Abstract
Background
Herein, we identified miRNA signatures that were able to differentiate malignant prostate cancer from benign prostate hyperplasia and revealed the therapeutic potential of these miRNAs against prostate cancer development.
Methods and results
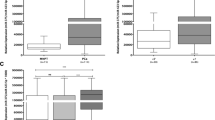
MicroRNA expressions were determined by qPCR. MTT was used for cell viability analysis and immunohistochemistry was performed for Bax/Bcl-2 staining. ELISA was used to measure MMP2/9 levels. Wound healing assay was used for the evaluation of cell migration. Notably, expression levels of miR-125b-5p, miR-145-5p and miR-221-3p were significantly reduced in prostate cancer patients as compared to BPH patients. Moreover, ectopic expression of miR-125b-5p, miR-145-5p and miR-221-3p resulted in significant inhibition of cell proliferation and altered cell morphology. Also, expression level of Bax protein was increased while Bcl-2 level was reduced in cells treated with miR-125b-5p, miR-145-5p and miR-221-3p mimics. Enhanced expression of miR-125b-5p, miR-145-5p and miR-221-3p was also significantly altered the expression of caspase 3 and 8 levels. In addition, MMP9 levels were significantly reduced in cells ectopically expressing miR-221-3p. All miRNA mimics significantly interfered with the migration of prostate cancer cells.
Conclusions
Consequently, our findings point to an important role of these three miRNAs in prostate cancer and indicate that miR-125b-5p, miR-145-5p and miR-221-3p are potential therapeutic targets against prostate cancer.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68(6):394–424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A et al (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of ıncidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71(3):209–249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2020) Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin 70(1):7–30
Wang G, Zhao D, Spring DJ, DePinho RA (2018) Genetics and biology of prostate cancer. Genes Dev 32(17–18):1105–1140
Inoue J, Inazawa J (2021) Cancer-associated miRNAs and their therapeutic potential. J Hum Genet. https://doi.org/10.1038/s10038-021-00938-6
Winkle M, El-Daly SM, Fabbri M, Calin GA (2021) Noncoding RNA therapeutics—challenges and potential solutions. Nat Rev Drug Discov. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41573-021-00219-z
Huntzinger E, Izaurralde E (2011) Gene silencing by microRNAs: contributions of translational repression and mRNA decay. Nat Rev Genet 12(2):99–110
Jonas S, Izaurralde E (2015) Towards a molecular understanding of microRNA-mediated gene silencing. Nat Rev Genet 16(7):421–433
Bozgeyik E, Tepe NB, Bozdag Z (2020) Identification of microRNA expression signature for the diagnosis and prognosis of cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Pathol Res Pract 216(11):153159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prp.2020.153159
Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Bichi R, Zupo S, Noch E et al (2002) Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro-RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99(24):15524–15529. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.242606799
Cimmino A, Calin GA, Fabbri M, Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Shimizu M et al (2005) miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(39):13944–13949. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0506654102
Calin GA, Croce CM (2006) MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer 6(11):857–866. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc1997
Ruan K, Fang X, Ouyang G (2009) MicroRNAs: novel regulators in the hallmarks of human cancer. Cancer Lett 285(2):116–126
Bozgeyik I (2021) miRNA network associated with the TMPRSS2-ERG fusion in prostate cancer invasion. Meta Gene 29:100933
Chen X, Liang H, Guan D, Wang C, Hu X, Cui L et al (2013) A combination of Let-7d, Let-7g and Let-7i serves as a stable reference for normalization of serum microRNAs. PLoS ONE 8(11):e79652-e. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0079652
Ege B, Yumrutas O, Ege M, Pehlivan M, Bozgeyik I (2020) Pharmacological properties and therapeutic potential of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) in osteosarcoma. J Pharm Pharmacol 72(1):56–67
Szeliski K, Adamowicz J, Gastecka A, Drewa T, Pokrywczyńska M (2018) Modern urology perspectives on prostate cancer biomarkers. Central Eur J Urol 71(4):420
