Abstract
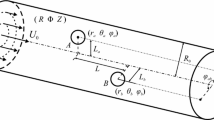
This article presents a theoretical study of electrokinetic motion of a negatively charged cubic nanoparticle in a three-dimensional nanochannel with a circular cross-section. Effects of the electrophoretic and the hydrodynamic forces on the nanoparticle motion are examined. Because of the large applied electric field over the nanochannel, the impact of the Brownian force is negligible in comparison with the electrophoretic and the hydrodynamic forces. The conventional theories of electrokinetics such as the Poisson–Boltzmann equation and the Helmholtz–Smoluchowski slip velocity approach are no longer applicable in the small nanochannels. In this study, and at each time step, first, a set of highly coupled partial differential equations including the Poisson–Nernst–Plank equation, the Navier–Stokes equations, and the continuity equation was solved to find the electric potential, ionic concentration field, and the flow field around the nanoparticle. Then, the electrophoretic and hydrodynamic forces acting on the negatively charged nanoparticle were determined. Following that, the Newton second law was utilized to find the velocity of the nanoparticle. Using this model, effects of surface electric charge of the nanochannel, bulk ionic concentration, the size of the nanoparticle, and the radius of the nanochannel on the nanoparticle motion were investigated. Increasing the bulk ionic concentration or the surface charge of the nanochannel will increase the electroosmotic flow, and hence affect the particle’s motion. It was also shown that, unlike microchannels with thin EDL, the change in nanochannel size will change the EDL field and the ionic concentration field in the nanochannel, affecting the particle’s motion. If the nanochannel size is fixed, a larger particle will move faster than a smaller particle under the same conditions.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ai Y, Qian S (2011) Electrokinetic particle translocation through a nanopore. Phys Chem Chem Phys 13:4060–4071. doi:10.1039/c0cp02267e
Bonthuis DJ, Meyer C, Stein D, Dekker C (2008) Conformation and dynamics of DNA confined in slitlike nanofluidic channels. Phys Rev Lett 101:108303
Chattopadhyay S, Kulkarni NV, Choudhury K, Prasad R, Shahee A, Raja Sekhar BN, Sen P (2011) Lattice expansion in ZnSe quantum dots. Mater Lett 65:1625–1627
Fine D, Grattoni A, Zabre E, Hussein F, Ferrari M, Liu X (2011) A low-voltage electrokinetic nanochannel drug delivery system. Lab Chip 11:2526–2534
Fox MB, Esveld DC, Valero A, Luttge R, Mastwijk HC, Bartels PV, van den Berg A, Boom RM (2006) Electroporation of cells in microfluidic devices: a review. Anal Bioanal Chem 385:474–485
Huh D, Mills KL, Burns MA, Thouless MD, Takayama S (2007) Tuneable elastomeric nanochannels for nanofluidicmanipulation. Nat Mater 6:424–428
Kadaksham ATJ, Singh P, Aubry N (2004) Dielectrophoresis of nanoparticles. Electrophoresis 25:3625–3632
Kang Y, Li D (2009) Electrokinetic motion of particles and cells in microchannels. Microfluid Nanofluid 6:431–460. doi:10.1007/s10404-009-0408-7
Keh HJ, Anderson JL (1985) Boundary effects on electrophoretic motion of colloidal spheres. J Fluid Mech 153:417–439
Kim M, Zydney AL (2004) Effect of electrostatic, hydrodynamic, and Brownian forces on particle trajectories and sieving in normal flow filtration. J Colloid Interface Sci 269:425–431. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2003.08.004
Kim K, Kwang HS, Song TH (2011) A numerical model for simulating electroosmotic micro- and nanochannel flows under non-Boltzmann equilibrium. Fluid Dyn Res 43(4):041401
Lee WG, Demirci U, Khademhosseini A (2009) Microscale electroporation: challenges and perspectives for clinical applications. Integr Biol 1:242–251
Lee SY, Yalchin SE, Joo SW, Baysal O, Qian S (2010) Diffusiophoretic motion of a charged spherical particle in a nanopore. J Phys Chem B 114:6437–6446. doi:10.1021/jp9114207
Li D, Daghighi Y (2010) Eccentric electrophoretic motion of a rectangular particle in a rectangular microchannel. J Colloid Interface Sci 342:638–642
Li WL, Tegenfeldt JO, Chen L, Austin RH, Chou SY, Kohl PA, Krotine J, Sturm JC (2003) Sacrificial polymers for nanofluidic channels in biological applications. Nanotechnology 14:578–583
Liu D, Maxey MR, Karniadakis GE (2005) Simulations of dynamic self-assembly of paramagnetic microspheres in confined microgeometries. J Micromech Microeng 15:2298–2308
