Abstract
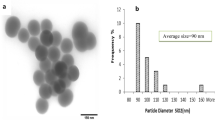
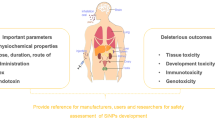
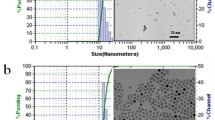
As the biosafety of nanotechnology becomes a growing concern, the in vivo nanotoxicity of NPs has drawn a lot of attention. Silica nanoparticles (SiNPs) have been widely developed for biomedical use, but their biodistribution and toxicology have not been investigated extensively in vivo. Although investigations of in vivo qualitative distribution of SiNPs have been reported, the time-dependent and quantitative informations about the distribution of SiNPs are still lacking. Here we investigated the long-term (30 days) quantitative tissue distribution, and subcellular distribution, as well as potential toxicity of two sizes of intravenously administered SiNPs in mice using radiolabeling, radioactive counting, transmission electron microscopy and histological analysis. The results indicated that SiNPs accumulate mainly in lungs, liver and spleen and are retained for over 30 days in the tissues because of the endocytosis by macrophages, and could potentially cause liver injury when intravenously injected.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aderem A (2003) Phagocytosis and the inflammatory response. J Infect Dis 187:S340–S345
Bagwe RP, Hilliard LR, Tan W (2006) Surface modification of silica nanoparticles to reduce aggregation and nonspecific binding. Langmuir 22:4357–4362
Bao G, Bao XR (2005) Shedding light on the dynamics of endocytosis and viral budding. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:9997–9998
Chithrani BD, Chan WC (2007) Elucidating the mechanism of cellular uptake and removal of protein-coated gold nanoparticles of different sizes and shapes. Nano Lett 7:1542–1550
Chithrani BD, Ghazani AA, Chan WC (2006) Determining the size and shape dependence of gold nanoparticle uptake into mammalian cells. Nano Lett 6:662–668
Choi J, Burns AA, Williams RM, Zhou Z, Flesken-Nikitin A, Zipfel WR, Wiesner U, Nikitin AY (2007) Core-shell silica nanoparticles as fluorescent labels for nanomedicine. J Biomed Opt 12:064007
Fabian E, Landsiedel R, Ma-Hock L, Wiench K, Wohlleben W, van Ravenzwaay B (2008) Tissue distribution and toxicity of intravenously administered titanium dioxide nanoparticles in rats. Arch Toxicol 82:151–157
Fischer HC, Chan WC (2007) Nanotoxicity: the growing need for in vivo study. Curr Opin Biotechnol 18:565–571
Gao H, Shi W, Freund LB (2005) Mechanics of receptor-mediated endocytosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:9469–9474
He X, Nie H, Wang K, Tan W, Wu X, Zhang P (2008) In Vivo Study of biodistribution and urinary excretion of surface-modified silica nanoparticles. Anal Chem 10:364–371
Hirsch LR, Stafford RJ, Bankson JA, Sershen SR, Rivera B, Price RE, Hazle JD, Halas NJ, West JL (2003) Nanoshell-mediated near-infrared thermal therapy of tumors under magnetic resonance guidance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:13549–13554
Huo Q, Liu J, Wang LQ, Jiang Y, Lambert TN, Fang E (2006) A new class of silica cross-linked micellar core-shell nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 128:6447–6453
Iezzi EB, Duchamp JC, Harich K, Glass TE, Lee HM, Olmstead MM, Balch AL, Dorn HC (2002) A symmetric derivative of the trimetallic nitride endohedral metallofullerene, Sc3N@C80. J Am Chem Soc 124:524–525
Jain TK, Reddy MK, Morales MA, Leslie-Pelecky DL, Labhasetwar V (2008) Biodistribution, clearance, and biocompatibility of iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles in rats. Mol Pharm 5:316–327
Kim J, Lee JE, Lee J, Yu JH, Kim BC, An K, Hwang Y, Shin CH, Park JG, Hyeon T (2006) Magnetic fluorescent delivery vehicle using uniform mesoporous silica spheres embedded with monodisperse magnetic and semiconductor nanocrystals. J Am Chem Soc 128:688–689
Li SD, Huang L (2008) Pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of nanoparticles. Mol Pharm 5:496–504
