Abstract
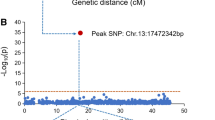
As the second most destructive disease in soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr), Phytophthora root or stem-rot (PRR) of soybean, which was caused by Phytophthora sojae (P. sojae), could lead to a 10–40% or complete yield loss annually. Researches were needed to perform to identify the P. sojae-resistant germplasm and to better understand the genetic basis of P. sojae resistance in soybean. A total of 225 diverse soybean cultivars and 109 recombinant inbred lines (RILs) derived from crossing ‘DongnongL-28’ (resistant to P. sojae race 1) and ‘Hefeng 25’ (susceptible to P. sojae race 1) were used to evaluate P. sojae race 1 resistance. These 225 soybean cultivars were sequenced using the Specific Locus Amplified Fragment Sequencing (SLAF-seq) approach, and 28,722 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were obtained from the mapping of resistant loci through genome-wide association. Eight quantitative trait nucleotides (QTNs) were associated with resistance to P. sojae race 1. The QTN on Chr.03 was colocalised according to linkage mapping of the RILs. A total of 18 candidate genes were predicted in the flanking region of the colocalised locus on Chr.03. There were stress response-related motifs, such as cis-acting regulatory elements involved in salicylic acid or MeJA responsiveness, in the 1-kb upstream region of sixteen genes. Quantitative RT-PCR showed that the Glyma.03G033700 was induced by P. sojae race 1. Association analysis for Rps loci showed that Glyma.03G033700 and Glyma.03G033800 were the candidates near peak SNP. The identified loci along with the candidate genes could be valuable for studying the molecular mechanisms underlying soybean resistance to P. sojae race 1 and breeding resistant varieties.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Athow KL, Laviolette FA, Hahn ACL, Ploper LD (1986) Genes for resistance to Phytophthora megasperma f. sp. glycinea in PI 273483D, PI 64747, PI 274212, PI 82312N, and PI 340046. Soybean Genet Newslett 13(13):119–131
Bradbury PJ, Zhang Z, Kroon DE, Casstevens TM, Ramdoss Y, Buckler ES (2007) TASSEL: software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 23(19):2633–2635
Burnham KD, Dorrance AE, Francis DM, Fioritto RJ, Martin SKS (2003a) Rps8, a new locus in soybean for resistance to Phytophthora sojae. Crop Sci 43:101–105
Burnham KD, Dorrance AE, VanToai TT, Martin SKS (2003b) Quantitative trait loci for partial resistance to Phytophthora sojae in soybean. Crop Sci 43:1610–1617
Cheng YB, Ma QB, Ren HL, Xia QJ, Song EL, Tan ZY, Li SX, Zhang GY, Nian H (2017) Fine mapping of a Phytophthora-resistance gene RpsWY in soybean (Glycine max L.) by high-throughput genome-wide sequencing. Theor Appl Genet 130:1041–1051
Demirbas A, Rector BG, Lohnes DG, Fioritto RJ, Graef GL, Cregan PB, Shoemaker RC, Specht JE (2001) Simple sequence repeat markers linked to the soybean Rps genes for Phytophthora resistance. Crop Sci 44:1220–1227
Dorrance AE, Schmitthenner AF (2000) New sources of resistance to Phytophthora sojae in the soybean plant introductions. Plant Dis 84(12):1303–1308
Dorrance AE, McClure SA, St. Martin SK (2003) Effect of partial resistance on Phytophthora root and stem rot incidence and yield of soybeans in Ohio. Plant Dis 87:308–312
Fan AY, Wang XM, Fang XP, Wu XF, Zhu ZD (2009) Molecular identification of Phytophthora resistance gene in soybean cultivar Yudou 25. Acta Agron Sin 35:1844–1850
Gao HY, Narayanan NN, Ellison L, Bhattacharyya MK (2005) Two classes of highly similar coiled coil-nucleotide binding-leucine rich repeat genes isolated from the Rps1-k locus encode Phytophthora resistance in soybean. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 18:1035–1045
