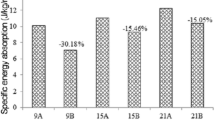
Armours are usually manufactured from polymer matrix composites and used for both military and non-military purposes in different seasons, climates, and regions. The mechanical properties of the composites depend on temperature, which also affects their ballistic characteristics. The armour is used to absorb the kinetic energy of a projectile without any major injury to a person. Therefore, besides a high strength and lightness, a high damping capacity is required to absorb the impact energy transferred by the projectile. The ballistic properties of a Kevlar 29/polyvinyl butyral composite are investigated under varied temperatures in this study. The elastic modulus of the composite is determined from the natural frequency of composite specimens at different temperatures by using a damping monitoring method. Then, the backside deformation of composite plates is analysed experimentally and numerically employing the finite-element program Abaqus. The experimental and numeric results obtained are in good agreement.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. L. Lee, T. F. Walsh, S. T. Won, H. M. Patts, J. W. Song, and A. H. Mayer, “Penetration failure mechanisms of armor-grade fiber composites under impact,” J. Compos. Mater., 35, No. 18, 1605–1633 (2001).
M. P. Flanagan, M. A. Zikry, J. W. Wall, and A. El-Shiekh, “An experimental investigation of high velocity impact and penetration failure modes in textile composites,” J. Compos. Mater., 33, No. 12, 1080–1103 (1999).
Y. S. Lee, E. D. Wetzel, and N. J. Wagner, “The ballistic impact characteristics of Kevlar woven fabrics impregnated with a colloidal shear thickening fluid,” J. Mater. Sci., 38, 2825–2833 (2003).
Y. Duan, M. Keefe, T. A. Bogetti, and B. A. Cheeseman, “Modeling friction effects on the ballistic impact behavior of a single-ply high-strength fabric,” Int. J. Impact Eng., 31, 996–1012 (2005).
Y. Duan, M. Keefe, T. A. Bogetti, and B. Powers, “Finite element modeling of transverse impact on a ballistic fabric,” Int. J. Mech. Sci., 48, 33–43 (2006).
W. R. Novotny, E. Cepus, A. Shahkarami, R. Vaziri, and A. Poursartip, “Numerical investigation of the ballistic efficiency of multi-ply fabric armours during the early stages of impact,” Int. J. Impact Eng., 34, 71–88 (2007).
M. A. G. Silva, C. Cismasiu, and C. G. Chiorean, “Numerical simulation of ballistic impact on composite laminates,” Int. J. Impact Eng., 31, 289–306 (2005).
Bohong Gu and Xin Ding, “A refined quasi-microstructure model for finite element analysis of three-dimensional braided composites under ballistic penetration,” J. Compos. Mater., 39, No. 8, 685–710 (2005).
A. Halvorsen, A. Salehi-Khojn, M. Mahinfalah, and R. Nakhaei-Jazar, “Temperature effects on the impact behavior of fiberglass and fiberglass/Kevlar sandwich composites,” Appl. Compos. Mater., 13, 369–383 (2006).
M. Colakoglu, O. Soykasap, and T. Ozek, “Experimental and numerical investigations on the ballistic performance of polymer matrix composites used in armor design,” Appl. Compos. Mater., 14, No. 1, 47–58 (2007).
M. Colakoglu, “Investigation of the ballistic performance of two different polymer matrix composites,” Key Eng. Mater., 348-349, 241–244 (2007).
M. Colakoglu, “Effect of temperature on frequency and damping properties of polymer matrix composites,” Adv. Compos. Mater., 17, 111–124 (2008).
Selection and Application Guide to Personal Body Armor. NIJ Guide 100–01. The National Institute of Justice’s National Law Enforcement and Corrections Technology Center, USA (2001).
ABAQUS/Standard User’s Manual, Version 6.7, Abaqus Simulia Inc., Providence, RI, USA (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Russian translation in Mekhanika Kompozitnykh Materialov, Vol. 46, No. 1, pp. 49–60, January-February, 2010.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soykasap, O., Colakoglu, M. Ballistic performance of a Kevlar-29 woven fibre composite under varied temperatures. Mech Compos Mater 46, 35–42 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11029-010-9124-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11029-010-9124-3