Abstract
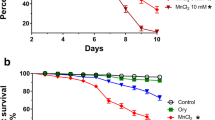
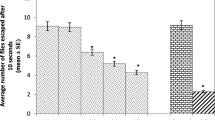
Exposure to environmental toxicants has been linked with the onset of different neurodegenerative diseases in animals and humans. Here, we evaluated the toxic effects of co-exposure to iron and rotenone at low concentrations in Drosophila melanogaster. Adult wild-type flies were orally exposed to rotenone (50.0 µM) and ferrous sulfate (FeSO4; 1.0 and 10.0 µM) through the diet for 10 days. Thereafter, we evaluated markers of oxidative damage (Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2), Nitric Oxide (NO), Protein Carbonyl, and malondialdehyde (MDA)), antioxidant status (catalase, Glutathione S-Transferase (GST), Total Thiol (T-SH) and Non-protein Thiol (NPSH), neurotransmission (monoamine oxidase; MAO and acetylcholinesterase, AChE) and mitochondrial respiration. The results indicated that flies fed rotenone and FeSO4 had impaired locomotion, reduced survival rate, and AChE activity with a corresponding increase in MAO activity when compared with the control (p < 0.05). Furthermore, rotenone and FeSO4 significantly decreased the antioxidant status with a concurrent accumulation of NO, MDA, and H2O2. Additionally, the activity of complex 1 and mitochondria bioenergetic capacity was compromised in the flies. These findings suggest that the combination of rotenone and FeSO4 elicited a possible synergistic toxic response in the flies and therefore provided further insights on the use of D. melanogaster in toxicological studies.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data is available upon request. Contact Adeola O. adedara at adedaraadeola@yahoo.co.uk.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Abolaji AO, Adedara AO, Adie MA, Vicente-Crespo M, Farombi EO (2018) Resveratrol prolongs lifespan and improves 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2, 3, 6-tetrahydropyridine induced oxidative damage and behavioural deficits in Drosophila melanogaster Biochem Biophys Res Commun 503(2):1042–1048
Abolaji AO, Kamdem JP, Farombi EO, Rocha JBT (2013) Drosophila melanogaster as a promising model organism in toxicological studies. Arch Bas App Med 1:33–38
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Akinade TC, Babatunde OO, Adedara AO, Adeyemi OE, Otenaike TA, Ashaolu OP, Johnson TO, Terriente-Felix A, Whitworth AJ, Abolaji AO (2022) Protective capacity of carotenoid trans-astaxanthin in rotenone-induced toxicity in Drosophila melanogaster. Sci Rep 12(1):4594. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-08409-4
Anet A, Olakkaran S, Purayil AK, Puttaswamygowda GH (2019) Bisphenol A induced oxidative stress mediated genotoxicity in Drosophila melanogaster J Hazard Mater 370:42–53
Angelova PR, Abramov AY (2016) Functional role of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in physiology. Free Radic Biol Med 100:81–85
Bazinet RP, Layé S (2014) Polyunsaturated fatty acids and their metabolites in brain function and disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 15(12):771–785
Beard JL, Connor JR (2003) Iron status and neural functioning. Annu Rev Nutr 23(1):41–58
Belaidi AA, Bush AI (2016) Iron neurochemistry in Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease: targets for therapeutics. J Neurochem 139:179–197
Boovarahan SR, Kurian GA (2018) Mitochondrial dysfunction: A key player in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular diseases linked to air pollution. Rev Environ Health 33(2):111–122
Bresgen N, Eckl PM (2015) Oxidative stress and the homeodynamics of iron metabolism. Biomolecules 5(2):808–847
Cannon JR, Greenamyre JT (2011) The role of environmental exposures in neurodegeneration and neurodegenerative diseases. Toxicol Sci 124(2):225–250
Chin-Chan M, Navarro-Yepes J, Quintanilla-Vega B (2015) Environmental pollutants as risk factors for neurodegenerative disorders: Alzheimer and Parkinson diseases. Front Cell Neurosci 9:124
