Abstract
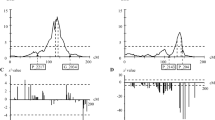
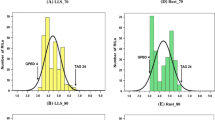
In this study we used amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) and microsatellite (short sequence repeat or SSR) markers to identify a major quantitative trail locus (QTL) for yellow spot (Mycovellosiella koepkei) disease resistance in sugarcane. A bi-parental cross between a resistant variety, M 134/75, and a susceptible parent, R 570, generated a segregating population of 227 individuals. These clones were evaluated for yellow spot infection in replicated field trials in two locations across two consecutive years. A χ2-test (χ2 at 98% confidence level) of the observed segregation pattern for yellow spot infection indicated a putative monogenic dominant inheritance for the trait with a 3 (resistant):1(susceptible) ratio. The AFLP and SSR markers identified 666 polymorphisms as being present in the resistant parent and absent in the susceptible one. A genetic map of M 134/75 was constructed using 557 single-dose polymorphisms, resulting in 95 linkage groups containing at least two markers based on linkages in coupling. QTL analysis using QTLCartographer v1.17d and MAPMAKER/QTL v1.1 identified a single major QTL located on LG87, flanked by an AFLP marker, actctc10, and an SSR marker, CIR12284. This major QTL, which was found to be linked at 14 cM to an AFLP marker, was detected with LOD 8.7, had an additive effect of −10.05% and explained 23.8% of the phenotypic variation of yellow spot resistance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aljanabi SM, Forget L, Dookun A (1999) An improved and rapid protocol for the isolation of polysaccharide and polyphenol-free sugarcane DNA. Plant Mol Biol Rep 17:1–8
Aljanabi SM, Honeycutt RJ, McClelland M, Sobral BWS (1993) A genetic linkage map of Saccharum spontaneum (L.) ‘SES 208’. Genetics 134:1249–1260
Aljanabi SM, Honeycutt RH, Sobral BWS (1994) Chromosome assortment in Saccharum. Theor Appl Genet 89:959–963
Autrey LJC, Ricaud C, Sullivan S, Dhayan S (1983) Control of yellow spot disease of sugarcane by aerial application of fungicide. Sugar Y Azucar 78:23–25
Basten CJ, Weir BS, Zeng Z-B (2001) QTL Cartographer. Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, N.C.
Brandes EW, Sartoris GB, Grassl CO (1939) Assembling and evaluating wild forms of sugarcane and closely related plants. Proc Int Soc Sugarcane Technol Congr 6:128–154
Burner DM, Legendre BL (1993) Chromosome transmission and meiotic stability of sugarcane (Saccharum spp.) hybrid derivatives. Crop Sci 33:600–606
Clayton WD, Renvoize SA (1986) Genera Graminum. Grasses of the world. Kew Bulletin Additional Series XIII, Royal Botanical Gardens, Kew. Her Majesty’s Stationery Office, London
Cordeiro GM, Casu R, McIntyre CL, Manners JM, Henry RJ (2001) Microsatellite markers from sugarcane (Saccharum sp.) ESTs cross transferable to Erianthus and sorghum. Plant Sci 160:1115–1123
Daniels J, Roach BT (1987) Taxonomy and evolution in breeding. In: Heinz DJ (ed) Sugar cane improvement through breeding. Elsevier Press, Amsterdam, pp 7–84
Daugrois JH, Grivet L, Roques D, Hoarau JY, Lombard H, Glaszmann JC, D’Hont A (1996) A putative major gene for rust resistance linked with a RFLP markers in sugarcane cultivar ‘R570’. Theor Appl Genet 92:1059–1064
D’Hont A, Rao PS, Feldmann P, Grivet L, Islam-Faridi N, Taylor P, Glaszmann JC (1995) Identification and characterization of sugarcane intergeneric hybrids, Saccharum officinarum×Erianthus arundinaceus, with molecular markers and DNA in situ hybridization. Theor Appl Genet 91:320–326
D’Hont A, Grivet L, Feldmann P, Rao PS, Berding N, Glaszmann JC (1996) Characterisation of the double genome structure of modern sugarcane cultivars, (Saccharum spp.) by molecular cytogenetics. Mol Gen Genet 250:405–413
