Abstract
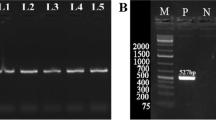
The kisspeptin/GPR54 pathway is crucial in the process of puberty onset. Six pairs of primers were designed to clone goat GPR54 and scan polymorphisms and one pair of primers to detect polymorphisms of GPR54 in sexual precocious and sexual late-maturing goat breeds. A DNA fragment of 4258 bp of goat GPR54 was obtained, which contains an open reading frame (ORF) of 1137 bp and encodes 378 amino acids, having a high homology with other mammals. The protein was predicted to have seven transmembrane regions. There were no base pair variation in exons 1–4 and three base changes (G4014A, G4136A and C4152T) in exon 5 by sequencing and the three mutations may have some correlation with sexual precocity in goats. For the 4152 locus, the Jining Grey goat does with genotype TT and CT had 1.02 and 0.84 (P < 0.01) kids more than those with genotype CC, respectively. No significant difference (P > 0.05) was found in litter size between TT and CT genotypes in Jining Grey goat. For the other two loci, no significant difference (P > 0.05) was found in litter size between different genotypes in Jining Grey goats. The present study preliminarily indicated an association between allele T of the 4152 locus in GPR54 and high litter size in Jining Grey goats.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee DK, Nguyen T, O’Neill GP, Cheng R, Liu Y, Howard AD, Coulombe N, Tan CP, Tang-Nguyen AT, George SR, O’Dowd BF (1999) Discovery of a receptor related to the galanin receptors. FEBS Lett 446(1):103–107
Muir AI, Chamberlain L, Elshourbagy NA, Michalovich D, Moore DJ, Calamari A, Szekeres PG, Sarau HM, Chambers JK, Murdock P, Steplewski K, Shabon U, Miller JE, Middleton SE, Darker JG, Larminie CG, Wilson S, Bergsma DJ, Emson P, Faull R, Philpott KL, Harrison DC (2001) AXOR12, a novel human G protein-coupled receptor, activated by the peptide KiSS-1. J Biol Chem 276(31):28969–28975
Kotani M, Detheux M, Vandenbogaerde A, Communi D, Vanderwinden JM, Poul EL, Brézillon S, Tyldesley R, Suarez-Huerta N, Vandeput F, Blanpain C, Schiffmann SN, Vassart G, Parmentier M (2001) The metastasis suppressor gene KiSS-1 encodes kisspeptins, the natural ligands of the orphan G proteincoupled receptor GPR54. J Biol Chem 276:34631–34636
Ohtaki T, Shintani Y, Honda S, Matsumoto H, Hori A, Kanehashi K, Terao Y, Kumano S, Takatsu Y, Masuda Y, Ishibashi Y, Watanabe T, Asada M, Yamada T, Suenaga M, Kitada C, Usuki S, Kurokawa T, Onda H, Nishimura O, Fujino M (2001) Metastasis suppressor gene KiSS-1 encodes peptide ligand of a G-protein-coupled receptor. Nature 411(6837):613–617
Stafford LJ, Xia CZ, Ma WB, Cai Y, Liu MY (2002) Identification and characterization of mouse metastasis-suppressor KiSS1 and its G-protein-coupled receptor. Cancer Res 62:5399–5404
Castano JP, Martínez-Fuentes AJ, Gutiérrez-Pascual E, Vaudry H, Tena-Sempere M, Malagon MM (2009) Intracellular signaling pathways activated by kisspeptins through GPR54: do multiple signals underlie function diversity? Peptides 30:10–15
Funes S, Hedrick JA, Vassileva G, Markowitz L, Abbondanzo S, Golovko A, Yang S, Monsma FJ, Gustafson EL (2003) The KiSS-1 receptor GPR54 is essential for the development of the murine reproductive system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 312(4):1357–1363
Parhar IS, Ogawa S, Sakuma Y (2004) Laser-captured single digoxigenin-labeled neurons of gonadotropin-releasing hormone types reveal a novel G protein-coupled receptor (Gpr54) during maturation in cichlid fish. Endocrinology 145(8):3613–3618
Irwig MS, Fraley GS, Smith JT, Acohido BV, Popa SM, Cunningham MJ, Gottsch ML, Clifton DK, Steiner RA (2004) Kisspeptin activation of gonadotropin releasing hormone neurons and regulation of KiSS-1 mRNA in the male rat. Neuroendocrinology 80(4):264–272
Han SK, Gottsch ML, Lee KJ, Popa SM, Smith JT, Jakawich SK, Clifton DK, Steiner RA, Herbison AE (2005) Activation of gonadotropin-releasing hormone neurons by kisspeptin as a neuroendocrine switch for the onset of puberty. J Neurosci 25(49):11349–11356
