Abstract
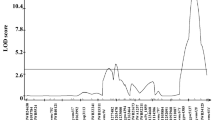
Ascochyta blight, caused by the fungus Ascochyta rabiei (Pass.) Labr., is a highly destructive disease of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) on a global basis, and exhibits considerable natural variation for pathogenicity. Different sources of ascochyta blight resistance are available within the cultivated species, suitable for pyramiding to improve field performance. Robust and closely linked genetic markers are desirable to facilitate this approach. A total of 4,654 simple sequence repeat (SSR) and 1,430 single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers were identified from a chickpea expressed sequence tag (EST) database. Subsets of 143 EST–SSRs and 768 SNPs were further used for validation and subsequent high-density genetic mapping of two intraspecific mapping populations (Lasseter × ICC3996 and S95362 × Howzat). Comparison of the linkage maps to the genome of Medicago truncatula revealed a high degree of conserved macrosynteny. Based on field evaluation of ascochyta blight incidence performed over 2 years, two genomic regions containing resistance determinants were identified in the Lasseter × ICC3996 family. In the S95362 × Howzat population, only one quantitative trait locus (QTL) region was identified for both phenotypic evaluation trials, which on the basis of bridging markers was deduced to coincide with one of the Lasseter × ICC3996 QTLs. Of the two QTL-containing regions identified in this study, one (ab_QTL1) was predicted to be in common with QTLs identified in prior studies, while the other (ab_QTL2) may be novel. Markers in close linkage to ascochyta blight resistance genes that have been identified in this study can be further validated and effectively implemented in chickpea breeding programs.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal G, Jhanwar S, Priya P, Singh VK, Saxena MS et al (2012) Comparative analysis of kabuli chickpea transcriptome with desi and wild chickpea provides a rich resource for development of functional markers. PLoS ONE 7(12):e52443. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0052443
Anbessa Y, Taran B, Warkentin TD, Tullu A, Vandenberg A (2009) Genetic analyses and conservation of QTL for ascochyta blight resistance in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Theor Appl Genet 119(4):757–765
Barbara T, Palma-Silva C, Paggi GM, Bered F, Fay MF, Lexer C (2007) Cross-species transfer of nuclear microsatellite markers: potential and limitations. Mol Ecol 16(18):3759–3767
Bertioli DJ, Moretzsohn MC, Madsen LH, Sandal N, Leal-Bertioli SC, Guimaraes PM, Hougaard BK, Fredslund J, Schauser L, Nielsen AM et al (2009) An analysis of synteny of Arachis with Lotus and Medicago sheds new light on the structure, stability and evolution of legume genomes. BMC Genomics 5:16
Buhariwalla HK, Jayashree B, Eshwar K, Crouch JH (2005) Development of ESTs from chickpea roots and their use in diversity analysis of the Cicer genus. BMC Plant Biol 5:16
Chabane K, Ablett GA, Cordeiro GM, Valkoun J, Henry RJ (2005) EST versus genomic derived microsatellites for genotyping wild and cultivated barley. Genet Res Crop Evol 52:903–909
Choi HK, Kim DJ, Uhm T, Limpens E, Lim H, Mun JH, Kalo P, Penmesta RV, Seres A, Kulikova O et al (2004) A sequence based genetic map of Medicago truncatula and comparison of marker colinearity with M. sativa. Genetics 166:1463–1502
Choi I-Y, Hyten DL, Matukumalli LK, Song Q, Chaky JM, Quigley CV, Chase K, Lark KG, Reiter RS, Yoon M-S, Hwang E-Y, Yi S-I et al (2007) A soybean transcript map: gene distribution, haplotype and single-nucleotide polymorphism analysis. Genetics 176:685–696
Choudhary S, Sethy NK, Shokeen B, Bhatia S (2009) Development of chickpea EST-SSR markers and analysis of allelic variation across related species. Theor Appl Genet 118(3):591–608
Choudhary S, Gaur R, Gupta S (2012a) EST-derived genic molecular markers: development and utilization for generating an advanced transcript map of chickpea. Theor Appl Genet 124(8):1449–1462
Choudhary P, Khanna SM, Jain PK, Bharadwaj C, Kumar J, Lakhera PC, Srinivasan R (2012b) Genetic structure and diversity analysis of the primary gene pool of chickpea using SSR markers. Genet Mol Res 11(2):891–905