D’Hont A, Ison D, Alix K, Roux C, Glaszmann JC (1998) Determination of basic chromosome numbers in the genus Saccharum by physical mapping of ribosomal RNA genes. Genome 41:221–225
Flor HH (1971) Current status of the gene-for-gene concept. Annu Rev Plant Phytopathol 9:275–296
Graham MA, Marek LF, Lohnes D, Cregan P, Schoemaker RC (2000) Expression and genome organization of resistance gene analogs in soybean. Genome 43:86–93
Guimarães CT, Sills GR, Sobral BWS (1997) Comparative mapping of andropogoneae: Saccharum L. (sugarcane) and its relation to sorghum and maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:14261–14266
Ha S, Moore PH, Heinz D, Kato S, Ohmido N, Fukui K (1999) Quantitative chromosome map of the polyploid Saccharum spontaneum by multicolor fluorescence in situ hybridization and imaging methods. Plant Mol Biol 39:1165–1173
Hoarau JY, Offmann B, D’Hont A, Risterucci AM, Roques J, Glaszmann JC, Grivet L (2001) Genetic dissection of a modern sugarcane cultivar (Saccharum spp.). I. Genome mapping with AFLP. Theor Appl Genet 103:84–97
Hoarau JY, Grivet L, Offmann B, Raboin LM, Diorflar JP, Payet J, Hellmann M, D’Hont A, Glaszmann JC (2002) Genetic dissection of a modern sugarcane cultivar (Saccharum spp.). II. Detection of QTLs for␣yield components. Theor Appl Genet 105:1027–1037
Hyne V, Kearsey MJ (1995) QTL analysis: further use of ‘marker regression’. Theor Appl Genet 91:471–476
Irvine JE (1999) Saccharum species as horticultural classes. Theor Appl Genet 98:186–194
Jansen RC, Van Ooijen JW, Stamp P, Lister C, Dean C (1995) Genotype by environment interaction in genetic mapping of multiple quantitative trait loci. Theor Appl Genet 91:33–37
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SE, Newberg L (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Michelmore RW, Meyers BC (1998) Clusters of resistance genes in plants evolve by divergent selection and a birth-and-death process. Genome Res 8:1113–1130
Ming R, Liu S-C, Lin Y-R, da Silva J, Wilson W, Braga D, Van Deynze A, Wenslaff TF, Wu KK, Moore PH (1998) Detailed alignment of Saccharum and sorghum chromosomes: comparative organization of closely related diploid and polyploid genomes. Genetics 150:1663–1682
Ming R, Liu SC, Moore PH, Irvine JE, Paterson AH (2001) QTL Analysis in a complex autopolyploid: genetic control of sugar content in sugarcane. Genome Res 11:2075–2084
Ming R, Liu SC, Bowers JE, Moore PH, Irvine JE, Paterson AH (2002) Construction of Saccharum consensus genetic map from two interspecific crosses. Crop Sci 42:570–583
Moore PH, Irvine JE (1991) Genome mapping of sugarcane and its potential contribution in improvement and selection of new varieties. Proc S Afr Sugarcane Technol Assoc 65:95–102
MSIRI-Mauritius Sugar Industry Research Institute (2002) MSIRI Annual Report, Réduit, Mauritius
Mudge J, Anderson WR, Kehrer RL, Fairbanks DJ (1996) A RAPD genetic map of Saccharum officinarum. Crop Sci 36:1362–1366
Ramdoyal K, Domaingue R, Sullivan S, Autrey LJC (1996) Studies on the inheritance of yellow spot (Mycovellosiella koepkei) disease in sugarcane. Proc Int Soc Sugarcane Technol Congr 22:540–547
Ricaud C (1970) Mauritius Sugar Industry Research Institute Annual Report 1969. Réduit, Mauritius, pp 68–71
Ricaud C (1974) Factors affecting yellow spot development, its control and effect on sugar yields. Proc Int Soc Sugarcane Technol Congr 15:354–364
Rossi M, Araujo PG, Paulet F, Garsmeur O, Dias VM, Chen H, Van Sluys MA, D’Hont A (2003) Genomic distribution and characterization of EST-derived resistance gene analogs (RGAs) in sugarcane. Mol Genet Genomics 269:406–419
SAS Institute (1990) SAS procedure guide, version 6, 3rd edn. SAS Institute, Cary, N.C.
