Abstract
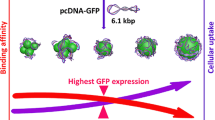
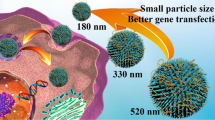
Mesoporous silica nanoparticles have been synthesized and functionalized with four different types of molecules containing amino groups, i.e., with primary amines only, with quaternary amines, with quaternized cyclic amines, or with polyethylenimine (PEI), which is formed by primary, secondary, and tertiary amines. These nanoparticles were then incubated with reporter plasmids and the ability of the resulting complexes to transfect human cells was studied. Only nanoparticles functionalized with PEI were efficient for transfection. The agglomeration behavior and the electrokinetic potential of the nanoparticle–plasmid complexes have been studied, as well as their cell internalization behavior using a fluorescent-labeled plasmid that allows its monitorization by confocal microscopy. The results indicate that the efficiency of PEI-functionalized nanoparticles for transfection resides to some extent in the different characteristics imparted to the nanoparticles regarding agglomeration and surface charge behavior.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akinc A, Thomas M, Klibanov AM, Langer R (2004) Exploring polyethylenimine-mediated DNA transfection and the proton sponge hypothesis. J Gene Med 7:657–663
Balas F, Manzano M, Colilla M, Vallet-Regí M (2008) L-Trp adsorption into silica mesoporous materials to promote bone formation. Acta Biomater 4:514–522
Deguchi S, Yamazaki T, Mukai S, Usami R, Horikoshi K (2007) Stabilization of C-60 nanoparticles by protein adsorption and its implications for toxicity studies. Chem Res Toxicol 20:854–858
Díaz B, Sánchez-Espinel C, Arruebo M, Faro J, de Miguel E, Magadan S, Yagüe C, Fernández-Pacheco R, Ibarra R, Santamaría J, González-Fernández A (2008) Assessing methods for blood cell cytotoxic responses to inorganic nanoparticles and nanoparticle aggregates. Small 4:2025–2034
Gemeinhart RA, Luo D, Saltzman WM (2005) Cellular fate of a modular dna delivery system mediated by silica nanoparticles. Biotechnol Prog 21:532–537
Hartmann M (2005) Ordered mesoporous materials for bioadsorption and biocatalysis. Chem Mater 17:4577–4593
Heister E, Lamprecht C, Neves V, Tilmacius C, Datas L, Flahaut E, Soula B, Hinterdorfer P, Coley HM, Silva SR, McFadden J (2010) Higher dispersion efficacy of functionalized carbon nanotubes in chemical and biological environments. ACS Nano 4:2615–2626
Kneuer C, Sameti M, Bakowsky U, Schiestel T, Schirra H, Schmidt H, Lehr CM (2000) A nonviral dna delivery system based on surface modified silica-nanoparticles can efficiently transfect cells in vitro. Bioconjugate Chem 11:926–932
Kozlowski A, Harris JM (2001) Improvements in protein PEGylation: pegylated interferons for treatment of hepatitis C. J Control Release 72:217–224
Kulak A, Lee YJ, Park YS, Yoon KB (2000) Orientation-controlled monolayer assembly of zeolite crystals on glass and mica by covalent linkage of surface-bound epoxide and amine groups. Angew Chem Int Ed 39:950–953
Liu Z, Robinson JT, Sun X, Dai H (2008) PEGylated nanographene oxide for delivery of water-insoluble cancer drugs. J Am Chem Soc 130:10876–10877
Lu J, Liong M, Zink JI, Tamanoi F (2007) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a delivery system for hydrophobic anticancer drugs. Small 3:1341–1346
Luo D, Saltzman WM (2000) Enhancement of transfection by physical concentration of DNA at the cell surface. Nat Biotechnol 18:893–895
Marcelo G, Tarazona MP, Saiz E (2005) Solution properties of poly (diallyldimethylammonium chloride) (PDDA). Polymer 46:2584–2594