Cogan NOI, Ponting RC, Vecchies A, Drayton MC, George J, Dracatos PM, Dobrowlski M, Sawbridge TI et al (2006) Gene-associated single nucleotide polymorphism discovery in perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). Mol Gen Genet 276:101–112
Cong B, Liu JP, Tanksley SD (2002) Natural alleles at a tomato fruit size quantitative trait locus differ by heterochronic regulatory mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(21):13606–13611
Flandez-Galvez H, Ford R, Pang EC, Taylor PW (2003a) An intraspecific linkage map of the chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) genome based on sequence ged microsatellite site and resistance gene analog markers. Theor Appl Genet 106(8):1447–1456. doi:10.1007/s00122-003-1199-y
Flandez-Galvez H, Ades PK, Ford R, Pang ECK, Taylor PWJ (2003b) QTL analysis for ascochyta blight resistance in an intraspecific population of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Theor Appl Genet 107:1257–1265
Galeano CH, Fernandez AC, Franco-Herrera N, Cichy KA, McLean PE, Vanderleyden J, Blair MW (2011) Saturation of an intra-gene pool linkage map: towards a unified consensus linkage map for fine mapping and synteny analysis in common bean. PLoS ONE 6:e28135
Garg R, Patel RK, Tyagi AK, Jain M (2011) De novo assembly of chickpea transcriptome using short reads for gene discovery and marker identification. DNA Res 18(1):53–63
Gaur R, Sethy NK, Choudhary S, Shokeen B, Gupta V, Bhatia S (2011) Advancing the STMS genomic resources for defining new locations on the intraspecific genetic linkage map of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). BMC Genomics 12:117
Gaur R, Azam S, Jeena G, Khan AW, Choudhary S, Jain M, Yadav G, Tyagi AK, Chattopadhyay D, Bhatia S (2012) High-throughput SNP discovery and genotyping for constructing a saturated linkage map of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). DNA Res 19(5):357–373
Gore MA, Wright MH, Ersoz ES, Bouffard P, Szekeres ES, Jarvie TP, Hurwitz BL, Narechania A, Harkins TT, Grills GS et al (2009) Large-scale discovery of gene-enriched SNPs. Plant Genome 2:121–133
Gujaria N, Kumar A, Dauthal P, Dubey A, Hiremath P, Prakash AB, Farmer A, Bhide M, Shah T, Gaur PM, Upadhyaya HD, Bhatia S, Cook DR, May GD, Varshney RK (2011) Development and use of genic molecular markers (GMMs) for construction of a transcript map of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Theor Appl Genet 122(8):1577–1589
Hiremath PJ, Farmer A, Cannon SB, Woodward J, Kudapa H, Tuteja R, Kumar A, Bhanuprakash A, Mulaosmanovic B, Gujaria N, Krishnamurthy L, Gaur PM, Kavikishor PB, Shah T, Srinivasan R, Lohse M, Xiao Y, Town CD, Cook DR, May GD, Varshney RK (2011) Large-scale transcriptome analysis in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.), an orphan legume crop of the semi-arid tropics of Asia and Africa. Plant Biotechnol J 9(8):922–931
Hiremath PJ, Kumar A, Penmetsa RV, Farmer A, Schlueter JA, Chamarthi SK, Whaley AM, Carrasquilla-Garcia N, Gaur PM, Upadhyaya HD, Kavi Kishor PB, Shah TM, Cook DR, Varshney RK (2012) Large-scale development of cost-effective SNP marker assays for diversity assessment and genetic mapping in chickpea and comparative mapping in legumes. Plant Biotechnol J 10(6):716–732
Huang S, Li R, Zhang Z, Li L, Gu X, Fan W, Lucas WJ, Wang X, Xie B, Ni P, Ren Y, Zhu H, Li J, Lin K, Jin W, Fei Z, Li G, Staub J, Kilian A, van der Vossen EAG, Wu Y, Guo J, He J, Jia Z, Ren Y, Tian G, Lu Y, Ruan J, Qian W, Wang M, Huang Q, Li B, Xuan Z, Cao J, Asan WuZ, Zhang J, Cai Q, Bai Y, Zhao B, Han Y, Li Y, Li X, Wang S, Shi Q, Liu S, Cho WK, Kim J-Y, Xu Y, Heller-Uszynska K, Miao H, Cheng Z, Zhang S, Wu J, Yang Y, Kang H, Li M, Liang H, Ren X, Shi Z, Wen M, Jian M, Yang H, Zhang G, Yang Z, Chen R, Liu S, Li J, Ma L, Liu H, Zhou Y, Zhao J, Fang X, Li G, Fang L, Li Y, Liu D, Zheng H, Zhang Y, Qin N, Li Z, Yang G, Yang S, Bolund L, Kristiansen K, Zheng H, Li S, Zhang X, Yang H, Wang J, Sun R, Zhang B, Jiang S, Wang J, Du Y, Li S (2009) The genome of the cucumber Cucumis sativus L. Nat Genet 41(12):1275–1281