Schon CC, Melchinger AE, Boppenmaier J, Bruklaus-Jung E, Herrmann RG, Seitzer JF (1994) RFLP mapping in maize: quantitative trait loci affecting testcross performance of elite European flint lines. Crop Sci 34:378–389
Shapiro SS, Wilk MB (1965) An analysis of variance test for normality (complete sample). Biometrica 52:591–611
Sills GR, Bridges WC, Aljanabi SM, Sobral BWS (1995) Genetic analysis of agronomic traits in a cross between sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.) and its presumed progenitor (S. robustum Brandes & Jesw. Ex Grassl). Mol Breed 1:355–363
da Silva JG, Honeycutt RJ, Burnquist W, Aljanabi SM, Sorrells ME, Tanksley SD, Sobral BWS (1995) Saccharum spontaneum L. ‘SES 208’ genetic linkage map combining RFLP and PCR-based markers. Mol Breed 1:165–179
da Silva J, Sorrells ME (1996) Linkage analysis in polyploids using molecular markers. In: Jauhar PR (ed) Methods of genome analysis in plants. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, pp 211–228
da Silva J, Sorrells ME, Burnquist WL, Tanksley SD (1993) RFLP linkage map and genome analysis of Saccharum spontaneum. Genome 36:782–792
Stuber CW, Lincoln SE, Wolff DW, Helenjaris T, Lander SE (1992) Identification of genetic factors contributing to heterosis in a hybrid from two elite maize inbred lines using molecular markers. Genetics 132:823–839
Tang X, Reid D, Frederick RD, Zhou J, Halterman DA, Jia Y, Martin GB (1996) Initiation of plant disease resistance by physical interaction of AvrPto and Pto kinase. Science 274:2060–2063
Tanksley SD (1993) Mapping polygenes. Annu Rev Genet 27:205–233
Veldboom LR, Lee M (1996) Genetic mapping of quantitative trait loci in maize in stress and non-stress environments: I. grain yield and yield components. Crop Sci 36:1310–1319
Vos P, Hogers R, Bleeker M, Reijans M, van der Lee T, Hornes M, Fritjters A, Pot J, Peleman J, Kuiper M, Zabeau M (1995) AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res 23:4407–4414
Wang S, Basten CJ, Zeng ZB (2003) WINDOWS QTL CARTOGRAPHER, ver. 2.0. Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, N.C. http://www.statgen.ncsu.edu/qtlcart/WQTLCart.htm
Wu KK, Burnquist W, Sorrells ME, Tew TL, Moore PH, Tanksley SD (1992) The detection and estimation of linkage in polyploids using single-dose restriction fragments. Theor Appl Genet 83:294–300
Zeng ZB (1994) Precision mapping of quantitative trait loci. Genetics 136:1457–1468
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Drs. Andrew Paterson and Ray Ming for the critical review and constructive comments of the manuscript, the International Consortium for Sugarcane Biotechnology for providing the sugarcane microsatellite primers, T. Olsen, Iowa State University, USA, for valuable assistant with SAS analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aljanabi, S., Parmessur, Y., Kross, H. et al. Identification of a major quantitative trait locus (QTL) for yellow spot (Mycovellosiella koepkei) disease resistance in sugarcane. Mol Breeding 19, 1–14 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-006-9008-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-006-9008-3