Gordon SG, Martin SKS, Dorrance AE (2006) Rps8 maps to a resistance gene rich region on soybean molecular linkage group F. Crop Sci 46:168–173
Grau CR, Dorrance AE, Bond J, Russin J (2004) Fungal diseases. Soybeans. In: Boerma HR, Specht JE (eds) Improvement, production and uses, 3rd edn. Agronomy Monogr, American Society of Agron, Madison, pp 679–763
Han YP, Teng WL, Yu KF, Poysa V, Anderson T, Qiu LJ, Lightfoot DA, Li WB (2008) Mapping QTL tolerance to Phytophthora root rot in soybean using microsatellite and RAPD/SCAR derived markers. Euphytica 162:231–239
Han Y, Zhang Y, Wu D, Zhao X, Teng W, Li D, Li W (2017) Identification of novel quantitative trait loci associated with tolerance to phytophthora root rot in the soybean cultivar Hefeng 25 using two recombinant inbred line populations. Can J Plant Sci 97:1–8
Holm S (1979) A simple sequentially rejective multiple test procedure. Scand J Stat 6(2):65–70
Huang J, Guo N, Li YH, Sun JT, Hu GJ, Zhang HP, Li YF, Zhang X, Zhao JM, Xing H, Qiu LJ (2016) Phenotypic evaluation and genetic dissection of resistance to Phytophthora sojae in the Chinese soybean mini core collection. BMC Genet 17:85
Jiang N, Cui J, Meng J, Luan YS (2018) A tomato nucleotide binding sites-leucine-rich repeat gene is positively involved in plant resistance to Phytophthora infestans. Phytopathology 108:980–987. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-12-17-0389-R
Kyle DE, Nickell CD, Nelson RL, Pedersen WL (1998) Response of soybean accessions from provinces in southern China to Phytophthora sojae. Plant Dis 82(5):555–559
Li BY, Ma SM (1999) The occurrence of soybean Phytophthora root rot and its control. Chin J Oil Crop Sci 21:47-50 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li XP, Han YP, Teng WL, Zhang SZ, Yu KF, Poysa V, Anderson T, Ding JJ, Li WB (2010) Pyramided QTL underlying tolerance to Phytophthora root rot in mega-environments from soybean cultivars ‘Conrad’ and ‘Hefeng 25’. Theor Appl Genet 121:651–658
Li Y, Sun S, Zhong C, Wang X, Wu X, Zhu Z (2017) Genetic mapping and development of co-segregating markers of RpsQ, which provides resistance to in soybean. Theor Appl Genet 130:1223–1233
Lin F, Zhao MX, Ping JQ, Johnson A, Zhang B, Abney TS, Hughes TJ, Ma JX (2013) Molecular mapping of two genes conferring resistance to Phytophthora sojae in a soybean landrace PI 567139B. Theor Appl Genet 126:2177–2185
Lipka AE, Tian F, Wang Q, Peiffer J, Li M, Bradbury PJ, Gore MA, Buckler ES, Zhang Z (2012) GAPIT: genome association and prediction integrated tool. Bioinformatics 28(18):2397–2399
Liu X, Huang M, Fan B, Buckler ES, Zhang Z (2016) Iterative usage of fixed and random effect models for powerful and efficient genome-wide association studies. PLoS Genet 12(2):e1005767
Marie-Cécile C, Lennart W, Jan S, Kim F, Sophie P, Alexandra J, Silke R, Jonathan J, Christine F (2014) The plasmodesmal protein PDLP1 localises to haustoria-associated membranes during downy mildew infection and regulates callose deposition. PLoS Pathog 10(11):e1004496
Niu JP, Guo N, Sun JT, Li LH, Cao YC, Li SG, Huang JL, Zhao JM, Zhao TJ, Xing H (2017) RpsHN fine mapping of a resistance gene that controls using recombinant inbred lines and secondary populations. Front Plant Sci 8:538
Ping JQ, Fitzgerald JC, Zhang CB, Lin F, Bai YH, Wang DC, Aggarwal R, Rehman M, Crasta O, Ma JX (2016) Identification and molecular mapping of Rps11, a novel gene conferring resistance to Phytophthora sojae in soybean. Theor Appl Genet 129:445–451
Sandhu D, Gao HY, Cianzio S, Bhattacharyya MK (2004) Deletion of a disease resistance nucleotide-binding-site leucine-rich-repeatlike sequence is associated with the loss of the Phytophthora resistance gene Rps4 in soybean. Genetics 168:2157–2167
Sandhu D, Schallock KG, Rivera-Velez N, Lundeen P, Cianzio S, Bhattacharyya MK (2005) Soybean phytophthora resistance gene Rps8 maps closely to the Rps3 region. J Hered 96:536–541