Li ZZ, Wen LX, Shao L, Chen JF (2004) Fabrication of porous hollow silica nanoparticles and their applications in drug release control. J Control Release 98:245–254
Lipski AM, Pino CJ, Haselton FR, Chen IW, Shastri VP (2008) The effect of silica nanoparticle-modified surfaces on cell morphology, cytoskeletal organization and function. Biomaterials 29:3836–3846
Mader H, Li X, Saleh S, Link M, Kele P, Wolfbeis OS (2008) Fluorescent silica nanoparticles. Ann NY Acad Sci 1130:218–223
Maynard AD, Aitken RJ, Butz T, Colvin V, Donaldson K, Oberdorster G, Philbert MA, Ryan J, Seaton A, Stone V, Tinkle SS, Tran L, Walker NJ, Warheit DB (2006) Safe handling of nanotechnology. Nature 444:267–269
Nakai T, Kanamori T, Sando S, Aoyama Y (2003) Remarkably size-regulated cell invasion by artificial viruses. Saccharide-dependent self-aggregation of glycoviruses and its consequences in glycoviral gene delivery. J Am Chem Soc 125:8465–8475
Oberdorster G, Oberdorster E, Oberdorster J (2005) Nanotoxicology: an emerging discipline evolving from studies of ultrafine particles. Environ Health Perspect 113:823–839
Opanasopit P, Nishikawa M, Hashida M (2002) Factors affecting drug and gene delivery: effects of interaction with blood components. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst 19:191–233
Pham KN, Fullston D, Sagoe-Crentsil K (2007) Surface modification for stability of nano-sized silica colloids. J Colloid Interface Sci 315:123–127
Roy I, Ohulchanskyy TY, Bharali DJ, Pudavar HE, Mistretta RA, Kaur N, Prasad PN (2005) Optical tracking of organically modified silica nanoparticles as DNA carriers: a nonviral, nanomedicine approach for gene delivery. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:279–284
Saba TM (1970) Physiology and physiopathology of the reticuloendothelial system. Arch Intern Med 126:1031–1052
Slowing II, Trewyn BG, Lin VS (2007) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for intracellular delivery of membrane-impermeable proteins. J Am Chem Soc 129:8845–8849
Sonavane G, Tomoda K, Makino K (2008) Biodistribution of colloidal gold nanoparticles after intravenous administration: effect of particle size. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 66:274–280
Stern ST, McNeil SE (2008) Nanotechnology safety concerns revisited. Toxicol Sci 101:4–21
Torchilin VP, Lukyanov AN, Gao Z, Papahadjopoulos-Sternberg B (2003) Immunomicelles: targeted pharmaceutical carriers for poorly soluble drugs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:6039–6044
Tsuji JS, Maynard AD, Howard PC, James JT, Lam CW, Warheit DB, Santamaria AB (2006) Research strategies for safety evaluation of nanomaterials, part IV: risk assessment of nanoparticles. Toxicol Sci 89:42–50
Wang JJ, Sanderson BJ, Wang H (2007) Cyto- and genotoxicity of ultrafine TiO2 particles in cultured human lymphoblastoid cells. Mutat Res 628:99–106
Yang J, Lee J, Kang J, Lee K, Suh JS, Yoon HG, Huh YM, Haam S (2008) Hollow silica nanocontainers as drug delivery vehicles. Langmuir 24:3417–3421
Zhang JS, Liu F, Huang L (2005) Implications of pharmacokinetic behavior of lipoplex for its inflammatory toxicity. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 57:689–698
Zhao X, Hilliard LR, Mechery SJ, Wang Y, Bagwe RP, Jin S, Tan W (2004) A rapid bioassay for single bacterial cell quantitation using bioconjugated nanoparticles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:15027–15032
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 30870680), Shanghai Sci-Tech Committee Foundation (no. 0752nm026) and Shanghai Leading Academic Discipline Project (no. S30206).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, G., Sun, J., Zhong, G. et al. Biodistribution and toxicity of intravenously administered silica nanoparticles in mice. Arch Toxicol 84, 183–190 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-009-0488-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-009-0488-x