Abstract
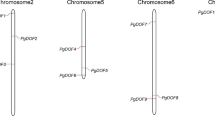
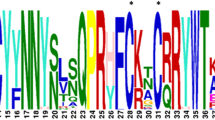
The DNA binding with One Finger (Dof) protein is a plant specific transcription factor involved in the regulation of wide range of processes. The analysis of whole genome sequence of pigeonpea has identified 38 putative Dof genes (CcDof) distributed on 8 chromosomes. A total of 17 out of 38 CcDof genes were found to be intronless. A comprehensive in silico characterization of CcDof gene family including the gene structure, chromosome location, protein motif, phylogeny, gene duplication and functional divergence has been attempted. The phylogenetic analysis resulted in 3 major clusters with closely related members in phylogenetic tree revealed common motif distribution. The in silico cis-regulatory element analysis revealed functional diversity with predominance of light responsive and stress responsive elements indicating the possibility of these CcDof genes to be associated with photoperiodic control and biotic and abiotic stress. The duplication pattern showed that tandem duplication is predominant over segmental duplication events. The comparative phylogenetic analysis of these Dof proteins along with 78 soybean, 36 Arabidopsis and 30 rice Dof proteins revealed 7 major clusters. Several groups of orthologs and paralogs were identified based on phylogenetic tree constructed. Our study provides useful information for functional characterization of CcDof genes.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Noguero M, Atif RM, Ochatt S, Thompson RD (2013) The role of the DNA-binding one zinc finger (DOF) transcription factor family in plants. Plant Sci 209:32–45
Yanagisawa S, Izui K (1993) Molecular-cloning of 2 DNA-binding proteins of maize that are structurally different but interact with the same sequence motif. J Biol Chem 268:16028–16036
DePaolis A, Sabatini S, DePascalis L, Costantino P, Capone I (1996) A rolB regulatory factor belongs to a new class of single zinc finger plant proteins. Plant J 10:215–223
Kisu Y, Esaka M, Suzuki M (1995) Putative zinc-binding domain of plant transcription factor, AOBP, is related to DNA-binding domains of steroid hormone receptors and GATA1. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B 71:288–292
Vicente-Carbajosa J, Moose SP, Parson RL, Schmidt RJ (1997) A maize zinc-finger protein binds the prolamin box in zein gene promoters and interacts with the basic leucine zipper transcriptional activator. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:7685–7690
Zhang B, Chen W, Foley RC, Buttner M, Singh KB (1995) Interactions between distinct types of DNA binding proteins enhances binding to ocs element promoter sequences. Plant Cell 7:2241–2252
Moreno-Risueno MA, Martinez M, Vicente-Carbajosa J, Carbonero P (2007) The family of DOF transcription factors: from green unicellular algae to vascular plants. Mol Genet Genomics 277:379
Lijavetzky D, Carbonero P, Vicente-Carbajosa J (2003) Genome-wide comparative phylogenetic analysis of the rice and Arabidopsis Dof gene families. BMC Evol Biol 3:17
Yang X, Tuskan GA, Cheng ZM (2006) Divergence of the Dofgene families in poplar, Arabidopsis, and rice suggests multiple modes of gene evolution after duplication. Plant Physiol 142:820–830
Shaw LM, McIntyre CL, Gresshoff PM, Xue GP (2009) Members of the Dof transcription factor family in Triticum aestivum are associated with light-mediated gene regulation. Funct Integr Genomics 9(4):485–498
Kushwaha H, Gupta S, Singh VK, Rastogi S, Yadav D (2011) Genome wide identification of Dof transcription factor gene family in Sorghum and its comparative phylogenetic analysis with rice and Arabidopsis. Mol Biol Rep 38:5037–5053
Guo Y, Qiu LJ (2013) Genome-wide analysis of the Dof transcription factor gene family reveals soybean-specific duplicable and functional characteristics. PLoS ONE 8(9):1–14
