Abstract
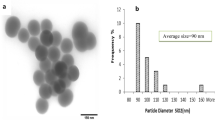
The nanotoxicology as a new subdiscipline of nanotechnology needs to be studied in vivo. To do so, it is essential to understand certain pharmacological information of the nanoparticles in vivo. Silica nanoparticles (SiNPs) have been developed for a number of biomedical uses; however, research on their tissular localization and excretion has been limited. In this study, we analyzed the localization of intravenously administered SiNPs with sizes of 20 and 80 nm in liver and spleen and quantitatively investigated the excretion of SiNPs through urine and feces. The results of the tissular localization study showed that the SiNPs were located in liver evenly; however, they were mainly accumulated in the white pulp of spleen. The quantitative excretory assay found the renal excretion being the main excretion pathway of SiNPs and indicated that the accumulated excretory rate of 80 nm SiNPs through urine was higher than that of 20 nm SiNPs because of the higher hemoconcentration. Further analysis of radioactive substances in the excreta showed the convincing confirmatory evidence that the SiNPs of both the sizes of 20 and 80 nm could be excreted through urine. These results provide important information on in vivo distribution and excretion of SiNPs.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burns AA, Vider J, Ow H, Herz E, Penate-Medina O, Baumgart M, Larson SM, Wiesner U, Bradbury M (2009) Fluorescent silica nanoparticles with efficient urinary excretion for nanomedicine. Nano Lett 9(1):442–448
Chapman AP, Antoniw P, Spitali M, West S, Stephens S, King DJ (1999) Therapeutic antibody fragments with prolonged in vivo half-lives. Nat Biotechnol 17(8):780–783
Chen Z, Chen H, Meng H, Xing G, Gao X, Sun B, Shi X, Yuan H, Zhang C, Liu R, Zhao F, Zhao Y, Fang X (2008) Bio-distribution and metabolic paths of silica coated CdSeS quantum dots. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 230(3):364–371
Cho M, Cho WS, Choi M, Kim SJ, Han BS, Kim SH, Kim HO, Sheen YY, Jeong J (2009) The impact of size on tissue distribution and elimination by single intravenous injection of silica nanoparticles. Toxicol Lett 189(3):177–183
Choi HS, Liu W, Misra P, Tanaka E, Zimmer JP, Itty Ipe B, Bawendi MG, Frangioni JV (2007a) Renal clearance of quantum dots. Nat Biotechnol 25(10):1165–1170
Choi J, Burns AA, Williams RM, Zhou Z, Flesken-Nikitin A, Zipfel WR, Wiesner U, Nikitin AY (2007b) Core-shell silica nanoparticles as fluorescent labels for nanomedicine. J Biomed Opt 12(6):064007
Dobrovolskaia MA, McNeil SE (2007) Immunological properties of engineered nanomaterials. Nat Nanotechnol 2(8):469–478
Fischer HC, Chan WC (2007) Nanotoxicity: the growing need for in vivo study. Curr Opin Biotechnol 18(6):565–571
Hagens WI, Oomen AG, de Jong WH, Cassee FR, Sips AJ (2007) What do we (need to) know about the kinetic properties of nanoparticles in the body? Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 49(3):217–229
He X, Nie H, Wang K, Tan W, Wu X, Zhang P (2008) In vivo study of biodistribution and urinary excretion of surface-modified silica nanoparticles. Anal Chem
Hirsch LR, Stafford RJ, Bankson JA, Sershen SR, Rivera B, Price RE, Hazle JD, Halas NJ, West JL (2003) Nanoshell-mediated near-infrared thermal therapy of tumors under magnetic resonance guidance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(23):13549–13554
Huo Q, Liu J, Wang LQ, Jiang Y, Lambert TN, Fang E (2006) A new class of silica cross-linked micellar core-shell nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 128(19):6447–6453
Iezzi EB, Duchamp JC, Harich K, Glass TE, Lee HM, Olmstead MM, Balch AL, Dorn HC (2002) A symmetric derivative of the trimetallic nitride endohedral metallofullerene, Sc3 N@C80. J Am Chem Soc 124(4):524–525
Li SD, Huang L (2008) Pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of nanoparticles. Mol Pharm 5(4):496–504
Liu Y, Miyoshi H, Nakamura M (2007) Novel drug delivery system of hollow mesoporous silica nanocapsules with thin shells: preparation and fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) release kinetics. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 58(2):180–187