Mao Z, Ji A, Yang K, He W, Hu Y, Zhang Q et al (2018) Diagnostic performance of PCA3 and hK2 in combination with serum PSA for prostate cancer. Medicine 97(42):e12806
Salameh A, Lee AK, Cardó-Vila M, Nunes DN, Efstathiou E, Staquicini FI et al (2015) PRUNE2 is a human prostate cancer suppressor regulated by the intronic long noncoding RNA PCA3. Proc Natl Acad Sci 112(27):8403–8408
Ozen M, Creighton CJ, Ozdemir M, Ittmann M (2008) Widespread deregulation of microRNA expression in human prostate cancer. Oncogene 27(12):1788–1793. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210809
Kim SW, Ramasamy K, Bouamar H, Lin AP, Jiang D, Aguiar RC (2012) MicroRNAs miR-125a and miR-125b constitutively activate the NF-kappaB pathway by targeting the tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced protein 3 (TNFAIP3, A20). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(20):7865–7870. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1200081109
Sun B, Zhang Y, Zhou L, Yin L, Li F, Li C et al (2019) The proliferation of cervical cancer is promoted by miRNA-125b through the regulation of the HMGA1. Onco Targets Ther 12:2767–2776. https://doi.org/10.2147/ott.S197740
Wang X, Zhang Y, Fu Y, Zhang J, Yin L, Pu Y et al (2015) MicroRNA-125b may function as an oncogene in lung cancer cells. Mol Med Rep 11(5):3880–3887. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2014.3142
Tsang FH, Au V, Lu WJ, Shek FH, Liu AM, Luk JM et al (2014) Prognostic marker microRNA-125b inhibits tumorigenic properties of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via suppressing tumorigenic molecule eIF5A2. Dig Dis Sci 59(10):2477–2487. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-014-3184-5
Li J, You T, Jing J (2014) MiR-125b inhibits cell biological progression of Ewing’s sarcoma by suppressing the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway. Cell Prolif 47(2):152–160. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.12093
Konoshenko MY, Bryzgunova OE, Lekchnov EA, Amelina EV, Yarmoschuk SV, Pak SV et al (2020) The ınfluence of radical prostatectomy on the expression of cell-free MiRNA. Diagnostics 10(8):600
Spizzo R, Nicoloso MS, Lupini L, Lu Y, Fogarty J, Rossi S, Zagatti B, Fabbri M, Veronese A, Liu X, Davuluri R, Croce CM, Mills G, Negrini M, Calin GA (2010) miR-145 participates with TP53 in a death-promoting regulatory loop and targets estrogen receptor-α in human breast cancer cells. Cell Death Differ 17(2):246–254. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2009.117
Ozen M, Karatas OF, Gulluoglu S, Bayrak OF, Sevli S, Guzel E et al (2015) Overexpression of miR-145-5p inhibits proliferation of prostate cancer cells and reduces SOX2 expression. Cancer Invest 33(6):251–258. https://doi.org/10.3109/07357907.2015.1025407
Zhang P, Zhang M, Han R, Zhang K, Ding H, Liang C et al (2018) The correlation between microRNA-221/222 cluster overexpression and malignancy: an updated meta-analysis including 2693 patients. Cancer Manag Res 10:3371–3381. https://doi.org/10.2147/cmar.S171303
Gu Y, Lei D, Qin X, Chen P, Zou YM, Hu Y (2015) Integrated analysis reveals together miR-182, miR-200c and miR-221 can help in the diagnosis of prostate cancer. PLoS ONE 10(10):e0140862. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0140862
Funding
This work was supported by the Scientific Research Projects Fund of Eskisehir Osmangazi University by the Project Number: 2016-1228.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AK: Conceptualization, Methodology, Data curation, Writing—original draft, Writing—review & editing. AO: Methodology, Writing—review & editing. MO: Methodology, Writing—review & editing. CC: Methodology, Writing—review & editing. IB: Data curation, Software, Writing—review & editing. SK: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing—review & editing. RU: Conceptualization and Supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest to report.
Ethical approval
The present study was ethically approved by the non-interventional clinical research ethics committee of Eskisehir Osmangazi University (Approval Number: 14, April 13, 2016) in accordance with Helsinki declaration.
Informed consent
A written informed consent was obtained from all participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karadag, A., Ozen, A., Ozkurt, M. et al. Identification of miRNA signatures and their therapeutic potentials in prostate cancer. Mol Biol Rep 48, 5531–5539 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06568-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06568-7