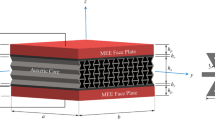
Based on the method of sampling surfaces, a hybrid finite-element model is developed for a three-dimensional analysis of laminated composite plates with piezoelectric patches. According to this method, the sampling surfaces inside the layers and piezoelectric patches parallel to the middle surface are selected, and displacements and electric potentials of these surfaces are introduced as unknown functions. The sampling surfaces are located inside the layers and patches at the nodes of Chebyshev polynomials that allows one to obtain numerical solutions asymptotically approaching the solutions of electroelasticity as the number of sampling surfaces tends to infinity. A method to determine the optimal voltages applied to the electrodes of piezoelectric patches that makes it possible to bring the plate to the desired shape by using the inverse piezoelectric effect is proposed.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. F. Crawley and K. B.Lazarus, “Induced strain actuation of isotropic and anisotropic plates,” AIAA J, 29, No. 6, 944-951 (1991).
D. A. Saravanos, “Mixed laminate theory and finite element for smart piezoelectric composite shell structures,” AIAA J., 35, No. 8, 1327-1333 (1997).
R. Lammering and S. Mesecke-Rischmann, “Multi-field variational formulations and related finite elements for piezoelectric shells,” Smart Mater. Struct., 12, No. 6, 904-913 (2003).
K. Y. Sze and L. Q. Yao, “Modelling smart structures with segmented piezoelectric sensors and actuators,” J. Sound Vib., 235, No. 3, 495-520 (2000).
K. Y. Sze, L. Q. Yao, and S. Yi, “A hybrid stress ANS solid-shell element and its generalization for smart structure modelling. Part II: Smart structure modelling,” Int. J. Numer. Meth. Eng., 48, No. 4, 565-582 (2000).
S. Zheng, X. Wang, and W. Chen, “The formulation of a refined hybrid enhanced assumed strain solid shell element and its application to model smart structures containing distributed piezoelectric sensors/actuators,” Smart Mater. Struct., 13, No. 4, N43-N50 (2004).
X. G. Tan and L. Vu-Quoc, “Optimal solid shell element for large deformable composite structures with piezoelectric layers and active vibration control,” Int. J. Numer. Meth. Eng., 64, No. 15, 1981-2013 (2005).
S. Klinkel and W. Wagner, “A geometrically non-linear piezoelectric solid shell element based on a mixed multi-field variational formulation,” Int. J. Numer. Meth. Eng., 65, No. 3, 349-382 (2006).
S. Klinkel and W. Wagner, “A piezoelectric solid shell element based on a mixed variational formulation for geometrically linear and nonlinear applications,” Computers Struct., 86, No. 1-2, 38-46 (2008).
S. Lentzen, “Nonlinearly coupled thermopiezoelectric modelling and FE-simulation of smart structures,” Fortschritt-Berichte VDI, Reihe 20, Nr. 419. - Düsseldorf: VDI Verlag, (2009).
G. M. Kulikov and S. V. Plotnikova, “Solution of a coupled thermoelasticity problem based on a geometrically exact shell element,” Mech. Compos. Mater., 46, No. 4, 349-364 (2010).
G. M. Kulikov and S. V. Plotnikova, “Exact geometry piezoelectric solid-shell element based on the 7-parameter model,” Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct., 18, No. 2, 133-146 (2011).
G. M. Kulikov and S. V. Plotnikova, “Finite rotation piezoelectric exact geometry solid-shell element with nine degrees of freedom per node,” Comput. Mater. Continua., 23, No. 3, 233-264 (2011).
G. M. Kulikov and S. V. Plotnikova, “The use of 9-parameter shell theory for development of exact geometry 12-node quadrilateral piezoelectric laminated solid-shell elements,” Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct., 22, No. 6, 490-502 (2015).