Liu J, Wang M, Chen S, Robbins MO (2010) Molecular simulations of electroosmotic flows in rough nanochannels. J Comput Phys 229(20):7834–7847
Mijatovic D, Eijkel JCT, van den Berg A (2005) Technologies for nanofluidic systems: top-down vs. bottom-up: a review. Lab Chip 5:492–500
Morgan H, Green NG (2002) AC electrokinetic: colloids and nanoparticles. Research Studies Press Ltd, Baldock
Movahed S, Li D (2011a) Electrokinetic transport through nanochannels. Electrophoresis J 32:1259–1267
Movahed S, Li D (2011b) Microfluidics cell electroporation. Microfluid Nanofluid 10(4):703–734. doi:10.1007/s10404-010-0716-y
Movahed S, Li D (2012) Electrokinetic transport through the nanopores in cell membrane during electroporation. J Colloid Interface Sci 369(1):442–452
Oron D, Aharoni A, de Mello Donega C, van Rijssel J, Meijerink A, Banin U (2009) Universal role of discrete acoustic phonons in the low-temperature optical emission of colloidal quantum dots. Phys Rev Lett 102:177402
Pennathur S, Santiago JS (2005) Electrokinetic transport in nanochannels. 1. Theory. Anal Chem 77(21):6772–6781
Petsev DN, Lopez GP (2006) Electrostatic potential and electroosmotic flow in a cylindrical capillary filled with symmetric electrolyte: analytic solutions in thin double layer approximation. J Colloid Interface Sci 294(2):492–498
Qian S, Joo SW (2008) Analysis of self-electrophoretic motion of a spherical particle in a nanotube: effect of nonuniform surface charge density. Langmuir 24:4778–4784
Qian S, Joo SW, Hou WS, Zhao X (2008) Electrophoretic motion of a spherical particle with a symmetric nonuniform surface charge distribution in a nanotube. Langmuir 24:5332–5340
Rafieia M, Mohebpour SR, Daneshmand F (2012) Small-scale effect on the vibration of non-uniform carbon nanotubes conveying fluid and embedded in viscoelastic medium. Physica E 44(7–8):1372–1379
Reisner W, Larsen NB, Silahtaroglu A, Kristensen A, Tommerup N, Tegenfeldt JO, Flyvbjerg H (2010) Single-molecule denaturation mapping of DNA in nanofluidic channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(30):13294–13299
Shugai AA, Carnie SL (1999) Carnie electrophoretic motion of a spherical particle with a thick double layer in bounded flows. J Colloid Interface Sci 213:298–315
Tegenfeldt JO, Prinz C, Cao H, Huang RL, Austin RH, Chou SY, Cox EC, Sturm JC (2004) Micro- and nanofluidics for DNA analysis. Anal Bioanal Chem 378:1678–1692
Wang M, Chen S (2008) On applicability of Poisson–Boltzmann equation for micro- and nanoscale electroosmotic flows. Commun Comput Phys 3(5):1087–1099
Wu Z, Li D (2009) Induced-charge electrophoretic motion of ideally polarizable particles. Electrochim Acta 54:3960–3967
Wu Z, Gao Y, Li D (2009) Electrophoretic motion of ideally polarized particles in microchannels. Electrophoresis 30:773–781
Xuan X, Ye C, Li D (2005) Near-wall electrophoretic motion of spherical particles in cylindrical capillaries. J Colloid Interface Sci 289:286–290
Ye C, Li D (2002) Electrophoretic motion of spherical particle in a microchannel under gravitational field. J Colloid Interface Sci 251:331–338
Ye C, Li D (2004a) 3-D transient electrophoretic motion of a spherical particle in a T-shaped rectangular microchannel. J Colloid Interface Sci 272:480–488
Ye C, Li D (2004b) Electrophoretic motion of two particles in a rectangular microchannel. Microfluid Nanofluid 1:52–61
Ye C, Li D (2005) Eccentric electrophoretic motion of a spherical particle in a circular cylindrical microchannel. Microfluid Nanofluid 1:234–241
Yuan Z, Garcia A, Lopez GP, Petsev DN (2007) Electrokinetic transport and separations in fluidic nanochannels. Electrophoresis 28:595–610
Zangle TA, Mani A, Santiago JG (2010) Theory and experiments of concentration polarization and ion focusing at microchannel and nanochannel interfaces. Chem Soc Rev 39:1014–1035. doi:10.1039/B902074H
Zheng Z, Hansford DJ, Conlisk AT (2003) Effect of multivalent ions on electroosmotic flow in micro- and nanochannels. Electrophoresis 24:3006–3017. doi:10.1002/elps.200305561
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the financial support of the Canada Research Chair program and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council (NSERC) of Canada through a research grant to D. Li.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Movahed, S., Li, D. Electrokinetic motion of a rectangular nanoparticle in a nanochannel. J Nanopart Res 14, 1032 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-1032-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-1032-0