Schmitthenner AF (1985) Problems and progress in control of Phytophthora root rot of soybean. Plant Dis 69:362–368
Schneider R, Rolling W, Song Q, Cregan P, Dorrance AE, McHale LK (2016) Genome-wide association mapping of partial resistance to Phytophthora sojae in soybean plant introductions from the Republic of Korea. BMC Genomics 17:607
Shen CY, Su YC (1991) Discovery and preliminary studies of Phytophthora megasperma on soybean in China. Acta Phytopathol Sin 21: 298 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Sugimoto T, Yoshida S, Kaga A, Hajika M, Watanabe K, Aino M, Tatsuda K, Yamamoto R, Matoh T, Walker DR (2011) Genetic analysis and identification of DNA markers linked to a novel Phytophthora sojae resistance gene in the Japanese soybean cultivar Waseshiroge. Euphytica 182:133–145
Sugimoto T, Kato M, Yoshida S, Matsumoto I, Kobayashi T, Kaga A, Hajika M, Yamamoto R, Watanabe K, Aino M, Matoh T, Walker DR, Biggs AR, Ishimoto M (2012) Pathogenic diversity of Phytophthora sojae and breeding strategies to develop Phytophthora- resistant soybeans. Breed Sci 61:511–522
Sun S, Wu XL, Zhao JM, Wang YC, Tang QH, Yu DY, Gai JY, Xing H (2011) Characterization and mapping of RpsYu25, a novel resistance gene to Phytophthora sojae. Plant Breed 130:139–143
Sun X, Liu D, Zhang X, Li W, Liu H, Hong W, Jiang C, Guan N, Ma C, Zeng H, Xu C, Song J, Huang L, Wang C, Shi J, Wang R, Zheng X, Lu C, Wang X, Zheng H (2013) SLAF-seq: an efficient method of large-scale de novo SNP discovery and genotyping using high-throughput sequencing. PLoS One 8(3):e58700
Sun J, Guo N, Lei J, Li L, Hu G, Xing H (2014a) Association mapping for partial resistance to Phytophthora sojae in soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.). J Genet 93:355–363
Sun JT, Li LH, Zhao JM, Huang J, Yan Q, Xing H, Guo N (2014b) Genetic analysis and fine mapping of RpsJS, a novel resistance gene to Phytophthora sojae in soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr]. Theor Appl Genet 127:913–919
Tooley P, Grau C (1982) Identification and quantitative characterization of rate-reducing resistance to Phytophthora megasperma f. sp. glycinea in soybean seedlings. Phytopathology 72:727–733
Tucker DM, Saghai Maroof MA, Mideros S, Skoneczka JA, Nabati DA, Buss GR, Hoeschele I, Tyler BM, Martin SKST, Dorrance AE (2010) Mapping quantitative trait loci for partial resistance to Phytophthora sojae in a soybean interspecific cross. Crop Sci 50:628–635
Tyler BM (2007) Phytophthora sojae: root rot pathogen of soybean and model oomycete. Mol Plant Pathol 8(1):1–8
Wang HH, Waller LC, Tripathy S, Martin SKS, Zhou LC, Krampis K, Tucker DM, Mao YC, Hoeschele I, Maroof MAS, Tyler BM, Dorrance AE (2010) Analysis of genes underlying soybean quantitative trait loci conferring partial resistance to Phytophthora sojae. Plant Gen 3:23–40
Wang H, St. Martin SK, Dorrance AE (2012a) Comparison of phenotypic methods and yield contributions of quantitative trait loci for partial resistance to in soybean. Crop Sci 52(2):609–622
Wang H, Wijeratne A, Wijeratne S, Lee S, Taylor CG, St MS, McHale L, Dorrance AE (2012b) Dissection of two soybean QTL conferring partial resistance to Phytophthora sojae through sequence and gene expression analysis. BMC Genomics 13:428
Weng C, Yu K, Anderson TR, Poysa V (2001) Mapping genes conferring resistance to Phytophthora root rot of soybean, Rps1a and Rps7. J Hered 92(5):442–446
Weng CR, Yu KF, Anderson TR, Poysa V (2007) A quantitative trait locus influencing tolerance to Phytophthora root rot in the soybean cultivar ‘Conrad’. Euphytica 158:81–86
Wu XL, Zhang BQ, Sun S, Zhao JM, Yang F, Guo N, Gai JY, Xing H (2011a) Identification, genetic analysis and mapping of resistance to Phytophthora sojae of Pm28 in soybean. Agric Sci China 10(10):1506–1511
