic activity in the phenol hydroxylation of magnetically separable CuFe2O4-reduced graphene oxide. Ind Eng Chem Res 53:12566–12574
Zhao P, Feng X, Huang D, Yang GY, Astruc D (2015) Basic concepts and recent advances in nitrophenol reduction by gold- and other transition metal nanoparticles. Coordin Chem Rev 287:114–136
Zhu M, Meng D, Wang C, Diao G (2013) Facile fabrication of hierarchically porous CuFe2O4 nanospheres with enhanced capacitance property. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:6030–6037
Funding
This work was supported by the Foundation of Project for Innovative of Science and Technology of Shaanxi province (No. 2015KTCQ01-44) and the Guangxi Key Laboratory of Clean Pulping, Papermaking, and Pollution Control Opening Fund (KF 201711).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 361 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Zhao, D., Hou, C. et al. Facile one-pot synthesis of cellulose nanocrystal-supported hollow CuFe2O4 nanoparticles as efficient catalyst for 4-nitrophenol reduction. J Nanopart Res 20, 161 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-018-4259-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-018-4259-6