Hyten DL, Cannon SB, Song Q, Weeks N, Fickus EW, Shoemaker RC, Specht JE, Farmer AD, May GD, Cregan PB (2010) High-throughput SNP discovery through deep resequencing of a reduced representation library to anchor and orient scaffolds in the soybean whole genome sequence. BMC Genomics 11:38
Iruela M, Castro P, Rubio J, Cubero JI, Jacinto C, Millan T, Gil J (2007) Validation of a QTL for resistance to ascochyta blight linked to resistance to fusarium wilt race 5 in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Eur J Plant Pathol 119:29–37
Jaillon O, Aury J-M, Noel B, Policriti A, Clepet C, Casagrande A, Choisne N, Aubourg S, Vitulo N, Jubin C, Vezzi A, Legeai F, Hugueney P, Dasilva C, Horner D, Mica E, Jublot D, Poulain J, Bruyere C, Billault A, Segurens B, Gouyvenoux M, Ugarte E, Cattonaro F, Anthouard V, Vico V, Del Fabbro C, Alaux M, Di Gaspero G, Dumas V, Felice N, Paillard S, Juman I, Moroldo M, Scalabrin S, Canaguier A, Le Clainche I, Malacrida G, Durand E, Pesole G, Laucou V, Chatelet P, Merdinoglu D, Delledonne M, Pezzotti M, Lecharny A, Scarpelli C, Artiguenave F, Pe ME, Valle G, Morgante M, Caboche M, Adam-Blondon A-F, Weissenbach J, Quetier F, Wincker P, French-Italian P (2007) The grapevine genome sequence suggests ancestral hexaploidization in major angiosperm phyla. Nature 449(7161):463–467
Jain M, Misra G, Patel RK, Priya P, Jhanwar S, Khan AW, Shah N, Singh VK, Garg R, Jeena G, Yadav M, Kant C et al (2013) A draft genome sequence of the pulse crop species chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Plant J 74(5):715–729. doi:10.1111/tpj.12173
Jayakumar P, Gan PY, Gossen BD, Warkentin TD, Banniza S (2005) Ascochyta blight of chickpea: infection and host resistance mechanisms. Can J Plant Pathol 27:499–509
Jhanwar S, Priya P, Garg R, Parida SK, Tyagi AK, Jain M (2012) Transcriptome sequencing of wild chickpea as a rich resource for marker development. Plant Biotechnol J 10(6):690–702
Jones ES, Mahoney NL, Hayward MD, Armstead IP, Jones JG, Humphreys MO, King IP, Kishida T, Yamada T et al (2002) An enhanced molecular marker based genetic map of perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne) reveals comparative relationships with other Poaceae genomes. Genome 45:282–295
Kaur S, Cogan NOI, Pembleton LW, Shinozuka M, Savin KW, Materne M, Forster JW (2011) Transcriptome sequencing of lentil based on second-generation technology permits large-scale unigene assembly and SSR marker discovery. BMC Genomics 12:265
Kaur S, Pembleton L, Cogan N, Savin K, Leonforte T, Paull J, Materne M, Forster J (2012) Transcriptome sequencing of field pea and faba bean for discovery and validation of SSR genetic markers. BMC Genomics 13(1):104
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Kulheim C, Yeoh SH, Maintz J, Foley WJ, Moran GF (2009) Comparative SNP diversity among four Eucalyptus species for genes from secondary metabolite biosynthetic pathways. BMC Genomics 24:452
Labdi M, Robertson LD, Singh KB, Charrier A (1996) Genetic diversity and phylogenetic relationships among the annual Cicer species as revealed by isozyme polymorphism. Euphytica 88(3):181–188
Lichtenzveig J, BonWl DJ, Zhang HB, Shtienberg D, Abbo S (2006) Mapping quantitative trait loci in chickpea associated with time to Xowering and resistance to Didymella rabiei the causal agent of ascochyta blight. Theor Appl Genet 113:1357–1369
Madrid E, Rajesh PN, Rubio J, Gil J, Millan T, Chen W (2012) Characterization and genetic analysis of an EIN4-like sequence (CaETR-1) located in QTL(AR1) implicated in ascochyta blight resistance in chickpea. Plant Cell Rep 31:1033–1042
Madrid E, Chen W, Rajesh PN, Castro P, Millan T, Gil J (2013) Allele-specific amplification for the detection of ascochyta blight resistance in chickpea. Euphytica 189:183–190
Manly KF, Cudmore RH, Meer JM (2001) Map manager QTX, cross-platform software for genetic mapping. Mamm Genome 12:930–932
Mattioni C, Cherubini M, Taurchini D, Villani F, Martin MA (2010) Evaluation of genomic SSRs and EST-SSRs markers in genetic diversity studies in European chestnut populations. Acta Hort 866:151–156
McLean P, Mamidi S, McConnell M, Chikara S, Lee R (2010) Synteny mapping between common bean and soybean reveals extensive blocks of shared loci. BMC Genomics 11:184
