Abstract
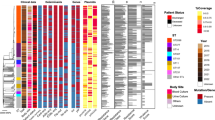
During 1998–2008, there were 31 strains of Gordonia species isolated from clinical specimens in our laboratory. Our identification of the 31 strains of Gordonia species showed that major pathogenic Gordonia species in Japan were classifiable, respectively into 14 and 13 strains of Gordonia sputi and Gordonia bronchialis. The four remaining strains were identified as three Gordonia species: G. aichiensis (2 strains), and G. terrae (1 strain), and G. otitidis (1 strain). Results of drug susceptibility tests for these 31 strains of Gordonia isolates are reported herein.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stackebrandt E, Rainey FA, Ward-Rainey NL. Proposal for a new hierarchic classification system, Actinobacteria classis nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1997;47:479–91.
Shen F-T, Ho M-J, Hunag H-R, Arum AB, Rekha PD, Young CC. Molecular detection and phylogenetic characterization of Gordonia species in heavily oil-contaminated soils. Res Microbiol. 2008;150:522–9. doi:10.1016/j.resmic.2008.07.004.
Euzeby JP. List of prokaryotic names with standing in nomenclature. 2007. www.bacterio.net.
Shen FT, Goodfellow M, Jones AL, Chen YP, Arun AB, Lai WA, et al. Gordonia soli sp. nov., a novel actinomycete isolated from soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2006;56:2597–601. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.64492-0.
Tsukamura M. Numerical classification of Rhodococcus (formerly Gordona) organisms recently isolated from sputa of patients: description of Rhodococcus sputi Tsukamura sp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1978;128:169–81.
Jogan Martin T, DJ Murphy F, Natyshak I, Ewan EP. Rhodococcus infection of the skin with lymphadenitis in a nonimmunocompromised girl. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1991;24:328–32. doi:10.1016/0190-9622(91)70044-3.
Drancourt M, McNeil MM, Brown JM, Lasker BA, Maurin M, Choux M, et al. Brain abscess due to Gordona terrae in an immunocompromised child: case report and review of infections caused by G. terrae. Clin Infect Dis. 1994;19:258–62.
Iida S, Taniguchi H, Kageyama A, Yazawa K, Chibana H, Murata S, et al. Gordonia otitidis sp. nov., isolated from a patient with external otitis. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2005;55:1871–6. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.63282-0.
Kageyama A, Iida S, Yazawa K, Kudo T, Suzuki S, Koga T, et al. Gordonia araii sp. nov. and Gordonia effusa sp. nov., isolated from patients in Japan. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2006;56:1817–21. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.64067-0.
Miyado S. Identification procedure at the genus level. In: Miyado S, Hamada M, Hotta K, Kudo T, Seino A, Suzuki K, Yokota A, editors. Identification manual of actinomycetes. Tokyo: Business Center for Academic Societies Japan; 2001.
Staneck JI, Roberts GD. Simplified approach to identification of aerobic actinomycetes by thin-layer chromatography. Appl Microbiol. 1974;28:226–31.
Minnikin DE, Hutschison IG, Galdicott AB, Goodfellow M. Thin-layer chromatography of methanolysates of mycolic acid-containing bacteria. J Chromatogr. 1980;188:221–33. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(00)88433-2.
Kang Y, Takeda K, Yazawa K, Mikami Y. Phylogenic studies of Gordonia species based on gyrB and secA1 gene analyses. Mycopathologia. 2009;167:95–105.
Kimura M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol. 1980;16:111–20. doi:10.1007/BF01731581.
Saitou N, Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol. 1987;4:406–25.
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ. CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighing, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994;22:4673–80. doi:10.1093/nar/22.22.4673.
Nagasawa Z, Manome I, Nagayama A. A rapid antimicrobial susceptibility test based on chemiluminescence assay and its application to screening of genotypes in vancomycin-resistant enterococci. J Infect Chemother. 2004;10:220–6. doi:10.1007/s10156-004-0329-z.
Lechevalier MP, Lechevalier HA. Chemical composition as a criterion in the classification of aerobic actinomycetes. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1970;24:278–88.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Grant-In-Aid for Scientific Research (C), and by a Program, through the Special Coordination Funds for Promoting Science and Technology from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, of the Japanese Government during 2006–2008 to YM. National BioResource Project (NBRP) also appreciates the gift of most of the Gordonia strains used in this work. We thank Ms Tomoko Sakai for her excellent technical assistance in DNA sequence analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11046-009-9269-6
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aoyama, K., Kang, Y., Yazawa, K. et al. Characterization of Clinical Isolates of Gordonia Species in Japanese Clinical Samples During 1998–2008. Mycopathologia 168, 175–183 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-009-9213-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-009-9213-9