Abstract
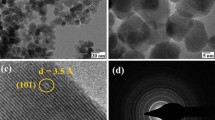
AIII group nitrides have attracted a great deal of attention in the last decades due to their applications in modern microelectronic and optoelectronic devices. In this paper, simple and controllable methods for a synthesis of InN nanoparticles in the form of nanodisks and skeletal nanostructures are presented. Careful control of the experimental conditions is necessary, as the thermal stability of InN at elevated temperatures is low. The morphology of nanoparticles was investigated by scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy combined with selected area diffraction. Profile analysis of powder X-ray diffraction data shows that the apparent size of the crystals along [001] direction decreases from the size larger than 100 nm for the low temperature syntheses to about 65 nm for the high temperature ones. Structural properties were investigated using X-ray diffraction, Raman, and photoluminescence spectroscopy. Thermal stability was probed by differential scanning calorimetry coupled with thermogravimetry in Ar and air atmospheres. Chemical composition and purity of InN are strongly dependent on temperature and duration of the synthesis.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrait N, Laval JP, Frit B, Roult G (1982) Structure Cristalline de l’Oxynitrofluorure d’Indium In32ON17F43. Acta Crystallogrs B 38:1088–1093
Agullo-Rueda F, Mendez EE, Bojarczuk B, Guha S (2000) Raman spectroscopy of wurtzite InN films grown on Si. Solid State Commun 115:19–21
Bai YJ, Liu ZG, Xu XG, Cui DL, Hao XP, Feng X, Wang QL (2002) Preparation of InN nanocrystals by solvo-thermal method. J Cryst Growth 241:189–192
Bhat SV, Biswas K, Rao CNR (2007) Synthesis and optical properties of In-doped GaN nanocrystals. Solid State Commun 141:325–328
Bungaro C, Rapcewicz K, Bernholc J (2000) Ab initio phonon dispersions of wurtzite AlN, GaN, and InN. Phys Rev B 61:6720–6725
Chitara B, Venkataprasad Bhat S, Vivekchand SRC, Gomathi A, Rao CVR (2008) White-light sources based on composites of GaN nanocrystals with conducting polymers and nanophosphors. Solid State Commun 147:409–413
Chitara B, Late DJ, Krupanidhi SB, Rao CNR (2010) Room-temperature gas sensors based on gallium nitride nanoparticles. Solid State Commun 150:2053–2056
Dahal R, Pantha B, Li J, Lin JY, Jiang HX (2009) InGaN/GaN multiple quantum well solar cells with long operating wavelengths. Appl Phys Lett 94:063505
Davydov VY et al (2002a) Band gap of InN and In-rich InxGa1-xN alloys (0.36 < x < 1). Phys Status Solidi B 230:R4–R6
Davydov VY et al (2002b) Absorption and emission of hexagonal InN. Evidence of narrow fundamental band gap. Phys Status Solidi 229:R1–R3
Fasol G (1996) Room-temperature blue gallium nitride laser diode. Science 272:1751–1752
Fu SP, Chen YF (2004) Effective mass of InN epilayers. Appl Phys Lett 85:1523–1525
Gonzalez D, Lozano JG, Herrera M, Morales FM, Ruffenach S, Briot O, Garcia R (2010) Phase mapping of aging process in InN nanostructures: oxygen incorporation and the role of the zinc blende phase. Nanotechnology 21:185706
Gwo S, Wu CL, Shen CH, Chang WH, Hsu TM, Wang JS, Hsu JT (2004) Heteroepitaxial growth of wurtzite InN films on Si(111) exhibiting strong near-infrared photoluminescence at room temperature. Appl Phys Lett 84:3765–3767
Hasan MT, Bhuiyan AG, Yamamoto A (2008) Two dimensional electron gas in InN-based heterostructures: effects of spontaneous and piezoelectric polarization. Solid·State Electron 52:134–139
Hsieh JC, Yun DS, Hu E, Belcher AM (2010) Ambient pressure, low-temperature synthesis and characterization of colloidal InN nanocrystals. J Mater Chem 20:1435–1437
Ikuta K, Inoue Y, Takai O (1998) Optical and electrical properties of InN thin films grown on ZnO/alpha-Al2O3 by RF reactive magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films 334:49–53