Moreno MT, Cubero JI (1978) Variation in Cicer arietinum L. Euphytica 27:465–485
Muchero W, Diop NN, Bhat PR, Fenton RD, Wanamrker S, Pottorff M, Hearne S, Cisse N, Fatokun C, Ehlers JD, Roberts PA, Close TJ (2009) A consensus genetic map of cowpea [Vigna unguiculata (L) Walp.] and synteny based on EST-derived SNPs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:18159–18164
Nayak SN, Zhu H, Varghese N, Datta S, Choi HK, Horres R, Jungling R, Singh J, Kishor PB, Sivaramakrishnan S, Hoisington DA, Kahl G, Winter P, Cook DR, Varshney RK (2010) Integration of novel SSR and gene-based SNP marker loci in the chickpea genetic map and establishment of new anchor points with Medicago truncatula genome. Theor Appl Genet 120:1415–1441
Radhika P, Gowda SJ, Kadoo NY, Mhase LB, Jamadagni BM, Sainani MN, Chandra S, Gupta VS (2007) Development of an integrated intraspecific map of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) using two recombinant inbred line populations. Theor Appl Genet 115:209–216
Ren Y, Zhao H, Kou Q, Jiang J, Guo S, Zhang H, Hou W, Zou X, Sun H, Gong G, Levi A, Xu Y (2012) A high resolution genetic map anchoring scaffolds of the sequenced watermelon genome. PLoS ONE 7:e29453
Schuelke M (2000) An economic method for the fluorescent labeling of PCR fragments. Nat Biotechnol 18:233–234
Sefera T, Abebie B, Gaur PM, Assefa K, Varshney RK (2011) Characterisation and genetic diversity analysis of selected chickpea cultivars of nine countries using simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers. Crop Pasture Sci 62:177–187
Singh KB, Hawtin GC, Nene YL, Reddy MV (1981) Resistance in chickpeas to Ascochyta rabiei. Plant Dis 65:586–587
Subbaiyan GK, Waters DLE, Katiyar SK, Sadananda AR, Vaddadi S, Henry RJ (2012) Genome-wide DNA polymorphisms in elite indica rice inbreds discovered by whole-genome sequencing. Plant Biotechnol J 10:623–634
Thudi M, Bohra A, Nayak SN, Varghese N, Shah TM, Penmetsa RV, Thirunavukkarasu N, Gudipati S, Gaur PM, Kulwal PL, Upadhyaya HD, Kavikishor PB, Winter P, Kahl G, Town CD, Kilian A, Cook DR, Varshney RK (2011) Novel SSR markers from BAC-end sequences, DArT arrays and a comprehensive genetic map with 1,291 marker loci for chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). PLoS ONE 6:e27275
Udupa SM, Baum M (2003) Genetic dissection of pathotype-specific resistance to ascochyta blight disease in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) using microsatellite markers. Theor Appl Genet 106:1196–1202
van der Knaap E, Tanksley SD (2003) The making of a bell pepper-shaped tomato fruit: identification of loci controlling fruit morphology in yellow stuffer tomato. Theor Appl Genet 107:139–147
Varshney RK, Hiremath PJ, Lekha P, Kashiwagi J, Balaji J, Deokar AA, Vadez V, Xiao Y, Srinivasan R, Gaur PM, Siddique KHM, Town CD, Hoisington DA (2009) A comprehensive resource of drought- and salinity-responsive ESTs for gene discovery and marker development in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). BMC Genomics 10:523
Varshney RK, Song C, Saxena RK, Azam S, Yu S, Sharpe AG, Cannon S, Baek J, Rosen BD, Taran B et al (2013) Draft genome sequence of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) provides a resource for trait improvement. Nat Biotechnol 31:240–248
Voorips RE (2002) MapChart: software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J Hered 93:77–78
Wang S, Basten CJ, Zeng Z-B (2012) Windows QTL Cartographer 2.5. Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC. (http://statgen.ncsu.edu/qtlcart/WQTLCart.htm)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by funding from the Victorian Department of Environment and Primary Industries and the Grains Research and Development Council, Australia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Amber Stephens and Maria Lombardi have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11032_2013_9950_MOESM1_ESM.xls
Details of all SSR markers used in linkage mapping analysis: This file contains a list of all SSR marker assays including those that are public and those developed as part of the present study, along with statistics on amplification efficiency and polymorphism rate (XLS 45 kb)
11032_2013_9950_MOESM2_ESM.xls