Jiang Y, Zeng B, Zhao H, Zhang M, Xie S, Lai J (2012) Genome-wide transcription factor gene prediction and their expressional tissue-specificities in maize. J Integr Plant Biol 54:616–630
Hernando AS, González CV, Carbonero P, Barrero SC (2012) The family of DOF transcription factors in Brachypodium distachyon: phylogenetic comparison with rice and barley DOFs and expression profiling. BMC EvolBiol 12:202–216
Cai X, Zhang Y, Zhang C, Zhang T, Hu T, Ye J, Zhang J, Wang T, Li H, Ye Z (2013) Genome-wide Analysis of Plant-specific Dof Transcription Factor Family in Tomato. J Integr Plant Biol 55(6):552–566
Yanagisawa S, Schmidt RJ (1999) Diversity and similarity among recognition sequences of Dof transcription factors. Plant J 17(2):209–214
Yanagisawa S (2001) The transcriptional activation domain of the plant-specific Dof1 factor functions in plant, animal, and yeast cells. Plant Cell Physiol 42:813–822
Diaz I, Martinez M, Isabel-La Moneda I, Rubio-Somoza I, Carbonero P (2005) The DOF protein, SAD, interacts with GAMYB in plant nuclei and activates transcription of endosperm-specific genes during barley seed development. Plant J 42:652–662
RuBiol-Somoza I, Martinez M, Abraham Z, Diaz I, Carbonero P (2006) Ternary complex formation between HvMYBS3 and other factors involved in transcriptional control in barley seeds. Plant J 47(2):269–281
Kawakatsu T, Yamamoto MP, Touno SM, Yasuda H, Takaiwa F (2009) Compensation and interaction between RISBZ1 and RPBF during grain filling in rice. Plant J 59:908–920
Zou X, Neuman D, Shen QJ (2008) Interactions of Two Transcriptional Repressors and Two Transcriptional Activators in Modulating Gibberellin Signaling in Aleurone Cells. Plant Physio 148(1):176–186
Yanagisawa S (1995) A novel DNA-binding domain that may form a single zinc finger motif. Nucleic Acids Res 23:3403–3410
Yanagisawa S (1996) DOF DNA binding proteins contain a novel zinc finger motif. Trends Plant Sci 1:213–214
Yanagisawa S (1997) Dof DNA binding domains of plant transcription factors contribute to multiple protein-protein interactions. Eur J Biochem 250:403–410
Kang HG, Singh KB (2000) Characterization of salicylic acid-responsive, Arabidopsis Dof domain proteins: overexpression of OBP3 leads to growth defects. Plant J 21(4):329–339
Diaz I, Vicente-Carbajosa J, Abraham Z, Martinez M, Isabel- LaMoneda I, Carbonero P (2002) The GAMYB protein from barley interacts with the DOF transcription factor BPBF and activates endosperm-specific genes during seed development. Plant J 29:401–414
Mena M, Vicente-Carbajosa J, Schmidt RJ, Carbonero P (1998) An endosperm-specific DOF protein from barley, highly conserved in wheat, binds to and activates transcription from the prolamin-box of a native B-hordein promoter in barley endosperm. Plant J. 16:53–62
Mena M, Cejudo FJ, Isabel-Lamoneda I, Carbonero P (2002) A Role for the DOF Transcription Factor BPBF in the Regulation of Gibberellin-Responsive Genes in Barley Aleurone. Plant Physiol 130:111–119
Dong G, Ni Z, Nie X, Sun Q (2007) Wheat DOF transcription factor WPBF interacts with TaQM and activates transcription of an alpha-gliadin gene during wheat seed development. Plant Mol Biol 63:73–84
Yamamoto MP, Onodera Y, Touno SM, Takaiwa F (2006) Synergism between RPBF DOF and RISBZ1 bZIP Activators in Regulation of Rice Seed Expression Genes. Plant Physiol 141:1694–1707
Kushwaha H, Gupta N, Singh VK, Kumar A, Yadav D (2008) In silico analysis of PCR amplified DOF (DNA binding with one finger) transcription factor domain and cloned genes from cereals and millets. Online J of Bioinform 9(2):130–143
Guo Y, Qin G, Gu H, Qu LJ (2009) Dof5.6/HCA2, a Dof transcription factor gene, regulates interfascicular cambium formation and vascular tissue development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 21:3518–3534
Gardiner J, Sherr I, Scarpella E (2010) Expression of DOF genes identifies early stages of vascular development in Arabidopsis leaves. Int J Dev Biol 54:1389–1396
