Abstract
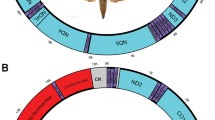
The complete mitochondrial (mt) genome sequences of Neobenedenia melleni were determined and compared with those of Benedenia seriolae and B. hoshinai. This circular genome comprises 13,270 bp and includes all 36 typical mt genes found in flatworms. Total AT content of N. melleni is 75.9 %. ATG is the most common start codon, while nad4L is initiated by GTG. All protein-coding genes are predicted to terminate with TAG and TAA. N. melleni has the trnR with a TCG anticodon, which is the same to B. seriolae but different from B. hoshinai (ACG). The mt gene arrangement of N. melleni is similar to that of B. seriolae and B. hoshinai with the exception of three translocations (trnF, trnT and trnG). The overlapped region between nad4L and nad4 was found in the N. melleni mt genome, which was also reported for the published Gyrodactylus species, but it was not found in those of B. seriolae and B. hoshinai, which are non-coding regions instead. The present study provides useful molecular characters for species or strain identification and systematic studies of this parasite.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deveney MR, Chisholm LA, Whittington ID (2001) First published record of the pathogenic monogenean parasite Neobenedenia melleni (Capsalidae) from Australia. Dis Aquat Organ 46:79–82. doi:10.3354/dao046079
Kaneko JJ, Yamada R, Brock JA, Nakamura RM (1988) Infection of tilapia Oreochromis mossambicus (Trewavas), by a marine monogenean, Neobenedenia melleni (MacCallum, 1927) Yamaguti, 1963 in Kaneohe Bay, Hawaii, USA, and its treatment. J Fish Dis 11:295–300. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2761.1988.tb01225.x
Ellis EP, Watanabe WO (1993) The effects of the hyposalinity on eggs, juveniles and adults of the marine monogenean, Neobenedenia melleni treatment of ecto-parasitosis in seawater-cultured tilapia. Aquaculture 117:15–27. doi:10.1016/0044-8486(93)90119-J
Deveney MR, Chisholm LA, Whittington ID (2001) First published record of the pathogenic monogenean parasite Neobenedenia melleni (Capsalidae) from Australia. Dis Aquat Organ 46:79–82. doi:10.3354/dao046079
Paperna I (1991) Diseases caused by parasites in the aquaculture of warm water fish. Annu Rev Fish Dis 1:155–194. doi:10.1016/0959-8030(91)90028-I
Leong TS, Colorni A (2002) Infection diseases of warm water fish in marine and brackish waters. In: Woo PTK, Bruno DW, Lim LHS (eds) Diseases and disorders of finfish in cage culture. CABI Publishing, London, pp 193–230
Yamaguti S (1963) Systema helminthum, vol IV. Interscience Publishers, New York, Monogenea and Aspidocotylea
Whittington ID, Horton MA (1996) A revision of Neobenedenia Yamaguti, 1963 (Monogenea: Capsalidae) including a redescription of N. melleni (MacCallum, 1927) Yamaguti, 1963. J Nat Hist 30:1113–1156. doi:10.1080/00222939600770611
Li AX, Wu XY, Ding XJ, Lin RQ, Xie MQ, Lun ZR, Zhu XQ (2005) PCR-SSCP as a molecular tool for the identification of Benedeniinae (Monogenea: Capsalidae) from marine fish. Mol Cell Probe 19:35–39. doi:10.1016/j.mcp.2004.09.002
Whittington ID, Deveney MR, Morgan JAT, Chisholm LA, Adlard RD (2004) A preliminary phylogenetic analysis of the Capsalidae (Platyhelminthes: monogenea: Monopisthocotylea) inferred from large subunit rDNA sequences. Parasitology 128:511–519. doi:10.1017/S0031182004004901
Ghikas DV, Kouvelis VN, Typas MA (2010) Phylogenetic and biogeographic implications inferred bt mitochondrial intergenic region analyses and ITS1-5.8S-ITS2 of the entomopathogenic fungi Beauveria bassiana and B. brongniartii. BMC Microbiol 10:174. doi:10.1186/1471-2180-10-174
Park JK, Kim KH, Kang S, Kim W, Eom KS, Littlewood DTJ (2007) A common origin of complex life cycles in parasitic flatworms: evidence from the complete mitochondrial genome of Microcotyle sebastis (Monogenea: Platyhelminthes). BMC Evol Biol 7:11. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-7-11
Zhang J, Wu X, Xie M, Li A (2012) The complete mitochondrial genome of Pseudochauhanea macrorchis (Monogenea: Chauhaneidae) revealed a highly repetitive region and a gene rearrangement hot spot in Polyopisthocotylea. Mol Biol Rep 39:8115–8125. doi:10.1007/s11033-012-1659-z
