Abstract
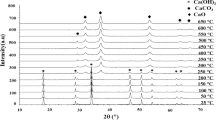
Structure and magnetic state of aerosol FeCu nanoparticles of 10–30 nm size with Cu content of 0.6–92.1 at.% have been examined by X-ray diffraction and Mössbauer spectroscopy. The FeCu particles have been shown to consist of an iron core surrounded by a copper and Fe oxide shell. With increasing Cu content the iron core having a bcc structure is reduced down to its complete disappearance followed by vanishing ferromagnetism of the particles. Within the copper content from 4.9 to 74.3 at.% the bcc and fcc phases coexist, with the fcc phase having a lattice constant close to that of pure copper and the bcc lattice constant being slightly higher than that for pure Fe due to embedding Cu atoms into the Fe lattice. At Fe-rich FeCu samples a presence of two-spin (ferromagnetic and paramagnetic) components of the fcc Fe is also observed. In the case of a thin copper shell there is only the ferromagnetic fcc Fe, whereas with further thickening of the shell both spin states of the fcc Fe appear existing up to a 20% Cu content. For FeCu samples with a higher Cu content they disappear due to oxidation of the copper grains. The Cu-rich samples with Cu content higher 80 at.% have a fcc structure, with the lattice constant being slightly higher than that of copper and they are paramagnetic. A slight increase of the lattice constant is due to the penetration of small iron aggregations into the Cu grains. In contact with air, the FeCu particles become covered with Fe3O4 and Cu2O. Their long-term exposure to ambient conditions leads to further oxidation process of Cu2O to CuO.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahams SC, Guttman L, Kasper JS (1962) Neutron diffraction determination of antiferromagnetism in face-centered cubic (γ) iron. Phys Rev 127:2052–2055
Bakkaloğlu ÖF (1998) A magnetic study of sputtered Fe/Cu multilayer films. J Magn Magn Mater 182:324–328
Baldokhin YV, Petrov YI (1992) Two states of the face-centered-cubic structure in iron discovered while investigating the Mössbauer spectra and the thermal expansion of small particles. Sov Phys Dokl 37:563–565
Bandyopadhyay B, Pahari B, Ghoshray K (2007) Magnetization and 63Cu NMR studies on granular FeCu alloys. Phys Rev B 76:214424
Barro MJ, Navarro E, Agudo P, Hernando A, Crespo P, Garsía-Escorial A (1997) Structural evolution during milling of diluted solid solutions of Fe–Cu. Mater Sci Forum 235–238:553–558
Brand RA (1987) Improving the validity of hyperfine field distributions from magnetic alloys. Part 1: Unpolarized source. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res B 28:398–416
Chien CL, Liou SH, Kofalt D, Yu W, Egami T, McGuire TR (1986) Magnetic properties of FexCu100−x solid solutions. Phys Rev B 33:3247–3250
Chubing P, Daosheng D (1994) Magnetic properties and magnetoresistance in granular Fe–Cu alloys. J Appl Phys 76:2986–2990
Chubing P, Haiying C, Guozhong L, Daosheng D (1994) Magnetic properties of FexCu1−x granular alloy films. J Appl Phys 76:7102–7104
Crespo P, Hernando A, Yavari R, Drbohlav O, García-Escorial A, Barandiaran JM, Orúe I (1993) Magnetic behavior of metastable fcc Fe–Cu after thermal treatments. Phys Rev B 48:7134–7139
Crespo P, Hernando A, Garcia-Escorial A, Kemner KM, Harris VG (1994) Extended X-ray-absorption fine-structure studies of heat-treated fcc-Fe50Cu50 powders processed via high-energy ball milling. J Appl Phys 76:6322–6324
Crespo P, Menéndes N, Tornero JD, Barro MJ, Barandiarán JM, Garsía-Escorial A, Hernando A (1998) Mössbauer spectroscopy evidence of a spinodal mechanism for the thermal decomposition of fcc FeCu. Acta Mater 46:4161–4166