Messager S, Chatzidaki EE, Ma D, Hendrick AG, Zahn D, Dixon J, Thresher RR, Malinge I, Lomet D, Carlton MB, Colledge WH, Caraty A, Aparicio SA (2005) Kisspeptin directly stimulates gonadotropin-releasing hormone release via G protein-coupled receptor 54. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(5):1761–1766
Seminara SB, Messager S, Chatzidaki EE, Thresher RR, Acierno JS, Shagoury JK, Bo-Abbas Y, Kuohung W, Schwinof KM, Hendrick AG, Zahn D, Dixon J, Kaiser UB, Slaugenhaupt SA, Gusella JF, O’Rahilly S, Carlton MBL, Crowley WF, Aparicio SAJR, Colledge WH (2003) The GPR54 gene as a regulator of puberty. N Engl J Med 349(17):1614–1627
Navarro VM, Castellano JM, Fernandez-Fernandez R, Barreiro ML, Roa J, Sanchez-Criado JE, Aguilar E, Dieguez C, Pinilla L, Tena-Sempere M (2004) Developmental and hormonally regulated messenger ribonucleic acid expression of KiSS-1 and its putative receptor, GPR54, in rat hypothalamus and potent luteinizing hormone-releasing activity of KiSS-1 peptide. Endocrinology 145(10):4565–4574
Shahab M, Mastronardi C, Seminara SB, Crowley WF, Ojeda SR, Plant TM (2005) Increased hypothalamic GPR54 signaling: a potential mechanism for initiation of puberty in primates. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(6):2129–2134
Plant TM, Ramaswamy S, Dipietro MJ (2006) Repetitive activation of hypothalamic G protein-coupled receptor 54 with intravenous pulses of kisspeptin in the juvenile monkey (Macaca mulatta) elicits a sustained train of gonadotropin-releasing hormone discharges. Endocrinology 147(2):1007–1013
Li S, Ren J, Yang G, Guo Y, Huang L (2008) Characterization of the porcine kisspeptins receptor gene and evaluation as candidate for timing of puberty in sows. J Anim Breed Genet 125(4):219–227
Shahed A, Young KA (2009) Differential ovarian expression of KiSS-1 and GPR-54 during the estrous cycle and photoperiod induced recrudescence in Siberian Hamsters (Phodopus sungorus). Mol Reprod Dev 76:444–452
Kuohung W, Kaiser UB (2006) GPR54 and KiSS-1: role in the regulation of puberty and reproduction. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 7(4):257–263
Tena-Sempere M (2006) GPR54 and kisspeptin in reproduction. Hum Reprod Update 12(5):631–639
Navarro VM, Tena-Sempere M (2008) The KiSS-1/GPR54 system: putative target for endocrine disruption of reproduction at hypothalamic-pituitary unit? Int J Androl 31(2):224–232
de Roux N, Genin E, Carel JC, Matsuda F, Chaussain JL, Milgrom E (2003) Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism due to loss of function of the KiSS1-derived peptide receptor GPR54. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(19):10972–10976
Lanfranco F, Gromoll J, von Eckardstein S, Herding EM, Nieschlag E, Simoni M (2005) Role of sequence variations of the GnRH receptor and G protein-coupled receptor 54 genes in male idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. Eur J Endocrinol 153(6):845–852
Semple RK, Achermann JC, Ellery J, Farooqi IS, Karet FE, Stanhope RG, O’Rahilly S, Aparicio SA (2005) Two novel missense mutations in G protein-coupled receptor 54 in a patient with hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90(3):1849–1855
Cerrato F, Shagoury J, Kralickova M, Dwyer A, Falardeau J, Ozata M, Van Vliet G, Bouloux P, Hall JE, Hayes FJ, Pitteloud N, Martin KA, Welt C, Seminara SB (2006) Coding sequence analysis of GNRHR and GPR54 in patients with congenital and adult-onset forms of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. Eur J Endocrinol 155(Suppl 1):S3–S10
Pallais JC, Bo-Abbas Y, Pitteloud N, Crowley WFJ, Seminara SB (2006) Neuroendocrine, gonadal, placental, and obstetric phenotypes in patients with IHH and mutations in the G-protein coupled receptor, GPR54. Mol Cell Endocrinol 254–255:70–77