Liu T, Li L, Teng X, Huang X, Liu H, Chen D, Ren J, He J, Tang F (2011) Single and repeated dose toxicity of mesoporous hollow silica nanoparticles in intravenously exposed mice. Biomaterials 32(6):1657–1668
Lund U, Rippe A, Venturoli D, Tenstad O, Grubb A, Rippe B (2003) Glomerular filtration rate dependence of sieving of albumin and some neutral proteins in rat kidneys. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 284(6):F1226–F1234
Maynard AD, Aitken RJ, Butz T, Colvin V, Donaldson K, Oberdorster G, Philbert MA, Ryan J, Seaton A, Stone V, Tinkle SS, Tran L, Walker NJ, Warheit DB (2006) Safe handling of nanotechnology. Nature 444(7117):267–269
Oberdorster G, Oberdorster E, Oberdorster J (2005) Nanotoxicology: an emerging discipline evolving from studies of ultrafine particles. Environ Health Perspect 113(7):823–839
Ozgo M, Skrzypczak W, Drzezdzon D, Lepczynski A, Dratwa-Chalupnik A, Michalek K, Herosimczyk A (2009) Urinary excretion of low molecular weight proteins in goats during the neonatal period. J Physiol Pharmacol 60(Suppl 3):119–125
Prescott LF, McAuslane JA, Freestone S (1991) The concentration-dependent disposition and kinetics of inulin. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 40(6):619–624
Roy I, Ohulchanskyy TY, Bharali DJ, Pudavar HE, Mistretta RA, Kaur N, Prasad PN (2005) Optical tracking of organically modified silica nanoparticles as DNA carriers: a nonviral, nanomedicine approach for gene delivery. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(2):279–284
Slowing II, Trewyn BG, Lin VS (2007) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for intracellular delivery of membrane-impermeable proteins. J Am Chem Soc 129(28):8845–8849
Takizawa Y, Nishimura H, Morota T, Tomisawa H, Takeda S, Aburada M (2004) Pharmacokinetics of TJ-8117 (Onpi-to), a drug for renal failure (I): Plasma concentration, distribution and excretion of [3H]-(-)epicatechin 3-O-gallate in rats and dogs. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 29(2):91–101
Tsuji JS, Maynard AD, Howard PC, James JT, Lam CW, Warheit DB, Santamaria AB (2006) Research strategies for safety evaluation of nanomaterials, part IV: risk assessment of nanoparticles. Toxicol Sci 89(1):42–50
van Schooneveld MM, Vucic E, Koole R, Zhou Y, Stocks J, Cormode DP, Tang CY, Gordon RE, Nicolay K, Meijerink A, Fayad ZA, Mulder WJ (2008) Improved biocompatibility and pharmacokinetics of silica nanoparticles by means of a lipid coating: a multimodality investigation. Nano Lett 8(8):2517–2525
Wang JX, Fan YB, Gao Y, Hu QH, Wang TC (2009) TiO2 nanoparticles translocation and potential toxicological effect in rats after intraarticular injection. Biomaterials 30(27):4590–4600
Xie G, Sun J, Zhong G, Shi L, Zhang D (2010) Biodistribution and toxicity of intravenously administered silica nanoparticles in mice. Arch Toxicol 84(3):183–190
Yang J, Lee J, Kang J, Lee K, Suh JS, Yoon HG, Huh YM, Haam S (2008) Hollow silica nanocontainers as drug delivery vehicles. Langmuir 24(7):3417–3421
Zhao X, Hilliard LR, Mechery SJ, Wang Y, Bagwe RP, Jin S, Tan W (2004) A rapid bioassay for single bacterial cell quantitation using bioconjugated nanoparticles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(42):15027–15032
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from Shanghai Sci-Tech Committee Foundation (no. 0752nm026 & 08DZ2291600), Shanghai Leading Academic Discipline Project (no. S30206) and Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (no. Y4110665). The authors would like to acknowledge Professor Liyi Shi for kindly providing the SiNPs and helpful discussions during the early stage of this investigation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, G., Sun, J. & Zhong, G. Tissular localization and excretion of intravenously administered silica nanoparticles of different sizes. J Nanopart Res 14, 671 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-011-0671-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-011-0671-x