Abstract
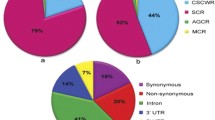
A large number of maize single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) candidate sequences have been generated and deposited in public databases. However, very little work has been done to date to comprehensively characterize those SNPs and identify a set of markers, which potentially would have high impact in molecular genetics research and breeding programs. Here we describe a multi-step process to identify highly polymorphic gene-based SNPs among ~130,000 public markers. A set of 695 highly polymorphic SNPs (minor allele frequency value >0.3), identified within exons, 5′ and 3′ untranslated regions of genes, were converted into four of the most popular high-throughput genotyping assays that include Illumina’s GoldenGate and Infinium chemistries, Life Technologies’ TaqMan assay and KBioSciences’ KASPar assay. The term “versatile” was applied to 162 gene-based SNPs that were successfully converted into all four chemistries and had perfect genotypic clustering patterns. This subset of discovered versatile SNP markers represents a universal tool for application in various molecular genetics and breeding projects in maize, where genotyping is based on one of the four above-mentioned chemistries. This study demonstrated that despite the availability of millions of discovered SNPs in maize, only a very small portion of those polymorphisms could be utilized for the development of robust, versatile assays, and has real practical value in marker-assisted selection.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen JR, Lübberstedt T (2003) Functional markers in plants. Trends Plant Sci 11:554–560
Baird NA, Etter PD, Atwood TS, Currey MC, Shiver AL, Lewis ZA, Selker EU, Cresko WA, Johnson EA (2008) Rapid SNP discovery and genetic mapping using sequenced RAD markers. PLoS One 3:e3376
Barbazuk WB, Emrich SJ, Chen HD, Schnable P (2007) SNP discovery via 454 transcriptome sequencing. Plant J 51:910–918
Barker G, Edwards KJ (2009) A genome-wide analysis of single nucleotide polymorphism diversity in the world’s major cereal crops. Plant Biotechnol J 7:318–325
Chandrasekar A, Riju A, Sithara K, Anoop A, Eapen SJ (2009) Identification of single nucleotide polymorphism in ginger using expressed sequence tags. Bioinformation 4:119–122
Chen W, Mingus J, Mammadov J, Backlund JE, Greene T, Thompson S, Kumpatla S (2010) KASPar: a simple and cost-effective system for SNP genotyping. In: Final program, abstract and exhibit guide of the XVIII international conference on the status of plant and animal genome research, San Diego, CA, 9–13 Jan 2010
Ching A, Caldwell KS, Jung M, Dolan M, Smith OS, Tingey S, Morgante M, Rafalski AJ (2002) SNP frequency, haplotype structure and linkage disequilibrium in elite maize inbred lines. BMC Genomics 3:19
Collins DW, Jukes TH (1994) Rates of transition and transversion in coding sequences since the human-rodent divergence. Genomics 20:386–396
Ebersberger I, Metzler D, Schwarz C, Pääbo S (2002) Genomewide comparison of DNA sequences between humans and chimpanzees. Am J Hum Genet 70:1490–1497
Fan JB, Oliphant A, Shen R, Kermani BG, Garcia F, Gunderson KL, Hansen M, Steemers F, Butler SL, Deloukas P, Galver L, Hunt S, McBride C, Bibikova M, Rubano T, Chen J, Wickham E, Doucet D, Chang W, Campbell D, Zhang B, Kruglyak S, Bentley D, Haas J, Rigault P, Zhou L, Stuelpnagel J, Chee MS (2003) Highly parallel SNP genotyping. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 68:69–78
Ganal M, Polley A, Durstewitz G, Thompson M, Hansen M (2010) A 50 K SNP infinium chip for maize genome analysis. In: Program and abstracts of 52nd annual maize genetics conference, Riva del Garda (Trento), Italy, 18–21 Mar 2010
Gore MA, Chia JM, Elshire RJ, Sun Q, Ersoz ES, Hurwitz BL, Peiffer JA, McMullen MD, Grills GS, Ross-Ibarra J, Ware DH, Buckler ES (2009a) A first-generation haplotype map of maize. Science 326:1115
Gore MA, Wright MH, Ersoz ES, Bouffard P, Szekeres ES, Jarvie TP, Hurwitz BL, Narechania A, Harkins TT, Grills GS, Ware DH, Buckler ES (2009b) Large-scale discovery of gene-enriched SNPs. Plant Genome 2:121–133
Gupta PK, Rustgi S, Mir RR (2008) Array-based high-throughput DNA markers for crop improvement. Heredity 101:5–18
Jones E, Chu WC, Ayele M, Ho J, Bruggeman E, Yourstone K, Rafalksi A, Smith OS, McMullen MD, Bezawada C, Warren L, Babayev J, Basu S, Smith S (2009) Development of single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers for use in commercial maize (Zea mais L.) germplasm. Mol Breed 24:165–176
Keller I, Bensasson D, Nichols RA (2007) Transition-transversion bias is not universal: a counter example from grasshopper pseudogenes. PLoS zgenet 3:e22. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen0030022
Lai J, Li R, Xu X, Jin W, Xu M, Zhao H, Xiang Z, Song W, Ying K, Zhang M, Jiao Y, Ni P, Zhang J, Li D, Guo X, Ye K, Jian M, Wang B, Zheng H, Liang H, Zhang X, Wang S, Chen A, Li J, Fu Y, Springer NM, Yang H, Wang J, Dai J, Schnable PS, Wang J (2010) Genome-wide patterns of genetic variation among elite maize inbred lines. Nature Genet 42:1027–1030
