Abstract
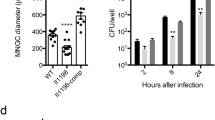
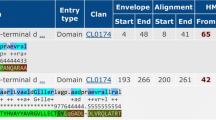
Infection with mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) can cause different outcomes in hosts with variant genetic backgrounds. Previously, we identified an intracellular pathogen resistance 1 (Ipr1) gene with the role of resistance of MTB infection in mice model. However, until now, its binding proteins have been little known even for its human homology, SP110. In this study, the homology for mouse Ipr1 in canines was found to have an extra domain structure, h.1.5.1. And 30 potential candidate proteins were predicted to bind canine Ipr1, which were characterized of the interacting structure with the h.1.5.1. Among them, MYBBP1A was verified to bind with both Ipr1 and eGFP-Ipr1 in mouse macrophage J774A.1 clone 21 cells using co-immunoprecipitation method. And with the constructed high-confidence Ipr1-involved network, we suggested that Ipr1 might be involved in apoptosis pathway via MYBBP1A.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kramnik I (2008) Genetic dissection of host resistance to mycobacterium tuberculosis: The sst1 locus and the Ipr1 gene. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 321:123–148
Pan H, Yan BS, Rojas M, Shebzukhov YV, Zhou HW, Kobzik L, Higgins DE, Daly MJ, Bloom BR, Kramnik I (2005) Ipr1 gene mediates innate immunity to tuberculosis. Nature 434:767–772
Apt A, Kramnik I (2009) Man and mouse TB: contradictions and solutions. Tuberculosis 89:195–198
Liu L, Li Y, Lin J, Liang Q, Sheng X, Wu J, Huang R, Liu S (2009) Connexin43 interacts with Caveolin-3 in the heart. Mol Biol Rep 6. doi: 10.1007/s11033-009-9584-5
Zheng D, Sun Y, Gu S, Ji C, Zhao W, Xie Y, Mao Y (2009) LNX (Ligand of Numb-protein X) interacts with RhoC, both of which regulate AP-1-mediated transcriptional activation. Mol Biol Rep 8. doi: 10.1007/s11033-009-9754-5
Yang L, Liu N, Hu X, Zhang W, Wang T, Li H, Zhang B, Xiang S, Zhou J, Zhang J (2009) CK2 phosphorylates TNFAIP1 to affect its subcellular localization and interaction with PCNA. Mol Biol Rep 10. doi: 10.1007/s11033-009-9863-1
Borutinskaite VV, Magnusson KE, Navakauskiene R (2010) alpha-Dystrobrevin distribution and association with other proteins in human promyelocytic NB4 cells treated for granulocytic differentiation. Mol Biol Rep 1. doi: 10.1007/s11033-010-9965-9
Park J, Bolser D (2001) Conservation of protein interaction network in evolution. Genome Inform 12:135–140
Aloy P, Russell RB (2003) InterPreTS: protein interaction prediction through tertiary structure. Bioinformatics 19:161–162
McGuffin LJ, Street SA, Bryson K, Sorensen SA, Jones DT (2004) The genomic threading database: a comprehensive resource for structural annotations of the genomes from key organisms. Nucleic Acids Res 32:D196–D199
Winter C, Henschel A, Kim WK, Schroeder M (2006) SCOPPI: a structural classification of protein–protein interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res 34:D310–D314
Pan H, Mostoslavsky G, Eruslanov E, Kotton DN, Kranmik I (2008) Dual-promoter lentiviral system allows inducible expression of noxious proteins in macrophages. J Immunol Methods 329:31–44
Jianmin Wu J, Ovaska Kristian, Westermarck Jukka, Tomi PM, Hautaniemi S (2009) Integrated network analysis platform for protein–protein interactions. Nat Methods 6:75–77
Lu L, Lu H, Skolnick J (2002) MULTIPROSPECTOR: an algorithm for the prediction of protein–protein interactions by multimeric threading. Proteins 49:350–364