Inushima T, Shiraishi T, Davydov VY (1999) Phonon structure of InN grown by atomic layer epitaxy. Solid State Commun 110:491–495
Justice J, Kadiyala A, Dawson J, Korakakis D (2013) Group III-nitride based electronic and optoelectronic integrated circuits for smart lighting applications. MRS Proc 1492:123–128
Juza R, Hahn H (1940) Untersuchungen über die nitride von cadmium, gallium, indium und germanium. Metallamide und metallnitride. Z Anorg Allgem Chem 244:111–124
Kaczmarczyk G et al (2000) Lattice dynamics of hexagonal and cubic InN: Raman-scattering experiments and calculations. Appl Phys Lett 76:2122–2124
Kam KC, Deepak FL, Gundiah G, Rao CNR, Cheetham AK (2004) Properties of nanostructured GaN prepared by different methods. Solid State Sci 6:1107–1112
Kuzmik J, Georgakilas A (2011) Proposal of high-electron mobility transistors with strained InN channel. IEEE Trans Electron Devices 58:720–724
Leitner J, Marsik P, Sedmidubsky D, Ruzicka K (2004) High temperature enthalpy, heat capacity and other thermodynamic functions of solid InN. J Phys Chem Solids 65:1127–1131
Maleyre W, Briot O, Ruffenach S (2004) MOVPE growth of InN films and quantum dots. J Cryst Growth 269:15–21
Matsuoka T (2005) Progress in nitride semiconductors from GaN to InN—MOVPE growth and characteristics. Superlattices Microstruct 37:19–32
Matsuoka T, Okamoto H, Nakao M, Harima H, Kurimoto E (2002) Optical bandgap energy of wurtzite InN. Appl Phys Lett 81:1246–1248
Nakamura S, Senoh N, Iwasa N, Nagahama S (1995) High-brightness InGaN blue, green and yellow light-emitting diodes with quantum-well structures. Jpn J Appl Phys Part 2 34:L797–L799
Osamura K, Ohtsuki A, Shingu PH, Murakami Y, Nakajima K (1972) Fundamental absorption-edge in GaN, InN and their alloys. Solid State Commun 11:617–621
Paszkowicz W et al (1999) Lattice parameters, density and thermal expansion of InN microcrystals grown by the reaction of nitrogen plasma with liquid indium. Philos Mag A 79:1145–1154
Sardar K, Rao CNR (2005) AlN nanocrystals by new chemical routes. Solid State Sci 7:217–220
Schofield PS, Zhou WZ, Wood P, Samuel IDW, Cole-Hamilton DJ (2004) Nanoparticles from the decomposition of the complex [InN3(CH2CH2CH2NMe2)2]. J Mater Chem 14:3124–3126
Schwenzer B, Loeffler L, Seshadri R, Keller S, Lange FF, DenBaars SP, Mishra UK (2004) Preparation of indium nitride micro- and nanostructures by ammonolysis of indium oxide. J Mater Chem 14:637–641
Sofer Z et al (2013) Rapid thermal synthesis of GaN nanocrystals and nanodisks. J Nanopart Res 15:1530
Tansley TL, Foley CP (1986) Optical band-gap of indium nitride. J Appl Phys 59:3241–3244
Westra KL, Lawson RPW, Brett MJ (1988) The effects of oxygen contamination on the properties of reactively sputtered indium nitride films. J Vac Sci Technol A 6:1730–1732
Wu J et al (2002) Unusual properties of the fundamental band gap of InN. Appl Phys Lett 80:3967–3969
Wu CZ, Li TW, Lei LY, Hu SQ, Liu Y, Xie Y (2005) Indium nitride from indium iodide at low temperatures: synthesis and their optical properties. New J Chem 29:1610–1615
Xiao JP, Xie Y, Tang R, Luo W (2003) Benzene thermal conversion to nanocrystalline indium nitride from sulfide at low temperature. Inorg Chem 42:107–111
Acknowledgments
The project was supported by Czech Science Foundation (Project No. 13-20507S). Financial support was received from specific university research (MSMT No 20/2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Šimek, P., Sedmidubský, D., Klímová, K. et al. Synthesis of InN nanoparticles by rapid thermal ammonolysis. J Nanopart Res 16, 2805 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-014-2805-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-014-2805-4