Abstract
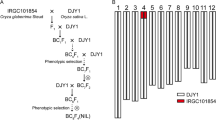
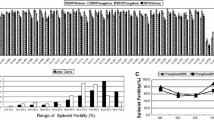
Asian cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.) and African cultivated rice (Oryza glaberrima Steud.) are the two main cultivated rice species in the world, with strong heterosis in their F1 hybrids. However, hybrid sterility is a major barrier, although significant heterosis has been observed. In this study, an F1 pollen semi-sterility locus, S19, was identified on rice chromosome 3 by using near-isogenic lines derived from repeated backcross and marker-assisted selection. The typical pollen semi-sterility was observed in F1 hybrids between S19-NIL and Dianjingyou 1. Cytological study of pollen developmental stages indicated that pollen abortion occurred at the late binucleate stage because of a starch accumulation obstacle in some pollen grains. Molecular analysis revealed that the semi-sterility was caused by the abortion of most male gametophytes carrying the S19 allele from the japonica variety Dianjingyou 1. In a population of 12,780 F2 plants derived from S19-NIL/Dianjingyou 1, the S19 locus was fine-mapped to a chromosomal region of 54 kb based on BAC clones of cv. Nipponbare. Interestingly, an addition of a DNA fragment of about 89 kb to the 54-kb region was found in S19-NIL based on BAC clones of O. glaberrima. Gene prediction analysis identified 12 open reading frames (ORF) based on the region of Dianjingyou 1, while 32 ORFs were predicted in S19-NIL. Map-based cloning of this gene will help us to understand the underlying mechanism of hybrid sterility between the two cultivated rice species.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- InDel:
-
Insertion–deletion
- MAS:
-
Marker-assisted selection
- MMC:
-
Microspore mother cell
- NERICA:
-
New rice for Africa
- NIL:
-
Near-isogenic line
- ORF:
-
Open reading frame
- QTL:
-
Quantitative trait locus
- SUMO:
-
Small ubiquitin-like modifier
- SSR:
-
Simple sequence repeat
References
Attere A, Fatokun C (1983) Reaction of Oryza glaberrima accessions to rice yellow mottle virus. Plant Dis 67:420–421
Chang TT (1976) The origin, evolution, cultivation, dissemination, and diversification of Asian and African rices. Euphytica 25:425–441
Chen X, Temnykh S, Xu Y, Cho YG, McCouch SR (1997) Development of a microsatellite framework map providing genome-wide coverage in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 95:553–567
Chen JJ, Ding JH, Ouyang YD, Du HY, Yang JY, Cheng K, Zhao J, Qiu SQ, Zhang XL, Yao JL, Liu KD, Wang L, Xu CG, Li XH, Xue YB, Xia M, Ji Q, Lu JF, Xu ML, Zhang QF (2008) A triallelic system of S5 is a major regulator of the reproductive barrier and compatibility of indica-japonica hybrids in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:11436–11441
Dellaporta SL, Wood J, Hicks JB (1983) A plant DNA mini preparation: VersionII. Plant Mol Biol Rep 1:19–21
Eshed Y, Zamir D (1995) An introgression line population of Lycopersicon pennellii in the cultivated tomato enables the identification and fine mapping of yield-associated QTL. Genetics 141:1147–1162
Feng JH, Lu YG, Liu XD, Xu XB (2001) Pollen development and its stages in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Chin J Rice Sci 1:21–28
Frary A, Nesbitt TC, Frary A, Grandillo S, Knaap EV, Cong B, Liu JP, Meller R, Alpert KB, Tanksley SD (2000) fw2.2: a quantitative trait locus key to the evolution of tomato fruit size. Science 289:85–88
Hu FY, Xu P, Deng XN, Zhou JW, Li J, Tao DY (2006) Molecular mapping of a pollen killer gene S29(t) in Oryza glaberrima and co-linear analysis with S22 in O.glumaepatatula. Euphytica 151:273–278
Ikeda R, Sokei Y, Akintayo I (2009) Seed fertility of F1 hybrids between upland rice NERICA cultivars and Oryza sativa L. or O. glaberrima Steud. Breed Sci 59:27–35
Ikehashi H, Araki H (1986) Genetics of F1 sterility in remote crosses of rice (Oryza sativa L.). In: RI IR (ed) Rice genetics. IRRI, Manila, pp 119–130
Jones M, Mande S, Aluko K (1997) Diversity and potential of Oryza glaberrima Steud. in upland rice breeding. Breed Sci 47(4):395–398
Koide Y, Onishi K, Nishimoto D, Baruah AR, Kanazawa A, Sano Y (2008) Sex-independent transmission ratio distortion system responsible for reproductive barriers between Asian and African rice species. New Phytol 179:888–900
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SE, Newburg L (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Law CN (1966) The location of genetic factors affecting a quantitative character in wheat. Genetics 53:487–498
Li WT, Zeng RZ, Zhang ZM, Ding XH, Zhang GQ (2006) Fine mapping of locus S-b for F1 pollen sterility in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Chin Sci Bull 51:675–680
Li J, Xu P, Deng XN, Zhou JW, Hu FY, Wan JM, Tao DY (2008) Identification of four genes for stable hybrid sterility and an epistatic QTL from a cross between Oryza sativa and Oryza glaberrima. Euphytica 164:699–708
Long YM, Zhao LF, Niu BX, Su J, Wu H, Chen YL, Zhang QY, Guo JX, Zhuang CX, Mei MT, Xia JX, Wang L, Wu HB, Liu YG (2008) Hybrid male sterility in rice controlled by interaction between divergent alleles of two adjacent genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:18871–18876