da Costa GM, De Grave E, Vandenberghe RE (1998) Mössbauer studies of magnetite and Al-substituted maghemites. Hyperfine Interact 117:207–243
Del Bianco L, Ballesteros C, Rojo JM, Hernando A (1998) Magnetically ordered fcc structure at the relaxed grain boundaries of pure nanocrystalline Fe. Phys Rev Lett 81:4500–4503
Donath M, Pickel M, Schmidt AB, Weinelt M (2009) Ferromagnetic Fe on Cu(001) throughout the fcc-like phase: arguing from the viewpoint of the electronic structure. J Phys 21:134004
Duc NH, Tuan NA, Fnidiki A, Dorien C, Teillet J, Ben Youssef J, Le Gall H (2002) Structural, magnetic and Mössbauer studies of Fe–Cu granular films. J Phys 14:6657–6666
Enzo S, Mulas G, Frattini R, Principi G, Gupta R, Cooper R, Cowlam N (1997a) A study of mechanically alloyed Cu70Fe30 by diffraction, spectroscopy and DSC. Mater Sci Forum 235–238:529–534
Enzo S, Mulas G, Frattini R, Cooper RJ, Cowlam N, Principi G (1997b) A study of phase separation in metastable Cu50Fe50 alloys by neutron diffraction and neutron small-angle scattering. Philos Mag B 76:471–482
Escorial AG, Filho WB, Drbohlav O, Cresco P, Urchulutegui M, Antisari MV, Hernando A, Yavari AR (1997) Contrast modulation during decomposition of supersaturated fcc Fe–Cu solid and liquid solutions. Mater Sci Forum 235–238:559–564
Gonser U, Meechan CJ, Muir AH, Wiedersich H (1963) Determination of Néel temperatures in fcc iron. J Appl Phys 34:2373–2378
Gorria P, Martinez-Blanco D, Blanco JA, Hernando A, Garitaonandia JS, Barquin LF, Campo J, Smith RI (2004) Invar effect in fcc-FeCu solid solutions. Phys Rev B 69:214421
Gorria P, Martinez-Blanco D, Blanco JA, Perez MJ, Hernando A, Barquin LF, Smith RI (2005) High-temperature induced ferromagnetism on γ-Fe precipitates in FeCu solid solutions. Phys Rev B 72:014401
Gradmann U, Isbert HO (1980) Ferromagnetic γ-iron films prepared on CuAu(111)-surfaces. J Magn Magn Mater 15–18:1109–1111
Guen MY, Petrov YI (1969) Dispersnye kondensaty metallicheskogo para (Dispersed metal vapor condensates). Uspekhi Khimii (Adv Chem) 38:2249–2278 (in Russian)
Guen MY, Ziskin MS, Petrov YI (1959) Issledovanie dispersnosti aerosolej alyuminiya v zavisimosti ot usloviy ikh obrazovaniya (Study of dispersion of Al aerosols depending on the conditions of their formation). Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR 127:366–368 (in Russian)
Guigue-Millot N, Keller N, Perriat P (2001) Evidence for the Verwey transition in highly nonstoichiometrie nanometric Fe-based ferrites. Phys Rev B 64:012402
Guo H, Ma X, Yang L, Shen B, Zhao J (1991) Structure, magnetic properties and stability of the interfaces in Fe/Cu multilayer. J Magn Magn Mater 99:199–203
Halbauer R, Gonser U (1983) Antiferromagnetism of fcc iron films. J Magn Magn Mater 35:55–56
Hernando A, Crespo P, Yavari AR, García-Escorial A, Barandiaran JM (1993a) Formation of γ-Fe by mechanical alloying of Cu–Fe? IEEE Trans Magn 29:2634–2636
Hernando A, Crespo P, García-Escorial A, Barandiaran JM (1993b) Comment on “Mechanically driven alloying of immiscible elements”. Phys Rev Lett 70:3521–3522
Hornstein F, Ron M (1974) Plastic deformation of a Cu-1.92 w/o Fe alloy. J Phys 35:C6-497–C6-500
Jiang JZ, Gonser U, Gente C, Borman R (1993) Thermal stability of the unstable fcc-Fe50Cu50 phase prepared by mechanical alloying. Appl Phys Lett 63:1056–1058
Jiang JZ, Pankhurst QA, Johnson CE, Gente C, Bormann R (1994) Magnetic properties of mechanically alloyed FeCu. J Phys 6:L227–L232
Jiang JZ, Gente C, Bormann R (1998) Mechanical alloying in the Fe–Cu system. Mater Sci Eng A 242:268–277