Livak KJ, Flood SJ, Marmaro J, Giusti W, Deetz K (1995) Oligonucleotide with fluorescent dyes at opposite ends provide a quenched probe system useful for detecting PCR product and nucleic acid hybridization. Genome Res 4:357–362
Mammadov JA, Chen W, Ren R, Pai R, Marchione W, Yalçin F, Witsenboer H, Greene TW, Thomspon SA, Kumpatla SP (2010) Development of highly polymorphic SNP markers from the complexity reduced portion of maize (Zea mays L.) genome for use in marker-assisted breeding. Theor Appl Genet 121:577–588
Mazumder B, Seshadri V, Fox PL (2003) Translation control by the 3′-UTR: the ends specify the means. Trends Biochem Sci 28:91–98
McMullen MD, Kresovich S, Villeda HS, Bradbury P, Li H, Sun Q, Flint-Garcia S, Thornsberry J, Acharya C, Bottoms C, Brown P, Browne C, Eller M, Guill K, Harjes C, Kroon D, Lepak N, Mitchell SE, Peterson B, Pressoir G, Romero S, Rosas MO, Salvo S, Yates H, Hanson M, Jones E, Smith S, Glaubitz JC, Goodman M, Ware D, Holland JB, Buckler ES (2009) Genetic properties of the maize nested association mapping population. Science 325:737–740
Morton BR, Bi IV, McMullen MD, Gaut BS (2006) Variation in mutation dynamics across the maize genome as a function of region and flanking base composition. Genetics 172:569–577
Nijman IJ, Kuipers S, Verheul M, Guryev V, Cuppen E (2008) A genome-wide SNP panel for mapping and association studies in the rat. BMC Genomics 9:95
Pickering BM, Willis AE (2005) The implications of structured 5′ untranslated regions on translation and disease. Semin Cell Dev Biol 16:39–47
SNP Line XL (2010) http://www.kbioscience.co.uk/instrumentation/SNPline/snp%20line%20XL.html. Accessed 23 Dec 2010
Steermers FJ, Gunderson KL (2007) Whole genome genotyping technologies on the BeadArrayTM platform. Biotechnol J 2:41–49
TaqMan® (2010) OpenArray® Genotyping instrument platform https://products.appliedbiosystems.com/ab/en/US/adirect/ab?cmd=catNavigate2&catID=605780&tab=DetailInfo. Accessed 23 Dec 2010
Van Orsouw N, Hogers RC, Janssen A, Yalcin F, Snoeijers S, Verstege E, Scheiders H, van der Poel H, van Oeveren J, Verstegen H, van Eijk MJT (2007) Complexity reduction of polymorphic sequences (CRoPS™): a novel approach for large-scale polymorphism discovery in complex genomes. PLoS One 11:1–10
Varshney R (2010) Gene-based marker systems in plants: high throughput approaches for marker discovery and genotyping. In: Mohan Jain S, Brar DS (eds) Molecular techniques in crop improvement, 2nd edn. Springer Science + Business Media B.V., Dordrecht, pp 119–142
Varshney R, Mahendar T, Aggarwal RK, Bőrner A (2007) Genic molecular markers in plants: development and applications. In: Varshney RK, Tuberosa R (eds) Genomics-assisted crop improvement, Vol 1 Genomics approaches and platforms. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 13–29
Wright WT, Heggarty SV, Young IS, Nicholls DP, Whittall R, Humphries SE, Graham CA (2008) Multiplex MassARRAY spectrometry (iPLEX) produces a fast and economical test for 56 familial hypercholesterolaemia-causing mutations. Clin Genet 74:463–468
Zhang Z, Gerstein M (2003) Patterns of nucleotide substitution, insertion and deletion in the human genome inferred from pseudogenes. Nucleic Acids Res 31:5338–5348
Zhao Z, Boerwinkle E (2002) Neighboring-nucleotide effects on single nucleotide polymorphisms: A study of 2.6 million polymorphisms across the human genome. Genome Res 12:1679–1686
Zhao Z, Fu YX, Hewett-Emmett D, Boerwinkle E (2003) Investigating single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) density in the human genome and its implications for molecular evolution. Gene 312:207–213
Zhao W, Canaran P, Jurkuta R, Fulton T, Glaubitz J, Buckler E, Doebley J, Gaut B, Goodman M, Holland J, Kresovich S, McMullen M, Stein L, Ware D (2006) Panzea: a database and resource for molecular and functional diversity in the maize genome. Nucleic Acids Res 34:D752–D757
Acknowledgments
We thank KeyGene N.V. Bioinformatics group for SNP annotation. We also thank Rebecca Aus of the Marker-Assisted Breeding Laboratory (MABL) of Dow AgroSciences for giving us access to the data regarding the application of markers from this study in various marker-assisted breeding projects. Special thanks go to Ryan Gibson of the Molecular Technology Development group and Amy Pierce of MABL of Dow AgroSciences for proof-reading and editing the manuscript. Finally, we would like to thank Dr. David Meyer, Head of Trait Genetics and Technologies of Dow AgroSciences for general support and help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mammadov, J., Chen, W., Mingus, J. et al. Development of versatile gene-based SNP assays in maize (Zea mays L.). Mol Breeding 29, 779–790 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-011-9589-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-011-9589-3