Tenenbaum-Rakover Y, Commenges-Ducos M, Iovane A, Aumas C, Admoni O, de Roux N (2007) Neuroendocrine phenotype analysis in five patients with isolated hypogonadotropic hypogonadism due to a L102P inactivating mutation of GPR54. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92(3):1137–1144
Colledge WH (2004) GPR54 and puberty. Trends Endocrinol Metab 15(9):448–453
Kaiser UB, Kuohung W (2005) KiSS-1 and GPR54 as new players in gonadotropin regulation and puberty. Endocrine 26(3):277–284
Chen Y, Zhao Z, Zhang J, He J (2008) Studies about high prolificacy gene of Jining grey goats. J Anim Sci Vet Med 27(6):62–64
Gong ZJ, Hou WJ, Dong XA, Qu GK, Wang JP, Xu GP (2003) The characteristics and management of Wendeng milk goat. Ecol Domest Anim 24(4):79–80
Mei BJ (2009) Genetic analysis on prolificacy in Inner Mongolia Cashmere Goat. Dissertation, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University
Zhang SW (2009) Annals of farm animal breeds in Liaoning Province. Liaoning Science and Technology Publishing House, Shenyang, p 104
Malan SW (2000) The improved Boer goat. Small Rumin Res 36(2):165–170
Tao XP, Wang H, Ju SC, Ni ZL, Diao XJ (2001) Preliminary study on reproductive performance of the Boer goat. China Herbiv 3(5):26–27
Tu YR (1989) The sheep and goat breeds in China. Shanghai Science and Technology Press, Shanghai, pp 88–90, 98–101
Greyling JP (2000) Reproduction traits in the Boer goat doe. Small Rumin Res 36(2):171–177
Luan X, Yu H, Wei X, Zhou Y, Wang W, Li P, Gan X, Wei D, Xiao J (2007) GPR54 polymorphisms in Chinese girls with central precocious puberty. Neuroendocrinology 86(2):77–83
Teles MG, Bianco SD, Brito VN, Trarbach EB, Kuohung W, Xu S, Seminara SB, Mendonca BB, Kaiser UB, Latronico AC (2008) A GPR54-activating mutation in a patient with central precocious puberty. N Engl J Med 358(7):709–715
Feng T, Zhao YZ, Chu MX, Zhang YJ, Fang L, Di R, Cao GL, Li N (2009) Association between sexual precocity and alleles of KISS-1 and GPR54 genes in goats. Anim Biotechnol 20(3):172–176
Rothschild M, Jacobson C, Vaske D, Tuggle C, Wang L, Short T, Eckardt G, Sasaki S, Vincent A, Mclaren D, Southwood O, Steen HVD, Mileham A, Plastow G (1996) The estrogen receptor locus is associated with a major gene influencing litter size in pigs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:201–205
Szreder T, Zwierzchowski L (2007) Estrogen receptors and their genes-potential markers of functional and production traits of farm animals. Mol Biol Rep 34:207–211
Hanrahan JP, Gregan SM, Mulsant P, Mullen M, Davis GH, Powell R, Galloway SM (2004) Mutations in the genes for oocyte-derived growth factors GDF9 and BMP15 are associated with both increased ovulation rate and sterility in Cambridge and Belclare sheep (Ovis aries). Biol Reprod 70:900–909
Lin HC, Liu GF, Wang AG, Kong LJ, Wang XF, Fu JL (2009) Effect of polymorphism in the leukemia inhibitory factor gene on litter size in Large White pigs. Mol Biol Rep 36:1833–1838
Chu MX, Wang XC, Jin M, Di R, Chen HQ, Zhu GQ, Fang L, Ma YH, Li K (2009) DNA polymorphism of 5′-flanking region of prolactin gene and its association with litter size in sheep. J Anim Breed Genet 126:63–68
Lan XY, Li MJ, Chen H, Zhang LZ, Jing YJ, Wei TB, Ren G, Wang X, Fang XT, Zhang CL, Lei CZ (2009) Analysis of caprine pituitary specific transcription factor-1 gene polymorphism in indigenous Chinese goats. Mol Biol Rep 36:705–709
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Key Technology R&D Program of China (No. 2008BADB2B01), National Natural Science Foundation of China (30871773), National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (2006AA10Z139), National Key Basic Research and Development Program of China (2006CB102105), the earmarked fund for Modern Agro-industry Technology Research System of China (nycytx-39).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, G.L., Chu, M.X., Fang, L. et al. Analysis on DNA sequence of GPR54 gene and its association with litter size in goats. Mol Biol Rep 38, 3839–3848 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0499-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0499-y