Wu XL, Zhou B, Sun S, Zhao JM, Chen SY, Gai JY, Xing H (2011b) Genetic analysis and mapping of resistance to Phytophthora sojae of Pm14 in soybean. Sci Agric Sin 44(3):456–460
Wu X, Zhou B, Zhao J, Guo N, Zhang B, Yang F (2011c) Identification of quantitative trait loci for partial resistance to phytophthora sojae in soybean. Plant Breeding 130(2): 144–149
Yao HY, Wang XM, Wu XF, Xiao YN, Zhu ZD (2010) Molecular mapping of Phytophthora resistance gene in soybean cultivar Zaoshu 18. J Plant Genet Res 11(2):213–217 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yu AL, Xu PF, Wang JS, Zhang SZ, Wu JJ, Li WB, Chen WY, Li NH, Fan SJ, Wang X, Jiang LY (2010) Genetic analysis and SSR mapping of gene resistance to Phytophthora sojae race 1 in soybean cv Suinong 10. Chin J Oil Crop Sci 32(4):462–466 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang JQ, Xia CJ, Duan CX, Sun SL, Wang XM, Wu XF, Zhu ZD (2013a) Identification and candidate gene analysis of a novel Phytophthora resistance gene Rps10 in a Chinese soybean cultivar. PLoS One 8(7):e69799
Zhang JQ, Xia CJ, Wang XM, Duan CX, Sun SL, Wu XF, Zhu ZD (2013b) Genetic characterization and fine mapping of the novel Phytophthora resistance gene in a Chinese soybean cultivar. Theor Appl Genet 126:1555–1561
Zhang ZN, Hao JJ, Yuan JZ, Song QJ, Hyten DL, Cregan PB, Zhang GR, Gu CH, Li M, Wang DC (2014) Phytophthora root rot resistance in soyean E00003. Crop Sci 54:492–499
Zhong C, Sun S, Li Y, Duan C, Zhu Z (2017) Next-generation sequencing to identify candidate genes and develop diagnostic markers for a novel Phytophthora resistance gene, RpsHC18, in soybean. Theor Appl Genet 131:525–538
Zhong C, Li YP, Sun SL, Duan CX, Zhu ZD (2019) Phytophthora sojae genetic mapping and molecular characterization of a broad-spectrum resistance gene in Chinese soybean. Int J Mol Sci 20(8):1809
Zhou Z, Jiang Y, Wang Z, Gou Z, Lyu J, Li W, Yu Y, Shu L, Zhao Y, Ma Y (2015) Resequencing 302 wild and cultivated accessions identifies genes related to domestication and improvement in soybean. Nat Biotechnol 33:408–414
Zhu ZD, Huo YL, Wang XM, Huang JB, Wu XF (2007) Molecular identification of a novel Phytophthora resistance gene in soybean. Acta Agron Sin 33(1):154–157
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the Heilongjiang Provincial Project (GJ2018GJ0098, GX17B002, JC2018007 and C2018016), the Chinese National Natural Science Foundation (31671717, 31471517), the National Key R & D Project (2016YFD0100304, 2017YFD0101302, and 2017YFD0101306-05), the National Project (2014BAD22B01, 2016ZX08004001-007), the Youth Leading Talent Project of the Ministry of Science and Technology in China (2015RA228), the National Ten-thousand Talents Program, Postdoctoral Fund in Heilongjiang Province (LBH-Z15017, LBH-Q17015), the national project (CARS-04-PS04), the ‘Youth Innovation Talent’ Project of the general undergraduate universities in Heilongjiang province (UNPYSCT-2016145), and the ‘Academic Backbone’ Project of Northeast Agricultural University (17XG22).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XZ, DFB and WW conceived the study and contributed to population development. CJZ and YJ contributed to genotyping. HPJ contributed to phenotypic evaluation. LJQ, YPH and WBL contributed to the experimental design and writing of the paper. All authors contributed to and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
The authors have adhered to the ethical responsibilities outlined by Molecuar Breeding.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, X., Bao, D., Wang, W. et al. Loci and candidate gene identification for soybean resistance to Phytophthora root rot race 1 in combination with association and linkage mapping. Mol Breeding 40, 100 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-020-01179-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-020-01179-9