Johanson GJ, McGirr MB, Wheeler DA (1970) Determination of the Néel temperature of face-centered-cubic iron. Phys Rev B 1:3208
Kaloshkin SD, Tomilin IA, Andrianov GA, Baldokhin YV, Shelekhov EV (1997) Phase transformations and hyperfine interactions in mechanically alloyed Fe–Cu solid solutions. Mater Sci Forum 235–238:565–570
Kaufmann L, Clougherty EV, Weiss RJ (1963) The lattice stability of metals-III. Iron. Acta Metall 11:323–335
Keune W, Lauer J, Williamson DL (1974) Mössbauer studies of FeCu thin films. J Phys 35:C6-473–C6-476
Keune W, Halbauer R, Gonser U, Lauer J, Williamson DL (1977) Antiferromagnetism of fcc Fe thin films. J Appl Phys 48:2976–2979
Keune W, Ezawa T, Macedo WAA, Glos U, Schletz KP, Kirschbaum U (1989) Magneto-volume effects in γ-Fe ultrathin films and small particles. Physica B 161:269–275
Klein J, Heck T, Campbell SJ, Aubertin F, Gonser U (1990) The activation energy for γ-Fe precipitates in CuFe. Hyperfine Interact 54:811–816
Kneller EF (1964) Magnetic and structural properties of metastable Fe-Cu solid solutions. J Appl Phys 35:2210–2211
Kuhrt C, Schultz L (1993) Magnetic properties of nanocrystalline mechanically alloyed Fe–M (M = Al, Si, Cu). IEEE Trans Magn 29:2667–2669
Lanotte L, Matteazzi P (1991) Magnetic behaviour of Fe1−x Cu x powders after milling. J Magn Magn Mater 101:178–180
Lutterrotti L, Gialanella S (1997) X-ray diffraction characterization of heavily deformed metallic specimens. Acta Mater 46:101–110
Macedo WAA, Keune W (1988) Magnetism of epitaxial fcc-Fe(100) films on Cu(100) investigated in situ by conversion-electron Mössbauer spectroscopy in ultrahigh vacuum. Phys Rev Lett 61:475–478
Macri PP, Rose P, Frattini R, Enzo S, Principi G, Hu WX, Cowlam N (1994a) A study of Fe50Cu50 produced by mechanical alloying and its thermal treatment. J Appl Phys 76:4061–4067
Macri PP, Enzo S, Cowlam N, Frattini R, Principi G, Hu WX (1994b) Mechanical alloying of immiscible Cu70TM30 alloys (TM = Fe, Co). Philos Mag B 71:249–259
Martinez B, Roig A, Obradors X, Molins E, Rouanet A, Monty C (1996) Magnetic properties of γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles obtained by vaporization condensation in a solar furnace. J Appl Phys 79:2580–2586
Matsui M, Chikazumi S (1978) Analysis of anomalous thermal expansion coefficient of Fe–Ni Invar alloys. J Phys Soc Jpn 45:458–465
Norton JT (1935) Solubility of copper in iron, and lattice changes during aging. Trans Am Inst Min Metall Eng 116:386–396
Özdemir Ö, Dunlop DJ, Moscowitz BM (1993) The effect of oxidation on the Verwey transition in magnetite. Geophys Res Lett 20:1671–1674
Pankhurst QA, Thomas MF, Johnson CE, Zquiak R, Zhang XX, Tejada J (1994) A Mössbauer study of Fe(5 Å) + Cu(50 Å) multilayers. IEEE Trans Magn 30:778–780
Pardavi-Horvath M, Takacs L (1993) Magnetic properties of copper-magnetite nanocomposites prepared by ball milling. J Appl Phys 73:6958–6960
Petrov YI (1982) Fizika malykh chastits (Physics of small particles). Nauka, Moscow (in Russian)
Petrov YI (1986) Klastery i malye chastitsy (Clusters and small particles). Nauka, Moscow (in Russian)
Petrov YI, Shafranovsky EA (2000) Features of ultrafine inorganic particle preparation by the gas evaporation method. BRAS Phys 64:1236–1244
Petrov YI, Shafranovsky EA (2001) Exhibition of high- and low-spin states of the high-temperature fcc phase in nanoparticles of Fe, Fe-rich and C0-rich alloys. J Nanopart Res 3:419–432
Randrianantoandro N, Mercier AM, Hervieu M, Greneche JM (2001) Direct phase transformation from hematite to maghemite during high energy ball milling. Mater Lett 47:150–158
Roig A, Zhang XX, Zuberek R, Tejada J, Molins E (1995) Magnetic properties of Fe/Cu multilayers. J Magn Magn Mater 140–144:559–560