E. Carrera, S. Brischetto, and P. Nali, Plates and Shells for Smart Structures: Classical and Advanced Theories for Modeling and Analysis, Chichester: John Wiley and Sons Ltd, (2011).
E. Carrera, S. Valvano, and G. M. Kulikov, “Multilayered plate elements with node-dependent kinematics for electromechanical problems,” Int. J. Smart Nano Mater., 9, No. 4, 279-317 (2018).
G. M. Kulikov and S. V. Plotnikova, “Three-dimensional exact analysis of piezoelectric laminated plates via a sampling surfaces method,” Int. J. Solids Struct., 50, No. 11-12, 1916-1929 (2013).
G. M. Kulikov, S. V. Plotnikova, and E. Carrera, “Hybrid-mixed solid-shell element for stress analysis of laminated piezoelectric shells through higher-order theories,” Adv. Struct. Mater., 81, 45-68 (2018).
G. M. Kulikov and S. V. Plotnikova, “Exact geometry SaS solid-shell element for 3D stress analysis of FGM piezoelectric structures,” Curved Layered Struct., 5, No. 1, 116-135 (2018).
H. Irschik, “A review on static and dynamic shape control of structures by piezoelectric actuation,” Eng. Struct., 24, No. 1, 5-11 (2002).
D. B. Koconis, L. P. Kollar, and G. S. Springer, “Shape control of composite plates and shells with embedded actuators. II. Desired shape specified,” J. Compos. Mater., 28, No. 5, 459-482 (1994).
A. O. Vatul’yan, A. V. Nasedkin, A. S. Skaliukh, A. N. Solovyev, and N. B. Lapitskaya, “Controlling the surface of a segmented bimorph plates,” Prikl. Mekh. Tekhn. Fiz., 36, No. 4, 131-136 (1995).
C. Y. Hsu, C. C. Lin, and L. Gaul, “Shape control of composite plates by bonded actuators with high performance configuration,” J. Reinf. Plast. Compos., 8, No. 2, 112-124 (1997).
K. Chandrashekhara and S. Varadarajan, “Adaptive shape control of composite beams with piezoelectric actuators,” J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct., 8, No. 2, 112-124 (1997).
C. Y. K. Chee, L. Tong, and G. P. Steven, “A buildup voltage distribution (BVD) algorithm for shape control of smart plate structures,” Comput. Mech., 26, No. 2, 115-128 (2000).
C. Y. K. Chee, L. Tong, and G. P. Steven, “Static shape control of composite plates using a slope-displacement-based algorithm,” AIAA J. 40, No. 8, 1611-1618 (2002).
S. D. Mota Silva, R. Ribeiro, J. D. Rodrigues, M. A. P. Vaz, and J. M. Monteiro, “The application of genetic algorithms for shape control with piezoelectric patches - an experimental comparison,” Smart Mater. Struct., 13, No. 1, 220-226 (2004).
K. M. Liew, X. Q. He, and S. A. Meguid, “Optimal shape control of functionally graded smart plates using genetic algorithm,” Comput. Mech., 33, No. 4, 245-253 (2004).
M. S. I. Shaik Dawood, L. Iannucci, and E. S. Greenhalgh, “Three-dimensional static shape control analysis of composite plates using distributed piezoelectric actuators,” Smart Mater. Struct., 17, No. 2, 1-10 (2008).
S. S. Vel and R. S. Batra, “Cylindrical bending of laminated plates with distributed and segmented piezoelectric actuators/sensors,” AIAA J., 38, No. 5, 857-867 (2000).
This work was supported by the Russian Scientific Fund (project No. 18-19-00092).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Mekhanika Kompozitnykh Materialov, Vol. 56, No. 5, pp. 821-840, September-October, 2020.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Plotnikova, S.V., Kulikov, G.M. Shape Control of Composite Plates with Distributed Piezoelectric Actuators in a Three-Dimensional Formulation. Mech Compos Mater 56, 557–572 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11029-020-09904-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11029-020-09904-3