Sequence information of all of the SSR primer pairs identified and designed using BatchPrimer3: This file contains all of the information (sequence information, orientation, sequence length, expected product length, expected position on Mt genome, Tm, GC content and SSR motif length) on SSR primer pairs designed using BatchPrimer 3 (XLS 2282 kb)
11032_2013_9950_MOESM3_ESM.xls
Details of the 768plex SNP-OPA design: This file contains names and sequence information for all SNP markers used for linkage mapping (XLS 199 kb)
11032_2013_9950_MOESM4_ESM.txt
Consensus sequences of 454 assembled contigs: The data represents the consensus sequences of 20,846 assembled contigs generated as a result of de novo assembly of chickpea ESTs (TXT 17941 kb)
11032_2013_9950_MOESM5_ESM.txt
Sequence information of 454 singletons: The data represents the sequence information on all the singletons generated from de novo assembly of chickpea ESTs. (TXT 21148 kb)
11032_2013_9950_MOESM6_ESM.xls
Characterization of a sub-set of EST-SSRs on wild and cultivated genotypes of chickpea. The table presents data on number and size of alleles amplified from screening of 96 EST-SSR primer pairs on 5 genotypes of chickpea (XLS 22 kb)
11032_2013_9950_MOESM7_ESM.emf
Representative clustering patterns generated by the Illumina GoldenGate® SNP Genotyping assay: The file contains an example of clustering patterns obtained from SNP genotyping assay on two mapping populations. The data point colour codes represent: red, AA (homozygous); blue, BB (homozygous); purple, AB (heterozygous); black, no call (missing data). (EMF 1068 kb)
11032_2013_9950_MOESM8_ESM.xls
Linkage map statistics from Lasseter x ICC3996 and S95362 x Howzat populations: This file contains details of different markers (SSRs and SNPs) and their corresponding positions on different LGs (XLS 80 kb)
11032_2013_9950_MOESM9_ESM.pptx
Comparison between genetic linkage maps of Lasseter x ICC3996 and S95362 x Howzat: This file shows the visual representation of all LGs from both Lasseter x ICC3996 and S95362 x Howzat maps, and the common marker loci between them (PPTX 283 kb)
11032_2013_9950_MOESM10_ESM.pptx
Synteny between genetic linkage maps of Lasseter x ICC3996 and S95362 x Howzat and Medicago truncatula chromosomes: This file shows the visual representation of all LGs from both Lasseter x ICC3996 and S95362 x Howzat maps and their syntenic relationships with Medicago truncatula (PPTX 189 kb)
11032_2013_9950_MOESM11_ESM.jpg
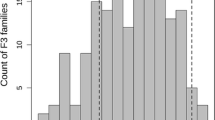
Frequency distribution of ascochyta blight disease score for two mapping populations: This file contains frequency histograms generated from ascochyta blight disease score from RILs of mapping populations A. S95362 x Howzat in 2005, B. Lasseter x ICC3996 in 2005, C. S95362 x Howzat in 2005, Howzat in 2009 and D. Lasseter x ICC3996 in 2009 (JPEG 150 kb)
11032_2013_9950_MOESM12_ESM.doc
Summary statistics for ascochyta blight resistance QTLs in chickpea: This table represents the data on QTL identification of ascochyta blight resistance in Lasseter x ICC3996 and S95362 X Howzat populations using simple interval mapping (SIM) and composite interval mapping (CIM) (DOC 37 kb)
11032_2013_9950_MOESM13_ESM.xlsx
BLAST analysis of SNP marker sequences flanking QTL regions to chickpea reference genome: This file contains the BLAST analysis data for sequences underpinning SNP loci flanking ab_QTL1 and ab_QTL2 against the chickpea reference genome (XLSX 12 kb)
11032_2013_9950_MOESM14_ESM.docx
Sequences of predicted candidate genes from comparison of flanking markers to reference genome of chickpea: This file contains the sequence information for three candidate genes predicted from the ascochyta blight resistance QTL-containing regions (DOCX 16 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stephens, A., Lombardi, M., Cogan, N.O.I. et al. Genetic marker discovery, intraspecific linkage map construction and quantitative trait locus analysis of ascochyta blight resistance in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Mol Breeding 33, 297–313 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-013-9950-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-013-9950-9