Abstract
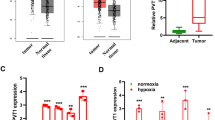
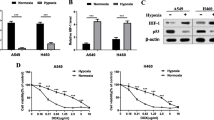
Survivin is a member of the inhibitor of apoptosis protein family that is overexpressed in various tumors and is important in restricting apoptosis. Understanding the molecular events of apoptosis may provide information for developing novel therapeutic agents targeting non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLCs). This study used three human NSCLC cell lines, NCI-H1299, SK-MES-1, and NCI-H460. Changes in apoptosis, the mRNA and protein expression of survivin under normoxia and hypoxia, with or without rapamycin treatment were analyzed. In addition, siRNA and ChIP assay were further applied to demonstrate the role of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1)α in regulating survivin expression regulation under hypoxia during rapamycin induced NSCLC cell apoptosis. Treatment with rapamycin resulted in significantly increased NSCLC cells apoptosis under hypoxia. We demonstrated for the first time that rapamycin inhibited hypoxia-induced survivin expression in NSCLC cell lines. We further demonstrated that HIF-1α participated in hypoxia-induced survivin expression, and that rapamycin inhibited hypoxia-induced HIF-1α expression by enhancing its degradation. The results above collectively showed that rapamycin inhibits HIF-1α-induced survivin expression under hypoxia to induce NSCLC apoptosis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Molina JR, Adjei AA, Jett JR (2006) Advances in chemotherapy of non-small cell lung cancer. Chest 130:1211–1219
Koh MY, Spivak-Kroizman TR, Powis G (2010) HIF-1alpha and cancer therapy. Recent Results Cancer Res 180:15–34
Volm M, Koomagi R (2000) Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1) and its relationship to apoptosis and proliferation in lung cancer. Anticancer Res 20:881–890
Giatromanolaki A, Koukourakis MI, Sivridis E, Turley H, Talks K, Pezzella F, Gatter KC, Harris AL (2001) Relation of hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha and 2 alpha in operable non-small cell lung cancer to angiogenic/molecular profile of tumors and survival. Br J Cancer 85:881–890
Swinson DE, Jones JL, Cox G, Richardson D, Harris AL, O’Byrne KJ (2004) Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha in non small cell lung cancer: relation to growth factor, protease and apoptosis pathway. Int J Cancer 111:43–50
Unruh A, Ressel A, Mohamed HG, Johnson RS, Nadrowitz R, Richter E, Katschinski DM, Wenger RH (2003) The hypoxa-inducible factor-1 alpha is a negative factor for tumor therapy. Oncogene 22:3213–3220
Hudson CC, Liu M, Chiang GG, Otterness DM, Loomis DC, Kaper F, Giaccia AJ, Abraham RT (2002) Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 expression and function by the mammalian target of rapamycin. Mol Cell Biol 22:7004–7014
Hay N (2005) The Akt-mTOR tango and its relevance to cancer. Cancer Cell 8:179–183
Memmott RM, Dennis PA (2009) Akt-dependent and -independent mechanisms of mTOR regulation in cancer. Cell Signal 21:656–664
Phillips RJ, Mestas J, Gharaee-Kermani M, Burdick MD, Sica A, Belperio JA, Keane MP, Strieter RM (2005) Epidermal growth factor and hypoxia-induced expression of CXC chemokine receptor 4 on non-small cell lung cancer cells is regulated by the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/PTEN/AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway and activation of hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha. J Biol Chem 280:22473–22481
Dowling RJ, Pollak M, Sonenberg N (2009) Current status and challenges associated with targeting mTOR for cancer therapy. BioDrugs 23:77–91
LaCasse EC, Baird S, Komeluk RG, Mackenzie AE (1998) The inhibitors of apoptosis (IAPs) and their emerging role in cancer. Oncogene 17:3247–3259
Altieri DC (2008) Survivin, cancer networks and pathway-directed drug discovery. Nat Rev Cancer 8:61–70
Strömberg T, Dimberg A, Hammarberg A, Carlson K, Osterborg A, Nilsson K, Jernberg-Wiklund H (2004) Rapamycin sensitizes multiple myeloma cells to apoptosis induced by dexamethasone. Blood 103:3138–3147
Oh SH, Jin Q, Kim ES, Khuri FR, Lee HY (2008) Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling pathway induces resistance to the apoptotic activities of SCH66336 (lonafarnib) through Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin-mediated increases in survivin expression. Clin Cancer Res 14:1581–1589
Xu R, Zhang P, Huang J, Ge SF, Lu J, Qian GX (2007) Sp1 and Sp3 regulate basal transcription of the survivin gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 356:229–286
Luo XR, Li JS, Niu Y, Miao L (2010) Targeted killing effects of double CD and TK suicide genes controlled by survivin promoter on gastric cancer cell. Mol Biol Rep 38:1201–1207
Chen YQ, Zhao CL, Li W (2009) Effect of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α on transcription of survivin in non-small cell lung cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 28:29
Zhang X, Chang A (2008) Molecular predictors of EGFR-TKI sensitivity in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Med Sci 5:209–217
Conde E, Angulo B, Tang M, Morente M, Torres-Lanzas J, Lopez-Encuentra A, Lopez-Rios F, Sanchez-Cespedes M (2006) Molecular context of the EGFR mutations: evidence for the activation of mTOR/S6K signaling. Clin Cancer Res 12:710–717
Morgillo F, Woo JK, Kim ES, Hong WK, Lee HY (2006) Heterodimerization of insulin-like growth factor receptor/epidermal growth factor receptor and induction of survivin expression counteract the antitumor action of erlotinib. Cancer Res 66:10100–10111
Derin D, Soydinç HO, Guney N, Tas F, Camlica H, Duranyildiz D, Yasasever V, Topuz E (2008) Serum levels of apoptosis biomarkers, survivin and TNF-alpha in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 59:240–245
Greijer AE, van der Wall E (2004) The role of hypoxia inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) in hypoxia induced apoptosis. J Clin Pathol 57:1009–1014
Vaira V, Lee CW, Goel HL, Bosari S, Languino LR, Altieri DC (2007) Regulation of survivin expression by IGF-1/mTOR signaling. Oncogene 26:2678–2684
Peng XH, Karna P, Cao Z, Jiang BH, Zhou M, Yang L (2006) Cross-talk between epidermal growth factor receptor and hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha signal pathways increases resistance to apoptosis by up-regulating survivin gene expression. J Biol Chem 281:25114–25903
Giordano RJ, Edwards JK, Tuder RM, Arap W, Pasqualini R (2009) Combinatorial ligand-directed lung targeting. Proc Am Thorac Soc 6:411–415
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, B., Yuping, S. & Ni, J. Rapamycin decreases survivin expression to induce NSCLC cell apoptosis under hypoxia through inhibiting HIF-1α induction. Mol Biol Rep 39, 185–191 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-0724-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-0724-3