Park IY, Kim IY, Yoo MK, Choi YJ, Cho MH, Cho CS (2008) Mannosylated polyethylenimine coupled mesoporous silica nanoparticles for receptor-mediated gene delivery. Int J Pharma 359:280–287
Radu DR, Lai CY, Jeftinija K, Rowe EW, Jeftinija S, Lin VSY (2004) A polyamidoamine dendrimer-capped mesoporous silica nanosphere-based gene transfection reagent. J Am Chem Soc 126:13216–13217
Rosenholm JM, Peuhu E, Eriksson JE, Sahlgren C, Lindén M (2009) Targeted intracellular delivery of hydrophobic agents using mesoporous hybrid silica nanoparticles as carrier systems. Nano Lett 9:3308–3311
Roshenholm J, Sahlgren C, Lindén M (2010) Cancer cell targeting and cell specific delivery by mesoporous silica nanoparticles. J Mater Chem 20:2707–2713
Sager TM, Porter DW, Robinson VA, Lindsley WG, Schwegler-Berry DE, Castranova V (2007) Improved method to disperse nanoparticles for in vitro and in vivo investigation of toxicity. Nanotoxicology 1:118–129
Tan K, Cheang P, Ho I, Lam P, Hui KM (2007) Nanosized bioceramic particles could function as efficient gene delivery vehicles with target specificity for the spleen. Gene Ther 14:828–835
Tantra R, Tompkins J, Quincey P (2010) Characterisation of the de-agglomeration effects of bovine serum albumin on nanoparticles in aqueous suspension. Colloid Surf B Biointerf 75:275–281
Tolnai G, Csempesz F, Kabai-Faix M, Kalman E, Keresztes Z, Kovacs AL, Ramsden JJ, Horvolgyi Z (2001) Preparation and characterization of surface-modified silica-nanoparticles. Langmuir 17:2683–2687
Torney F, Trewyn BG, Lin VSY, Wang K (2007) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles deliver DNA and chemicals into plants. Nat Nanotechnol 2:295–300
Xia T, Kovochich M, Liong M, Meng H, Kabehie S, George S, Zink JI, Nel AE (2009) Polyethyleneimine coating enhances the cellular uptake of mesoporous silica nanoparticles and allows safe delivery of siRNA and DNA constructs. ACS Nano 10:3273–3286
Yagüe C, Moros M, Grazú V, Arruebo M, Santamaría J (2008) Synthesis and stealthing study of bare and PEGylated silica micro- and nanoparticles as potential drug delivery vectors. Chem Eng J 137:42–53
Xu ZP, Zeng QH, Lu GQ, Yu AB (2006) Inorganic nanoparticles as carriers for efficient cellular delivery. Chem Eng Sci 61:1027–1040
Yiu HP, McBain SC, El Haj AJ, Dobson J (2007) A triple-layer design for polyethyleneimine-coated, nanostructured magnetic particles and their use in DNA binding and transfection. Nanotechnology 18:435601–435607
Yu J, Zhao H, Ye L, Yang H, Ku S, Yang N, Xiao N (2009) Effect of surface functionality of magnetic silica nanoparticles on the cellular uptake by glioma cells in vitro. J Mater Chem 19:1265–1270
Zeng W, Qian XF, Zhang YB, Yin J, Zhu ZK (2005) Organic modified mesoporous MCM-41 through solvothermal process as drug delivery system. Mater Res Bull 40:766–772
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants MAT2009-14695-C04-02 from the Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación, grants from Fundación Mutua Madrileña to NV, and from Fundación Ramón Areces to MA. VC is the recipient of a predoctoral award from Comunidad de Madrid. MA acknowledges the support from the 2006 Ramón y Cajal program (order ECI/158/2005). NV and FM-S are supported by program I3SNS and Sara Borrell, respectively, from Fondo de Investigaciones Sanitarias. We thank Laura Saldaña (CIBER-BBN and Hospital Universitario la Paz-IdiPAZ) for helpful suggestions and excellent technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cebrián, V., Yagüe, C., Arruebo, M. et al. On the role of the colloidal stability of mesoporous silica nanoparticles as gene delivery vectors. J Nanopart Res 13, 4097–4108 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-011-0353-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-011-0353-8