Rössler UK, Idzikowski B, Eckert D, Nenkov K, Müller K-H, Kopcewicz M, Grabias A (1999) Structural, magnetic and magnetotransport properties of melt-spun Fe10Cu90. IEEE Trans Magn 35:2841–2843
Schurer PJ, Scully B, Kowalewski M, Heinrich B (2001) Mössbauer investigation of the Fe/Cu interfaces in bcc Fe/Cu/Fe(0 0 1) structures. J Magn Magn Mater 224:65–75
Shafranovsky EA, Petrov YI (2004) Aerosol Fe nanoparticles with the passivating oxide shell. J Nanoparticle Res 6:71–90
Shafranovsky EA, Petrov YI, Casas Ll, Molins E (2009) Structure and composition of aerosol particles obtained on evaporation of a homogeneous FeCu(50.4 at%) alloy. Doklady Phys Chem 429:246–251
Sumiyama K, Nakamura Y, Tanaka K (1990) Mössbauer spectra and electronic structure of nonequilibrium Fe-Cu alloys produced by vapor quenching. Hyperfine Interact 53:143–158
Tang J (1997) Magnetic properties of a few material systems made by mechanical alloying and milling. Mater Sci Forum 235–238:819–824
Tanji Y (1971) Thermal expansion coefficient and spontaneous volume magnetostriction of Fe–Ni (fcc) alloys. J Phys Soc Jpn 31:1366–1373
Tholence JL, Tournier R (1970) One-impurity and interaction effects on the Cu:Fe magnetization. Phys Rev Lett 25:867–871
van Noort HM, den Broeder FJA, Draaisma HJG (1985) Mössbauer study of Cu–Fe composition-modulated thin films. J Magn Magn Mater 51:273–279
Vandenberghe RE, Barrero CA, da Costa GM, Van San E, De Grave E (2000) Mössbauer characterization of iron oxides and (oxy)hydroxides: the present state of the art. Hyperfine Interact 126:247–259
Vol AE (1966) Handbook of binary metallic systems; structure and properties, vol 2. Israel Program for Scientific Translations, Jerusalem (trans: Vol AE (1962) Stroenie i svoistva dvoinykh metallicheskikh system, vol 2. Fizmatgiz, Moscow, 982 p)
Weiss RJ (1963) The origin of the “Invar” effect. Proc Phys Soc 82:281–288
Williams JM, Blythe HJ, Fedosyuk VM (1995) An investigation of electrodeposited granular CuFe alloyed films. J Magn Magn Mater 155:355–357
Window B (1970) Hyperfine fields at 57Fe in copper iron alloys. J Phys C 3:S323–S329
Xiao G, Wang JQ, Xiong P (1993) Giant magnetoresistance and anomalous Hall effect in Co–Ag and Fe–Cu, Ag, Au, Pt granular alloys. IEEE Trans Magn 29:2694–2699
Yang Y, Zhu Y, Li Q, Ma X, Dong Y, Wamg G, Wei S (2001) Mechanical alloying, fine structure and thermal decomposition of nanocrystalline fcc-Fe60Cu40. Physica B 293:249–259
Yavary AR (1993) Yavari replies. Phys Rev Lett 70:3522
Yavary AR, Desré PJ, Benameur T (1992) Mechanically driven alloying of immiscible elements. Phys Rev Lett 68:2235–2238
Yousif A, Bouziane K, Elzain ME, Ren X, Berry FJ, Widatallah HM, Al Rawas A, Gismelseed A, Al-Omari IA (2004) Magnetic properties of nanocrystalline FexCu1−x alloys prepared by ball milling. Hyperfine Interact 156–157:213–221
Acknowledgments
The work is partially supported by Ministerio de Educación y Ciencia (projects Consolider CSD2007-41 and CTQ2009-12520-C03-03). The authors appreciate the Catalan Government for the financial support (Grant 2009SGR-203) and one of authors (E.A. Sh.) gratefully acknowledges financial support from the Catalan Government (Grant 2007PIV10021) during his visit to the ICMAB-CSIC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shafranovsky, E.A., Petrov, Y.I., Casas, L. et al. Structural and Mössbauer studies of aerosol FeCu nanoparticles in a wide composition range. J Nanopart Res 13, 4913 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-011-0470-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-011-0470-4