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT, Harris MA, Hill DP, Issel-Tarver L, Kasarskis A, Lewis S, Matese JC, Richardson JE, Ringwald M, Rubin GM, Sherlock G, Gene Ontology C (2000) Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Nat Genet 25:25–29
Collins MO, Husi H, Yu L, Brandon JM, Anderson CNG, Blackstock WP, Choudhary JS, Grant SGN (2006) Molecular characterization and comparison of the components and multiprotein complexes in the postsynaptic proteome. J Neurochem 97:16–23
Abul-Husn NS, Bushlin I, Moron JA, Jenkins SL, Dolios G, Wang R, Iyengar R, Ma’ayan A, Devi LA (2009) Systems approach to explore components and interactions in the presynapse. Proteomics 9:3303–3315
Jones LC, Okino ST, Gonda TJ, Whitlock JP (2002) Myb-binding protein 1a augments AhR-dependent gene expression. J Biol Chem 277:22515–22519
Fan M, Rhee J, St-Pierre J, Handschin C, Puigserver P, Lin JD, Jaeger S, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Spiegelman BM (2004) Suppression of mitochondrial respiration through recruitment of p160 myb binding protein to PGC-1 alpha: modulation by p38 MAPK. Genes Dev 18:278–289
Tavner FJ, Simpson R, Tashiro S, Favier D, Jenkins NA, Gilbert DJ, Copeland NG, Macmillan EM, Lutwyche J, Keough RA, Ishii S, Gonda TJ (1998) Molecular cloning reveals that the p160 myb-binding protein is a novel, predominantly nucleolar protein which may play a role in transactivation by Myb. Mol Cell Biol 18:989–1002
Bell DR, Poland A (2000) Binding of aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) to AhR-interacting protein—the role of hsp90. J Biol Chem 275:36407–36414
Shin S, Wakabayashi N, Misra V, Biswal S, Lee GH, Agoston ES, Yamamoto M, Kensler TW (2007) NRF2 modulates aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling: influence on adipogenesis. Mol Cell Biol 27:7188–7197
Wang F, Wang WL, Safe S (1999) Regulation of constitutive gene expression through interactions of Sp1 protein with the nuclear aryl hydrocarbon receptor complex. Biochemistry 38:11490–11500
Peng S, Lalani S, Leavenworth JW, Ho IC, Pauza ME (2007) c-Maf interacts with c-Myb to down-regulate Bcl-2 expression and increase apoptosis in peripheral CD4 cells. Eur J Immunol 37:2868–2880
Maurice D, Hooper J, Lang G, Weston K (2007) c-Myb regulates lineage choice in developing thymocytes via its target gene Gata3. EMBO J 26:3629–3640
Nomura T, Tanikawa J, Akimaru H, Kanei-Ishii C, Ichikawa-Iwata E, Khan MM, Ito H, Ishii S (2004) Oncogenic activation of c-Myb correlates with a loss of negative regulation by TIF1 beta and Ski. J Biol Chem 279:16715–16726
Yoshioka H, Geyer CB, Hornecker JL, Patel KT, McCarrey JR (2007) In vivo analysis of developmentally and evolutionarily dynamic protein–DNA interactions regulating transcription of the Pgk2 gene during mammalian spermatogenesis. Mol Cell Biol 27:7871–7885
Herzig S, Long FX, Jhala US, Hedrick S, Quinn R, Bauer A, Rudolph D, Schutz G, Yoon C, Puigserver P, Spiegelman B, Montminy M (2001) CREB regulates hepatic gluconeogenesis through the coactivator PGC-1. Nature 413:179–183
Puigserver P, Rhee J, Donovan J, Walkey CJ, Yoon JC, Oriente F, Kitamura Y, Altomonte J, Dong HJ, Accili D, Spiegelman BM (2003) Insulin-regulated hepatic gluconeogenesis through FOXO1-PGC-1 alpha interaction. Nature 423:550–555
Finck BN, Gropler MC, Chen ZJ, Leone TC, Croce MA, Harris TE, Lawrence JC, Kelly DP (2006) Lipin 1 is an inducible amplifier of the hepatic PGC-1 alpha/PPAR alpha regulatory pathway. Cell Metab 4:199–210