Lorieux M, Reversat C, Garcia Diaz SX, Denance C, Jouvenet N, Orieux Y, Bourger N, Pando-Bahuon A, Ghesquière A (2003) Linkage mapping of Has-1 0g, a resistance gene of African rice to the cyst nematode, Heterodera sacchari. Theor Appl Genet 107:691–696
Majerus V, Bertin P, Lutts S (2007) Effects of iron toxicity on osmotic potential, osmolytes and polyamines concentrations in Africa rice (Oryza glaberrima Steud.). Plant Sci 173:96–105
McCouch SR, Teytelman L, Xu Y, Lobos KB, Clare K, Walton M, Fu B, Maghirang R, Li Z, Xing YZ, Zhang Q, Kono I, Yano M, Fjellstrom R, Declerck G, Schneider D, Cartinhour S, Ware D, Stein L (2002) Development and mapping of 2240 new SSR markers for rice (Oryza sativa L.). DNA Res 9:199–207
Ohmido N, Fukui K (1995) Cytological studies of African cultivated rice, Oryza glaberrima. Theor Appl Genet 91:212–217
Oka HI (1974) Analysis of genes controlling F1 sterility in rice by the use of isogenic lines. Genetics 77:521–534
Sanguinetti CJ, Dias NE, Simpson AJG (1994) Rapid silver staining and recover of PCR products separated on polyacrylamide gels. Biotechniques 17:915–919
Sano Y (1990) The genic nature of gamete eliminator in rice. Genetics 125:183–191
Taguchi K, Doi K, Yoshimura A (1999) RFLP mapping of S19, a gene for F1 pollen semi-sterility found in backcross progeny of Oryza sativa and O.glaberrima. Rice Genet Newslett 16:70–71
Temnykh S, Park WD, Ayres N, Cartinour S, Hauck N, Lipovich L, Cho YG, Ishii T, McCouch SR (2000) Mapping and genome organization of microsatellite sequence in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 100:697–712
Wan J, Ikehashi H (1995) Identification of a new locus S-16 causing hybrid sterility in native rice varieties (Oryza sativa L.) from Tai-hu Lake region and Yunnan province, China. Breed Sci 45:161–170
Wan J, Yamaguchi Y, Kato H, Ikehashi H (1996) Two new loci for hybrid sterility in cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 92:183–190
Wang Y, Zhong ZZ, Zhao ZG, Jiang L, Bian XF, Zhang WW, Liu LL, Ikehashi H, Wan JM (2010) Fine mapping of a gene causing hybrid pollen sterility between Yunnan weedy rice and cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.) and phylogenetic analysis of Yunnan weedy rice. Planta 231:559–570
WARDA (2006) Providing what’s needed. In: WARDA annual report 2005–2006, pp. 8–11
Win KT, Kubo T, Miyazaki Y, Doi K, Yamagato Y, Yoshimura A (2009) Identification of two loci causing F1 pollen sterility in inter- and intraspecific crosses of rice. Breed Sci 59:411–418
Yamagata Y, Yamamoto E, Aya K, Win KT, Doi K, Sobrizal, Ito T, Kanamori H, Wu JZ, Matsumoto T, Matsuoka M, Ashikari M, Yoshimura A (2010) Mitochondrial gene in the nuclear genome induces reproductive barrier in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:1494–1499
Yano M, Sasaki T (1997) Genetic and molecular dissection of quantitative traits in rice. Plant Mol Biol 35:145–153
Yano M, Katayose Y, Ashikari M, Yamanouchi U, Monna L, Fuse T, Bala T, Yamamoto K, Umehara Y, Nagamura Y, Sasaki T (2000) Hd1, a major photoperiod sensitivity quantitative trait locus in rice, is closely related to the Arabidopsis flowering time gene CONSTANS. Plant Cell 12:2473–2483
Yogesh V, Aparna D, Patra B, Goel RK, Sidhu JS, Kuldeep S (2007) Identification of new sources of bacterial blight (Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae) resistance in wild Oryza species and O. glaberrima. Plant Genet Res 5:108–112
Zhang GQ, Lu YG, Zhang H, Yang JC, Liu GF (1994) Genetic studies of the hybrid sterility in cultivated rice (Oryza sativa). IV. Genotypes for F1 pollen sterility. Acta Genet Sin 21:34–41
Zhao ZG, Jiang L, Zhang WW, Yu CY, Zhu SS, Xie K, Tian H, Liu LL, Ikehashi H, Wan JM (2007) Fine mapping of S31, a gene responsible for hybrid embryo-sac abortion in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Planta 226:1087–1096
Zhu XH, Cao XZ, Zhu QS (1996) Cytological studies on spikelet sterility of Indica-Japonica hybrids in Rice. Chin J Rice Sci 10:71–78
Zhuang CX, Zhang GQ, Mei MT, Lu YG (1999) Molecular mapping of the S-a locus for F1 pollen sterility in cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.). Acta Genet Sin 26:213–218
Acknowledgments
This research is supported by the Transgene Program of China (2009ZX08009-107B), 863 Program of China (2006AA10A101), National Natural Science Foundation of China (30800679), Program of New Teacher by Education Department (200803071003), Jiangsu Science and Technology Development Program (BG2006301), Jiangsu Province Agricultural Germplasm Gene Pool Program (sx(2008)g08) and the 111 project (B08025).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
The authors Yunhui Zhang and Zhigang Zhao contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Zhao, Z., Zhou, J. et al. Fine mapping of a gene responsible for pollen semi-sterility in hybrids between Oryza sativa L. and O. glaberrima Steud. Mol Breeding 28, 323–334 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-010-9485-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-010-9485-2