Abstract
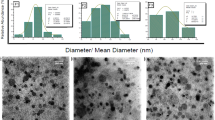
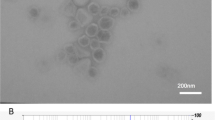
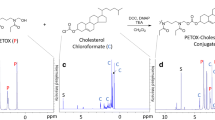
3,5-Bis(2-fluorobenzylidene)-4-piperidone (EF24) is an anti-proliferative diphenyldifluoroketone analog of curcumin with more potent activity. The authors describe a liposome preparation of EF24 using a “drug-in-CD-in liposome” approach. An aqueous solution of EF24 and hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HPβCD) inclusion complex (IC) was used to prepare EF24 liposomes. The liposome size was reduced by a combination of multiple freeze–thaw cycles. Co-encapsulation of glutathione inside the liposomes conferred them with the capability of labeling with imageable radionuclide Tc-99m. Phase solubility analysis of EF24-HPβCD mixture provided k 1:1 value of 9.9 M−1. The enhanced aqueous solubility of EF24 (from 1.64 to 13.8 mg/mL) due to the presence of HPβCD helped in the liposome preparation. About 19% of the EF24 IC was encapsulated inside the liposomes (320.5 ± 2.6 nm) by dehydration–rehydration technique. With extrusion technique, the size of 177 ± 6.5 nm was obtained without any effect on encapsulation efficiency. The EF24-liposomes were evaluated for anti-proliferative activity in lung adenocarcinoma H441 and prostate cancer PC-3 cells. The EF24-liposomes demonstrated anti-proliferative activity superior to that of plain EF24 at 10 μM dose. When injected in rats, the Tc-99m-labeled EF24-liposomes cleared from blood with an α-t 1/2 of 21.4 min and β-t 1/2 of 397 min. Tissue radioactivity counting upon necropsy showed that the majority of clearance was due to the uptake in liver and spleen. The results suggest that using “drug-in-CD-in liposome” approach is a feasible strategy to formulate an effective parenteral preparation of EF24. In vitro studies show that the liposomal EF24 remains anti-proliferative, while presenting an opportunity to image its biodistribution.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams BK, Cai J, Armstrong J, Herold M, Lu YJ, Sun A, Snyder JP, Liotta DC, Jones DP, Shoji M (2005) EF24, a novel synthetic curcumin analog, induces apoptosis in cancer cells via a redox-dependent mechanism. Anticancer Drugs 16:263–275
Akerley W, Choy H (1999) Single-agent paclitaxel and radiation for non-small cell lung cancer. Semin Radiat Oncol 9:85–89
American Cancer Society (2009) Cancer Statistics 2009 Presentation. American Cancer Society. http://www.cancer.org/docroot/PRO/content/PRO_1_1_Cancer_Statistics_2009_Presentation.asp
Anand P, Kunnumakkara AB, Newman RA, Aggarwal BB (2007) Bioavailability of curcumin: problems and promises. Mol Pharm 4:807–818
Anderson M, Omri A (2004) The effect of different lipid components on the in vitro stability and release kinetics of liposome formulations. Drug Deliv 11:33–39
Awasthi V, Goins B, Klipper R, Loredo R, Korvick D, Phillips WT (1998) Imaging experimental osteomyelitis using radiolabeled liposomes. J Nucl Med 39:1089–1094
Awasthi VD, Garcia D, Goins BA, Phillips WT (2003) Circulation and biodistribution profiles of long-circulating PEG-liposomes of various sizes in rabbits. Int J Pharm 253:121–132
Awasthi VD, Garcia D, Klipper R, Goins BA, Phillips WT (2004a) Neutral and anionic liposome-encapsulated hemoglobin: effect of postinserted poly(ethylene glycol)-distearoylphosphatidylethanolamine on distribution and circulation kinetics. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 309:241–248
Awasthi VD, Garcia D, Klipper R, Phillips WT, Goins BA (2004b) Kinetics of liposome-encapsulated hemoglobin after 25% hypovolemic exchange transfusion. Int J Pharm 283:53–62
