Abstract
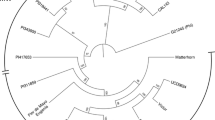
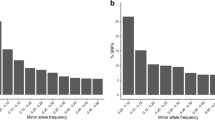
Genotyping by sequencing (GBS) is a technique to discover large numbers of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) within a sample pool. The standard version of the GBS method uses a pool of relatively large DNA fragments and is typically sequenced at low coverage (1×). This often results in mis-scoring of heterozygotes as homozygotes and a high rate (≥30 %) of missing data points. The purpose of this study was to improve the quality and the coverage of GBS data in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) in order to increase the number of SNPs available for genome-wide association studies (GWAS). An improved and Phaseolus-specific GBS method was developed, which utilizes an in silico digest of the bean genome to predict the best fragment density and length, a double digest with the restriction enzymes MseI and TaqαI, and size selection after library preparation to achieve a reduced fragment pool that can be sequenced at higher coverage. The study consisted of 25 diverse common bean genotypes belonging to the Mesoamerican gene pool and compared libraries using ApeKI fragments with MseI/TaqαI double-digest fragments. The new improved bean-specific GBS library provided a 3.8- to 12.5-fold increase in SNPs, based on a minimum coverage (3×, 5× and 8×). These results provide insight for future GBS library constructs, and how to achieve a higher SNP density for GWAS studies.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babraham Bioinformatics. http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/. Accessed 21 April 2015
Bennink M, Rondini E (2008) Dry beans and human health. The Bean Institute, pp 1–31
Catchen J, Hohenlohe P, Bassham S, Amores A, Cresko W (2013) Stacks: an analysis tool set for population genomics. Mol Ecol 22(11):3124–3140
Danecek P, Auton A, Abecasis G, Albers CA, Banks E, DePristo MA, Handsaker R, Lunter G, Marth G, Sherry ST, McVean G, Durbin R, 1000 Genomes Project Analysis Group (2011) The variant call format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics 27(15):2156–2215
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1987) A rapid DNA isolation procedure from small quantities of fresh leaf tissues. Phytochem Bull 19:11–15
Elshire RJ, Glaubitz JC, Sun Q, Poland JA, Kawamoto K, Buckler ES, Mitchell SE (2011) A robust, simple genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS) approach for high diversity species. PLoS ONE 6:e19379
Garden-Robinson J, McNeal K (2013) All about beans—nutrition, health benefits, preparation and use in menus. FN1643 (Revised), The Bean Institute, NDSU Extension Service, pp 1–16
Hamblin MT, Rabbi IY (2014) The effects of restriction-enzyme choice on properties of genotyping-by-sequencing libraries: a study in cassava (Manihot esculenta). Crop Sci 54:1–6
Hart JP, Griffiths PD (2015) Genotyping-by-sequencing enabled mapping and marker development for the by-2 potyvirus resistance allele in common bean. Plant Genome 8(1):1–14
Huang P, Feldman M, Schroder S, Bahri BA, Diao X, Zhi H, Estep M, Baxter I, Devos KM, Kellogg EA (2014) Population genetics of Setaria viridis, a new model system. Mol Ecol 23:4912–4925
Hyten DL, Song Q, Fickus EW, Quigley CV, Lim JS, Choi IY, Hwang EY, Pastor-Corrales M, Cregan PB (2010) High-throughput SNP discovery and assay development in common bean. BMC Genom 11:475–482
Illumina.com—Technology Spotlight: Illumina Sequencing Technology http://www.illumina.com/documents/products/techspotlights/techspotlight_sequencing.pdf. Accessed 17 April 2015
Illumina.com—Support: Questions & Answers http://support.illumina.com/sequencing/sequencing_instruments/cluster_station/questions.html. Accessed 21 April 2015
Koboldt D, Zhang Q, Larson D, Shen D, McLellan M, Lin L, Miller C, Mardis E, Ding L, Wilson R (2012) VarScan 2: somatic mutation and copy number alteration discovery in cancer by exome sequencing. Genome Res. doi:10.1101/gr.129684.111
Langmead B, Salzberg S (2012) Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat Methods 9:357–359
Matthes M, Singh R, Cheah S-C, Karp A (2001) Variation in oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.) tissue culture-derived regenerants revealed by AFLPs with methylation-sensitive enzymes. Theor Appl Genet 102:971–979
Moghaddam SM, Song Q, Mamidi S, Schmutz J, Lee R, Cregan P, Osorno JM, McClean PE (2014) Developing market class specific InDel markers from next generation sequence data in Phaseolus vulgaris L. Front Plant Sci 5:185
Osorno JM, McClean PE (2014) Common bean genomics and its applications in breeding programs. In: Gupta S, Nadarajan N, Gupta DS (eds) Legumes in the Omic Era, Springer, New York, pp 185–206
Poland JA, Brown PJ, Sorrells ME, Jannink J-L (2012) Development of high-density genetic maps for barley and wheat using a novel two-enzyme genotyping-by-sequencing approach. PLoS ONE 7:e32253
Rohland N, Reich D (2012) Cost-effective, high-throughput DNA sequencing libraries for multiplexed target capture. Genome Res 22:939–946
Russell J, Hackett C, Hedley P, Liu H, Milne L, Bayer M, Marshall D, Jorgensen L, Gordon S, Brennan R (2014) The use of genotyping by sequencing in blackcurrant (Ribes nigrum): developing high-resolution linkage maps in species without reference genome sequences. Mol Breeding 33:835–849
Schmutz J, McClean PE, Mamidi S, Wu GA, Cannon SB, Grimwood J, Jenkins J, Shu S, Song Q, Chavarro C, Torres-Torres M, Geffroy V, Moghaddam SM, Gao D, Abernathy B, Barry K, Blair M, Brick MA, Chovatia M, Gepts P, Goodstein DM, Gonzales M, Hellsten U, Hyten DL, Jia G, Kelly JD, Kudrna D, Lee R, Richard MMS, Miklas PN, Osorno JM, Rodrigues J, Thareau V, Urrea CA, Wang M, Yu Y, Zhang M, Wing RA, Cregan PB, Rokhsar DS, Jackson SA (2014) A reference genome for common bean and genome-wide analysis of dual domestications. Nat Genet 46:707–713
Sonah H, Bastien M, Iquira E, Tardivel A, Légaré G, Brian Boyle B, Normandeau E, Laroche J, Larose S, Jean M, Belzile F (2013) An Improved genotyping by sequencing (GBS) approach offering increased versatility and efficiency of SNP discovery and genotyping. PLoS ONE 8(1):e54603
USDA Economic Research Service (2012) Vegetables and pulses—dry beans. http://www.ers.usda.gov/topics/crops/vegetables-pulses/dry-beans.aspx. Accessed 21 April 2015
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by Agriculture and Food Research Initiative Competitive Grant No. 2013-67014-21367 from the USDA National Institute of Food and Agriculture. Partial funding for this work was also received from the Northarvest Bean Growers Association and the Dry Bean Checkoff Funds.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schröder, S., Mamidi, S., Lee, R. et al. Optimization of genotyping by sequencing (GBS) data in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Mol Breeding 36, 6 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-015-0431-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-015-0431-1