Kawakami Y, Tsuda M, Takahashi S, Taniguchi N, Esteban CR, Zemmyo M, Furumatsu T, Lotz M, Belmonte JCI, Asahara H (2005) Transcriptional coactivator PGC-1 alpha regulates chondrogenesis via association with Sox9. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:2414–2419
Garimella R, Liu X, Qiao W, Liang XY, Zuiderweg ERP, Riley MI, Van Doren SR (2006) Hsc70 contacts helix III of the J domain from polyomavirus T antigens: Addressing a dilemma in the chaperone hypothesis of how they release E2F from pRb. Biochemistry 45:6917–6929
Leshchyns’ka I, Sytnyk V, Richter M, Andreyeva A, Puchkov D, Schachner M (2006) The adhesion molecule CHL1 regulates uncoating of clathrin-coated synaptic vesicles. Neuron 52:1011–1025
Sugiki T, Taketomi Y, Kikuchi-Yanoshita R, Murakami M, Kudo I (2004) Association of N-myc downregulated gene 1 with heat-shock cognate protein 70 in mast cells. Biol Pharm Bull 27:628–633
Liu M, Chen XW, Jothi R (2009) Knowledge-guided inference of domain–domain interactions from incomplete protein–protein interaction networks. Bioinformatics 25:2492–2499
van den Berk LC, van Ham MA, te Lindert MM, Walma T, Aelen J, Vuister GW, Hendriks WJ (2004) The interaction of PTP-BL PDZ domains with RIL: an enigmatic role for the RIL LIM domain. Mol Biol Rep 31:203–215
Jiayu W, Zhu H, Ming X, Xiong W, Songbo W, Bocui S, Wensen L, Jiping L, Keying M, Zhongyi L, Hongwei G (2009) Mapping the interaction site of prion protein and Sho. Mol Biol Rep 8. doi: 10.1007/s11033-009-9722-0
Lagunas L, Bradbury CM, Laszlo A, Hunt CR, Gius D (2004) Indomethacin and ibuprofen induce Hsc70 nuclear localization and activation of the heat shock response in HeLa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 313:863–870
Dastoor Z, Dreyer JL (2000) Nuclear translocation and aggregate formation of heat shock cognate protein 70 (Hsc70) in oxidative stress and apoptosis. J Cell Sci 113:2845–2854
Chung JY, Kim JY, Kim WR, Lee SG, Kim YJ, Park JE, Hong YP, Chun YJ, Park YC, Oh S, Yoo KS, Yoo YH, Kim JM (2007) Abundance of aryl hydrocarbon receptor potentiates benzo[a]pyrene-induced apoptosis in Hepa1c1c7 cells via CYP1A1 activation. Toxicology 235:62–72
Selvakumaran M, Lin HK, Sjin RTT, Reed JC, Liebermann DA, Hoffman B (1994) The novel primary response gene MYD118 and the protooncogenes Myb, Myc, and Bcl-2 modulate transforming growth factor-beta-1-induced apoptosis of myeloidleukemia cells. Mol Cell Biol 14:2352–2360
Acknowledgement
We gratefully acknowledge Dr. Gustavo Mostoslavsky for his advices on the construction of lentivirus vectors and Dr. Jianmin Wu for his advices on the construction of PPI networks. This work was supported by grants AI49421 and P01 AI056296 from the National Institutes of Health and by the National Basic Research Program of China (Grant No. 2009CB918700).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file 1
Primary canine Ipr1’s candidate binding proteins (XLS 1249 kb)
Supplementary file 2
30 canine Ipr1’s potential binding candidate proteins (XLS 218 kb)
Supplementary file 3
The network function analysis results (XLS 34 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, L., Pan, H., Trzciński, K. et al. MYBBP1A: a new Ipr1’s binding protein in mice. Mol Biol Rep 37, 3863–3868 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0042-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0042-1