Papi M, Sabatini S, Bouchez D, Camilleri C, Costantino P, Vittorioso P (2000) Identification and disruption of an Arabidopsis zinc finger gene controlling seed Germination. Genes Dev 14:28–33
Papi M, Sabatini S, Altamura MM, Hennig L, Schafer E, Costantino P, Vittorioso P (2002) Inactivation of the phloem-specific Dof zinc finger gene DAG1 affects response to light and integrity of the testa of Arabidopsis seeds. Plant Physiol 128:411–417
Gualberti G, Papi M, Bellucci L, Ricci I, Bouchez D, Camilleri C, Costantino P, Vittorioso P (2002) Mutations in the Dof zinc finger genes DAG2 and DAG1 influence with opposite effects the germination of Arabidopsis seeds. Plant Cell 14:1253–1263
Gabriele S, Rizza A, Martone J, Circelli P, Costantino P, Vittorioso P (2010) The Dof protein DAG1 mediates PIL5 activity on seed germination by negatively regulating GA Biol synthetic gene AtGA3ox1. Plant J 61:312–323
Rueda-Romero P, Barrero-Sicilia C, Gomez-Cadenas A, Carbonero P, Onate-Sanchez L (2012) Arabidopsis thaliana DOF6 negatively affects germination in non-after-ripened seeds and interacts with TCP14. J Exp Bot 63(5):1937–1949
Yang CQ, Fang X, Wu XM, Mao YB, Wang LJ, Chen XY (2012) Transcriptional regulation of plant secondary metabolism. J Integr Plant Biol 54:703–712
Yang J, Yang MF, Zhang WP, Chenc F, Shen SH (2011) A putative flowering time related Dof transcription factor gene, JcDof3, is controlled by the circadian clock in Jatropha curcas. Plant Sci 181:667–674
Wei PC, Tan F, Gao XQ, Zhang XQ, Wang GQ, Xu H, Li LJ, Chen J, Wang XC (2010) Overexpression of AtDOF4.7, an Arabidopsis DOF family transcription factor, induces floral organ abscission deficiency Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 153(3):1031–1045
Yanagisawa S (2000) Dof1 and Dof2 transcription factors are associated with expression of multiple genes involved in carbon metabolism in maize. Plant J 21:281–288
Skirycz A, Reichelt M, Burow M, Birkemeyer C, Rolcik J, Kopka J, Zanor MI, Gershenzon J, Strnad M, Szopa J et al (2006) DOF transcription factor AtDOF1.1 (OBP2) is part of a regulatory network controlling glucosinolate Biolsynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant J 47:10–24
Iwamoto M, Higo K, Takano V (2009) Circadian clock and phytochrome regulated Dof like gene, Rdd1 is associated with grain size in rice. Plant, Cell Environ 32:592–603
Kumar R, Taware R, Gaur VS, Guru SK, Kumar A (2009) Influence of nitrogen on the expression of TaDof1 transcription factor in wheat and its relationship with photo synthetic and ammonium assimilating efficiency. Mol Biol Rep 36:2209–2220
Sugiyama T, Ishida T, Tabei N, Shigyo M, Konishi M, Yoneyama T, Yanagisawa S (2012) Involvement of PpDof1 transcriptional repressor in the nutrient condition-dependent growth control of protonemal filaments in Physcomitrella patens. J Exp Bot 63:3185–3197
Kim HS, Kim SJ, Abbasi N, Bressan RA, Yun DJ, Yoo SD (2010) The DOF transcription factor Dof5.1 influences leaf axial patterning by promoting Revoluta transcription in Arabidopsis. Plant J64:524–535
Negi J, Moriwaki K, Konishi M et al (2013) A Dof transcription factor, SCAP1, is essential for the development of functional stomata in Arabidopsis. CurrBiol 23:479–484
Maesen Vander LJG (1989) Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp. In: Maesen Vander LJG, Somaatmadja S (eds) Plant resources of South-East Asia No.1. Pulses. Pudoc/Prosea, Wageningen, The Netherlands., pp 39–42
Varshney RK, Penmetsa RV, Dutta S et al (2010) Pigeonpea genomics initiative (PGI): an international effort to improve crop productivity of pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan L.). Mol Breed 26(3):393–408
Singh NK, Gupta DK, Jayaswal PK et al (2012) The first draft of the pigeonpea genome sequence. J Plant Biochem Biotechnol 21(1):98–112
Guo A, He K, Liu D, Bai S, Gu S, Wei L, Luo J (2005) DATF: a database of Arabidopsis transcription factors. Bioinformatics 21(10):2568–2569
