Abstract
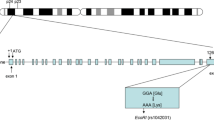
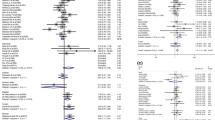
The proteasome system is a proteolytic pathway that regulates the expression of genes involved in inflammation. Recently, an association of a functional sequence variation, -8C/G, in the human proteasome subunit a type 6 gene (PSMA6) with the susceptibility to coronary artery disease (CAD) was reported. After that, several validation studies have been conducted among various ethnic populations, but the results have been inconsistent. To investigate this inconsistency and derive a more precise estimation of the relationship, a meta-analysis of 15,991 cases and 16,784 controls from 10 case–control studies was performed. Potential sources of heterogeneity including ethnicity, sample size and HWE status of study were also assessed. In a combined analysis, the summary per-allele OR for CAD of the -8C/G polymorphism was 1.09 (95 % CI: 1.02–1.16; P = 0.006). In the subgroup analysis by ethnicity, significantly increased risks were found in East Asians for the polymorphism; while no significant associations were found among Caucasians and other ethnic population in all genetic models. When restricted to studies concerning myocardial infarction patients, significant associations were detected in all genetic models. Furthermore, significant difference of PSMA6 mRNA expression was found between genotypes. In conclusion, this meta-analysis suggests that G allele of PSMA6-8C/G polymorphism is a risk factor associated with increased CAD susceptibility, but these associations vary in different ethnic populations.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CAD:
-
Coronary artery disease
- MI:
-
Myocardial infarction
- PSMA6:
-
Proteasome subunit α type 6
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- HWE:
-
Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
References
Yamada Y, Izawa H, Ichihara S, Takatsu F, Ishihara H, Hirayama H, Sone T, Tanaka M, Yokota M (2002) Prediction of the risk of myocardial infarction from polymorphisms in candidate genes. N Engl J Med 347:1916–1923
Broeckel U, Hengstenberg C, Mayer B et al (2002) A comprehensive linkage analysis for myocardial infarction and its related risk factors. Nat Genet 30:210–214
Topol EJ, Smith J, Plow EF, Wang QK (2006) Genetic susceptibility to myocardial infarction and coronary artery disease. Hum Mol Genet 15:R117–R123
Libby P (2002) Atherosclerosis in inflammation. Nature 420:868–874
Herrmann J, Ciechanover A, Lerman LO, Lerman A (2004) The ubiquitin–proteasome system in cardiovascular diseases-a hypothesis extended. Cardiovasc Res 61:11–21
Meiners S, Laule M, Rother W et al (2002) Ubiquitin–proteasome pathway as a new target for the prevention of restenosis. Circulation 105:483–489
Elliott PJ, Zollner TM, Boehncke WH (2003) Proteasome inhibition: a new anti-inflammatory strategy. J Mol Med 8:235–245
Ozaki K, Sato H, Iida A et al (2006) A functional SNP in PSMA6 confers risk of myocardial infarction in the Japanese population. Nat Genet 38:921–925
Holm K, Melum E, Franke A, Karlsen TH (2010) SNPexp—a web tool for calculating and visualizing correlation between HapMap genotypes and gene expression levels. BMC Bioinformatics 11:600
International HapMap Consortium (2003) The International HapMap Project. Nature 426:789–796
Stranger BE, Forrest MS, Dunning M et al (2007) Relative impact of nucleotide and copy number variation on gene expression phenotypes. Science 315:848–853
Mantel N, Haenszel W (1959) Statistical aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of disease. J Natl Cancer Inst 22:719–748
DerSimonian R, Laird N (1986) Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 7:177–188
Woolf B (1955) On estimating the relation between blood group and disease. Ann Hum Genet 19:251–253
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C (1997) Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 315:629–634
Sjakste T, Poudziunas I, Ninio E et al (2007) SNPs of PSMA6 gene–investigation of possible association with myocardial infarction and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Genetika 43:553–559
Takashima N, Shioji K, Kokubo Y, Okayama A, Goto Y, Nonogi H, Iwai N (2007) Validation of the association between the gene encoding proteasome subunit alpha type 6 and myocardial infarction in a Japanese population. Circ J 71:495–498
Bennett DA, Xu P, Clarke R, Zondervan K, Parish S, Palmer A, Cardon L, Peto R, Lathrop M, Collins R (2008) The exon 1-8C/G SNP in the PSMA6 gene contributes only a small amount to the burden of myocardial infarction in 6,946 cases and 2,720 controls from a United Kingdom population. Eur J Hum Genet 16:480–486
Barbieri M, Marfella R, Rizzo MR, Boccardi V, Siniscalchi M, Schiattarella C, Siciliano S, Lemme P, Paolisso G (2008) The −8 UTR C/G polymorphism of PSMA6 gene is associated with susceptibility to myocardial infarction in type 2 diabetic patients. Atherosclerosis 201:117–123
Liu X, Wang X, Shen Y, Wu L, Ruan X, Lindpaintner K, Yusuf S, Engert JC, Anand S, Tan X, Liu L (2009) The functional variant rs1048990 in PSMA6 is associated with susceptibility to myocardial infarction in a Chinese population. Atherosclerosis 206:199–203
Banerjee I, Pandey U, Hasan OM, Parihar R, Tripathi V, Ganesh S (2009) Association between inflammatory gene polymorphisms and coronary artery disease in an Indian population. J Thromb Thrombolysis 27:88–94
Alsmadi O, Muiya P, Khalak H, Al-Saud H, Meyer BF, Al-Mohanna F, Alshahid M, Dzimiri N (2009) Haplotypes encompassing the KIAA0391 and PSMA6 gene cluster confer a genetic link for myocardial infarction and coronary artery disease. Ann Hum Genet 73:475–483
Hinohara K, Nakajima T, Sasaoka T, Sawabe M, Lee BS, Ban J, Park JE, Izumi T, Kimura A (2009) Replication studies for the association of PSMA6 polymorphism with coronary artery disease in East Asian populations. J Hum Genet 54:248–251
Ikeda S, Tanaka N, Arai T, Chida K, Muramatsu M, Sawabe M (2012) Polymorphisms of LTA, LGALS2, and PSMA6 genes and coronary atherosclerosis: a pathological study of 1503 consecutive autopsy cases. Atherosclerosis 221:458–460
Kozak M (1997) Recognition of AUG and Alternative Initiator Codos Is Augmented by G in Position +4 but is not Generally Affected by the Nucleotides in Position +5 and +6. EMBO J 16:2482–2492
Kozak M (2002) Pushing the limits of the scanning mechanism for initiation of translation. Gene 299:1–34
Goldberg AL (2003) Protein degradation and protection against misfolded or damaged proteins. Nature 426:895–899
Coux O, Tanaka K, Goldberg AL (1996) Structure and functions of the 20S and 26S proteasomes. Annu Rev Biochem 65:801–847
Acknowledgments
The project as supported by a leadership award to H. W (PWRd2011-04) and by the key discipline construction funding (PWZxk201005) from the Pudong New Area Health Bureau, Shanghai, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Hairong Wang and Mei Jiang contributed equally to this study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Jiang, M., Zhu, H. et al. Quantitative assessment of the influence of PSMA6 variant (rs1048990) on coronary artery disease risk. Mol Biol Rep 40, 1035–1041 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-2146-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-2146-2