Awasthi V, Yee SH, Jerabek P, Goins B, Phillips WT (2007) Cerebral oxygen delivery by liposome-encapsulated hemoglobin: a positron-emission tomographic evaluation in a rat model of hemorrhagic shock. J Appl Physiol 103:28–38
Bekersky I, Fielding RM, Dressler DE, Lee JW, Buell DN, Walsh TJ (2002) Pharmacokinetics, excretion, and mass balance of liposomal amphotericin B (AmBisome) and amphotericin B deoxycholate in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 46:828–833
Bhardwaj U, Burgess DJ (2010) Physicochemical properties of extruded and non-extruded liposomes containing the hydrophobic drug dexamethasone. Int J Pharm 388:181–189
Brewster ME, Loftsson T (2007) Cyclodextrins as pharmaceutical solubilizers. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 59:645–666
Challa R, Ahuja A, Ali J, Khar RK (2005) Cyclodextrins in drug delivery: an updated review. AAPS PharmSciTech 6:E329–E357
Fatouros DG, Hatzidimitriou K, Antimisiaris SG (2001) Liposomes encapsulating prednisolone and prednisolone-cyclodextrin complexes: comparison of membrane integrity and drug release. Eur J Pharm Sci 13:287–296
Frank DW (1976) Physiological data of laboratory animals. In: Melby ECJ (ed) Physiological data of laboratory animals. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, pp 23–64
Frijlink HW, Visser J, Hefting NR, Oosting R, Meijer DK, Lerk CF (1990) The pharmacokinetics of beta-cyclodextrin and hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin in the rat. Pharm Res 7:1248–1252
Goins B, Klipper R, Rudolph AS, Cliff RO, Blumhardt R, Phillips WT (1993) Biodistribution and imaging studies of technetium-99m-labeled liposomes in rats with focal infection. J Nucl Med 34:2160–2168
Gould S, Scott RC (2005) 2-Hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin (HP-beta-CD): a toxicology review. Food Chem Toxicol 43:1451–1459
Higuchi T, Connors K (1965) Phase solubility techniques. Adv Anal Chem Instrum 4:127–212
Ishida T, Kiwada H (2008) Accelerated blood clearance (ABC) phenomenon induced by administration of PEGylated liposome. Yakugaku Zasshi 128:233–243
Ishida T, Harashima H, Kiwada H (2002) Liposome clearance. Biosci Rep 22:197–224
Ishida T, Wang X, Shimizu T, Nawata K, Kiwada H (2007) PEGylated liposomes elicit an anti-PEG IgM response in a T cell-independent manner. J Control Release 122:349–355
Kasinski AL, Du Y, Thomas SL, Zhao J, Sun SY, Khuri FR, Wang CY, Shoji M, Sun A, Snyder JP, Liotta D, Fu H (2008) Inhibition of IkappaB kinase-nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway by 3,5-bis(2-flurobenzylidene)piperidin-4-one (EF24), a novel monoketone analog of curcumin. Mol Pharmacol 74:654–661
Kirby C, Gregoriadis G (1984) Dehydration–rehydration vesicles (DRV): a new method for high yield drug entrapment in liposomes. Biotechnology 979–984
Kume Y, Maeda F, Harashima H, Kiwada H (1991) Saturable, non-Michaelis-Menten uptake of liposomes by the reticuloendothelial system. J Pharm Pharmacol 43:162–166
Lagisetty P, Powell DR, Awasthi V (2009) Synthesis and structural determination of 3,5-bis(2-fluorobenzylidene)-4-piperidone analogs of curcumin. J Mol Str 936:23–28
Landegren U (1984) Measurement of cell numbers by means of the endogenous enzyme hexosaminidase. Applications to detection of lymphokines and cell surface antigens. J Immunol Methods 67:379–388
Laverman P, Boerman OC, Oyen WJG, Corstens FHM, Storm G (2001) In vivo applications of PEG liposomes: unexpected observations. Critical reviews in therapeutic drug carrier systems 18:551–566
Laverman P, Boerman OC, Storm G (2003) Radiolabeling of liposomes for scintigraphic imaging. Methods Enzymol 373:234–248
Loftsson T, Hreinsdottir D, Masson M (2005a) Evaluation of cyclodextrin solubilization of drugs. Int J Pharm 302:18–28