Gao G, Zhong Y, Guo A, Zhu Q, Tang W, Zheng W, Gu X, Wei L, Luo J (2006) DRTF: a database of rice transcription factors. Bioinformatics 22(10):1286–1287
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J MolBiol 215(3):403–410
Pruitt KD, Tatusova T, Maglott DR (2007) NCBI reference sequences (RefSeq): a curated nonredundant sequence database of genomes, transcripts and proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 35:61–65
Stormo GD (2000) Gene-finding approaches for eukaryotes. Genome Res 10(4):394–397
Solovyev V, Kosarev P, Seledsov I, Vorobyev D (2006) Automatic annotation of eukaryotic genes, pseudogenes and promoters. Genome Biol 7(1):S.10.1–S.10.12
Punta M, Coggill PC, Eberhardt J et al (2012) The Pfam protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res 40:290–301
Sigrist CJA, de Castro E, Cerutti L, Cuche BA, Hulo N, Bridge A, Bougueleret L, Xenarios I (2013) New and continuing developments at PROSITE. Nucleic Acids Res 41(D1):D344–D347
Quevillon E, Silventoinen V, Pillai S, Harte N, Mulder N, Apweiler R, Lopez R (2005) InterProScan: protein domains identifier. Nucleic Acids Res 33:W116–W120
Falquet L, Pagni M, Bucher P, Hulo N, Sigrist CJ, Hofmann K, Bairoch A (2002) The PROSITE database, its status in 2002. Nucleic Acids Res 30(1):235–238
Brameier M, Krings A, Maccallum RM (2007) NucPred—predicting nuclear localization of proteins. Bioinformatics 23(9):1159–1160
Gasteiger E, Hoogland C, Gattiker A, Duvaud S, Wilkins MR, Appel RD, Bairoch A (2005) Protein identification and Analysis Tools on the ExPASy Server. In: Walker John M (ed) The Proteomics Protocols Handbook. Humana Press,
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucl Acids Res 25(24):4876–4882
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N et al (2011) MEGA5: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Using Maximum Likelihood, Evolutionary Distance, and Maximum Parsimony Methods. MolBiolEvol 28(10):2731–2739
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Cannon EK, Cannon SB (2011) Chromosome visualization tool: a whole genome viewer. Int J Plants Genomics doi: 10.1155/2011/373875
Cannon SB, Shoemaker RC (2012) Evolutionary and comparative analyses of the soybean genome. Breed Sci 61:437–444
Bailey TL, Elkan C (1994) Fitting a mixture model by expectation maximization to discover motifs in biopolymers. Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Intelligent Systems for Molecular Biology, AAAI Press, Menlo Park, California, 28-36
Lescot M, Hais PD, Thijs G, Marchal K, Moreau Y, Van de Peer Y, Rouz P, Rombauts S (2002) PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 30(1):325–327
Lavin M, Herendeen PS, Wojciechowski MF (2005) Evolutionary rates analysis of Leguminosae implicates a rapid diversification of lineages during the tertiary. SystBiol 54(4):575–594
Hollingsworth PM, Bateman RM, Gornall RJ (1999) Molecular Systematics and Plant Evolution. Publisher Taylor and Francis Limited
Gu X (1999) Statistical methods for testing functional divergence after gene duplication. Mol Biol Evol 16(12):1664–1674
Gu X (2001) Maximum-likelihood approach for gene family evolution under functional divergence. Mol Biol Evol 18(4):453–464
Pupko T, Pe’er I, Graur D, Hasegawa M, Friedman N (2002) A branch-and-bound algorithm for the inference of ancestral amino-acid sequences when the replacement rate varies among sites: application to the evolution of five gene families. Bioinformatics 18(8):1116–1123
Koralewski TE, Krutovsky KV (2011) Evolution of exon-intron structure and alternative splicing. PLoS One 6(3)e18055: 1-10
Le HH, Nott A, Moore MJ (2003) How introns influence and enhance eukaryotic gene expression. Trends Biochem Sci 28:215–220
Fedorova L, Fedorov A (2003) Introns in gene evolution. Genetica 118:123–131