Zhang J, Wu XY, Xie MQ, Xu XD, Li AX (2011) The mitochondrial genome of Polylabris halichoeres (Monogenea: Microcotylidae). Mitochondrial DNA 22:3–5. doi:10.3109/19401736.2011.588223
Littlewood DTJ, Lockyer AE, Webster BL, Johnston DA, Le TH (2006) The complete mitochondrial genomes of Schistosoma haematobium and Schistosoma spindale and the evolutionary history of mitochondrial genome changes among parasitic flatworms. Mol Phylogenet Evol 39(2):452–467. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2005.12.012
von Nickisch-Rosenegk M, Brown WM, Boore JL (2001) Complete sequence of the mitochondrial genome of the tapeworm Hymenolepis diminuta: gene arrangements indicate that Platyhelminths are Eutrochozoans. Mol Biol Evol 18(5):721–730
Arbogast BS, Kenagy GJ (2001) Comparative phylogeography as an integrative approach to historical biogeography. J Biogeogr 28(7):819–825. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2699.2001.00594.x
Gissi C, Iannelli F, Pesole G (2008) Evolution of the mitochondrial genome of Metazoa as exemplified by comparison of congeneric species. Heredity 101:301–320. doi:10.1038/hdy.2008.62
Perkins EM, Donnellan SC, Bertozzi T, Whittington ID (2010) Closing the mitochondrial circle on paraphyly of the Monogenea (Platyhelminthes) infers evolution in the diet of parasitic flatworms. Int J Parasitol 40(11):1237–1245. doi:10.1016/j.ijpara.2010.02.017
Kang S, Kim J, Lee J, Kim S, Min G, Park J (2012) The complete mitochondrial genome of an ectoparasitic monopisthocotylean fluke Benedenia hoshinai (Monogenea: Platyhelminthes). Mitochondrial DNA 23(3):176–178. doi:10.3109/19401736.2012.668900
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2007) Clustal W and clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23:2947–2948. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btm404
Lowe T, Eddy S (1997) tRNAscan-SE: a program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 25:955–964. doi:10.1093/nar/25.5.0955
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599. doi:10.1093/molbev/msm092
Le TH, Blair D, McManus DP (2002) Mitochondrial genomes of parasitic flatworms. Trends Parasitol 18(5):206–213. doi:10.1016/S1471-4922(02)02252-3
Yang Z, Nielsen R (2000) Estimating synonymous and nonsynonymous substitution rates under realistic evolutionary models. Mol Biol Evol 17:32–43
Jeon H, Kim K, Eom K (2007) Complete sequence of the mitochondrial genome of Taenia saginata: comparison with T. solium and T. asiatica. Parasitol Int 56:243–246. doi:10.1016/j.parint.2007.04.001
Wang Y, Wang C, Zhao G, Gao J, Li M, Zhu X (2011) The complete mitochondrial genome of Orientobilharzia turkestanicum supports its affinity with African Schistosoma spp. Infect Genet Evol 11:1964–1965. doi:10.1016/j.meegid.2011.08.030
Zhang DX, Hewitt GM (1997) Insect mitochondrial control region: a review of its structure, evolution and usefulness in evolutionary studies. Biochem Syst Ecol 25:99–120. doi:10.1016/S0305-1978(96)00042-7
Huyse T, Plaisance L, Webster BL, Mo TA, Bakke TA, Bachmann L, Littlewood DTJ (2007) The mitochondrial genome of Gyrodactylus salaris (Platyhelminthes: Monogenea), a pathogen of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Parasitology 134(Pt 5):739–747
Plaisance L, Huyse T, Littlewood DTJ, Bakke TA, Bachmann L (2007) The complete mitochondrial DNA sequence of the monogenean Gyrodactylus thymalli (Platyhelminthes: Monogenea), a parasite of grayling (Thymallus thymallus). Mol Biochem Parasit 154(2):190–194. doi:10.1016/j.molbiopara.2007.04.012
Huyse T, Buchmann K, Littlewood DTJ (2008) The mitochondrial genome of Gyrodactylus derjavinoides (Platyhelminthes: Monogenea)–a mitogenomic approach for Gyrodactylus species and strain identification. Gene 417(1–2):27–34. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2008.03.008
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by Key Projects in the National Science & Technology Pillar Program (Grant No. 2012BAD17B00).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Wu, X., Li, Y. et al. The complete mitochondrial genome of Neobenedenia melleni (Platyhelminthes: Monogenea): mitochondrial gene content, arrangement and composition compared with two Benedenia species. Mol Biol Rep 41, 6583–6589 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3542-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3542-6