Loftsson T, Jarho P, Masson M, Jarvinen T (2005b) Cyclodextrins in drug delivery. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 2:335–351
McCormack B, Gregoriadis G (1994) Entrapment of cyclodextrin-drug complexes into liposomes: potential advantages in drug delivery. J Drug Target 2:449–454
McCormack B, Gregoriadis G (1996) Comparative studies of the fate of free and liposome-entrapped hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin/drug complexes after intravenous injection into rats: implications in drug delivery. Biochim Biophys Acta 1291:237–244
McCormack B, Gregoriadis G (1998) Drugs-in-cyclodextrins-in-liposomes: an approach to controlling the fate of water insoluble drugs in vivo. Int J Pharm 162:59–69
Petty C (1982) Research techniques in the rats. Charles C. Thomas, Springfield, IL (USA)
Phillips WT, Rudolph AS, Goins B, Timmons JH, Klipper R, Blumhardt R (1992) A simple method for producing a technetium-99m-labeled liposome which is stable in vivo. Nucl Med Biol 19:539–547
Piel G, Piette M, Barillaro V, Castagne D, Evrard B, Delattre L (2007) Study of the relationship between lipid binding properties of cyclodextrins and their effect on the integrity of liposomes. Int J Pharm 338:35–42
Selvendiran K, Tong L, Vishwanath S, Bratasz A, Trigg NJ, Kutala VK, Hideg K, Kuppusamy P (2007) EF24 induces G2/M arrest and apoptosis in cisplatin-resistant human ovarian cancer cells by increasing PTEN expression. J Biol Chem 282:28609–28618
Sharma RA, McLelland HR, Hill KA, Ireson CR, Euden SA, Manson MM, Pirmohamed M, Marnett LJ, Gescher AJ, Steward WP (2001) Pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic study of oral Curcuma extract in patients with colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res 7:1894–1900
Stewart JC (1980) Colorimetric determination of phospholipids with ammonium ferrothiocyanate. Anal Biochem 104:10–14
Subramaniam D, May R, Sureban SM, Lee KB, George R, Kuppusamy P, Ramanujam RP, Hideg K, Dieckgraefe BK, Houchen CW, Anant S (2008) Diphenyl difluoroketone: a curcumin derivative with potent in vivo anticancer activity. Cancer Res 68:1962–1969
Sun A, Shoji M, Lu YJ, Liotta DC, Snyder JP (2006) Synthesis of EF24-tripeptide chloromethyl ketone: a novel curcumin-related anticancer drug delivery system. J Med Chem 49:3153–3158
Szebeni J (1998) The interaction of liposomes with the complement system. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst 15:57–88
Szebeni J, Baranyi L, Savay S, Bodo M, Morse DS, Basta M, Stahl GL, Bunger R, Alving CR (2000) Liposome-induced pulmonary hypertension: properties and mechanism of a complement-mediated pseudoallergic reaction. Am J Physiol 279:H1319–H1328
Walde P, Ichikawa S (2001) Enzymes inside lipid vesicles: preparation, reactivity and applications. Biomol Eng 18:143–177
Woodle MC, Newman MS, Working PK (1995) Biological properties of sterically stabilized liposomes. In: Lasic DD, Martin F (eds) Stealth liposomes. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 103–117
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the help of Ms. Prachi Vilekar (Graduate Student) in cell culture studies. The radiolabeling and biodistribution study was performed in the Small Animal Imaging Facility of the College of Pharmacy. This study was made possible by the financial support under the National Cancer Institute grant 1R03 CA143614-01.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agashe, H., Lagisetty, P., Sahoo, K. et al. Liposome-encapsulated EF24-HPβCD inclusion complex: a preformulation study and biodistribution in a rat model. J Nanopart Res 13, 2609–2623 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-010-0154-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-010-0154-5