Roy SW, Gilbert W (2006) The evolution of spliceosomal introns: patterns, puzzles and progress. Nat Rev Genet 7:211–221
Castillo-Davis CI, Mekhedov SL, Hartl DL, Koonin EV, Kondrashov FA (2002) Selection for short introns in highly expressed genes. Nat Genet 31:415–418
Martinez M, Rubio-Somoza I, Fuentes R, Lara P, Carbonero P, Diaz I (2005) The barley cystatin gene (Icy) is regulated by DOF transcription factors in aleurone cells upon germination. J Exp Bot 56:547–556
Singh K, Foley RC, Onate-Sanchez L (2002) Transcription factors in plant defense and stress responses. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:430–436
Ward JM, Cufr CA, Denzel MA, Neff MM (2005) The Dof transcription factor OBP3 modulates phytochrome and cryptochrome signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant cell 17:475–485
Park DH, Lim PO, Kim JS, Cho DS, Hong SH, Nam HG (2003) The ArabidopsisCOG1 gene encodes a Dof domain transcription factor and negatively regulates phytochrome signaling. Plant J 34:161–171
Fornara F, Panigrahi KC, Gissot L, Sauerbrunn N, Ruhl M, Jarillo JA, Coupland G (2009) ArabidopsisDOF transcription factors act redundantly to reduce CONSTANS expression and are essential for a photoperiodic flowering response. Dev Cell 17:75–86
Imaizumi T, Schultz TF, Harmon FG, Ho LA, Kay SA (2005) FKF1 F-box protein mediates cyclic degradation of a repressor of CONSTANS in Arabidopsis. Science 309:293–297
Li D, Yang C, Li X, Gan Q, Zhao X, Zhu L (2009) Functional characterization of rice OsDof12. Planta 229:1159–1169
Yang Z, Bielawski JP (2000) Statistical methods for detecting molecular adaptation. Trends Ecol Evol 15(12):496–503
Hurst LD (2002) The Ka/Ks ratio: diagnosing the form of sequence evolution. Trends Genet 18(9):486–487
Morgan CC, Loughran NB, Walsh TA, Harrison AJ, O’Connell MJ (2010) Positive selection neighboring functionally essential sites and disease –implicated regions of mammalian reproductive proteins. BMC Evol Biol 10:39
Khan AA, Janke A, Shimokawa T, Zhang H (2011) Phylogenetic analysis of kindlins suggests subfunctionalization of an ancestral unduplicated kindlin into three paralogs in vertebrates. Evol Bioinform Online 7:7–19
Mallika V, Sivakumar KC, Soniya EV (2011) Evolutionary Implications and Physicochemical Analyses of Selected Proteins of Type III Polyketide Synthase Family. Evol Bioinform Online 7:41–53
Varshney RK, Chen W, Li Y, Bharti AK, Saxena RK et al (2012) Draft genome sequence of pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan), an orphan legume crop of resource-poor farmers. Nat Biotechnol 30:83–89
Wang H, Zhang B, Hao Y, Huang J, Tian A, Liao Y, Zhang J, Chen S (2007) The soybean Dof-type transcription factor genes, GmDof4 and GmDof11, enhance lipid content in the seeds of transgenic Arabidopsis plants. Plant J 52:716–729
Acknowledgments
The financial support by Department of Science and Technology, Government of India, New Delhi in the form of Women Scientist-A fellowship (SR/WOS-A/LS-110/2012(G) to N. Malviya is thankfully acknowledged. S. Gupta acknowledges the CSIR, New Delhi for Senior Research Fellowship. The author wishes to acknowledge the Head, Department of Biotechnology, D.D.U. Gorakhpur University, Gorakhpur, INDIA for infrastructural support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11033_2014_3797_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Supplementary material 1 (DOCX 24 kb) Table S1. Complete list of identified cis-regulatory elements of CcDof genes of pigeonpea and their position. Table S2. Function of identified cis-regulatory elements
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malviya, N., Gupta, S., Singh, V.K. et al. Genome wide in silico characterization of Dof gene families of pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan (L) Millsp.). Mol Biol Rep 42, 535–552 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3797-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3797-y