Chotard C, Salecker I (2007) Glial cell development and function in the Drosophila visual system. Neuron Glia Biol 3(1):17–25
Dalle-Donne I, Rossi R, Colombo R, Giustarini D, Milzani A (2006) Biomarkers of oxidative damage in human disease. Clin Chem 52(4):601–623
Dancy BM, Brockway N, Ramadasan-Nair R, Yang Y, Sedensky MM, Morgan PG (2016) Glutathione S-transferase mediates an ageing response to mitochondrial dysfunction. Mech Ageing Dev 153:14–21
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82(1):70–77
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V Jr, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7(2):88–95
Fernandes EJ, Poetini MR, Barrientos MS, Bortolotto VC, Araujo SM, Musachio EAS, De Carvalho AS, Leimann FV, Gonçalves OH, Ramborger BP, Roehrs R (2021) Exposure to lutein-loaded nanoparticles attenuates Parkinson’s model-induced damage in Drosophila melanogaster: Restoration of dopaminergic and cholinergic system and oxidative stress indicators. Chem Biol Interact 340:109431
Figueira FH, de Quadros Oliveira N, de Aguiar LM, Escarrone AL, Primel EG, Barros DM, da Rosa CE (2017) Exposure to atrazine alters behaviour and disrupts the dopaminergic system in Drosophila melanogaster. Comp Biochem Physiol C: Toxicol Pharmacol 202:94–102
Green LC, Wagner DA, Glogowski J, Skipper PL, Wishnok JS, Tannenbaum SR (1982) Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15 N] nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem 126(1):131–138
Habig WH, Jakoby WB (1981) Assays for differentiation of glutathione S-Transferases. Methods Enzymol 77:398–405. Academic
Halliwell B (2017) Biochemistry of oxidative stress. Biochem Soc Trans 5:1147–1150
Han Y, Wang T, Li C, Wang Z, Zhao Y, He J, Fu L, Han B (2021) Ginsenoside Rg3 exerts a neuroprotective effect in rotenone-induced Parkinson’s disease mice via its anti-oxidative properties. Eur J Pharmacol 909:174413
Heinz S, Freyberger A, Lawrenz B, Schladt L, Schmuck G, Ellinger-Ziegelbauer H (2017) Mechanistic investigations of the mitochondrial complex I inhibitor rotenone in the context of pharmacological and safety evaluation. Sci Rep 7(1):1–13
Johnson SL, Iannucci J, Seeram NP, Grammas P (2020) Inhibiting thrombin improves motor function and decreases oxidative stress in the LRRK2 transgenic Drosophila melanogaster model of Parkinson’s disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 527(2):532–538
Jollow DJ, Mitchell JR, Zampaglione N, Gillette JR (1974) Bromobenzene-induced liver necrosis. Protective role of glutathione and evidence for 3, 4-bromobenzene oxide as the hepatotoxic metabolite. Pharmacology 11(3):151–169
Jones DN, Raghanti MA (2021) The role of monoamine oxidase enzymes in the pathophysiology of neurological disorders. J Chem Neuroanat 114:101957
Kaplan L, Chow BW, Gu C (2021) Neuronal regulation of the blood–brain barrier and neurovascular coupling. Nat Rev Neurosci 21:416–432
Kealy J, Greene C, Campbell M (2020) Blood-brain barrier regulation in psychiatric disorders. Neurosci Lett 726:133664
Kim J, Wessling-Resnick M (2014) Iron and mechanisms of emotional behavior. J Nutr Biochem 25(11):1101–1107
Kumar PP, Prashanth KH (2020) Diet with Low Molecular Weight Chitosan exerts neuromodulation in Rotenone induced Drosophila model of Parkinson’s disease. Food Chem Toxicol 146:111860
Li J, Li W, Jiang ZG, Ghanbari HA (2013) Oxidative stress and neurodegenerative disorders. Int J Mol Sci 14(12):24438–24475
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Macedo GE, de Brum Vieira P, Rodrigues NR, Gomes KK, Martins IK, Franco JL, Posser T (2020) Fungal compound 1-octen-3-ol induces mitochondrial morphological alterations and respiration dysfunctions in Drosophila melanogaster. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 206:111232
McEwen CM Jr (1971) Monoamine oxidase [rabbit serum]. Methods in enzymology, vol 17. Academic, Cambridge, pp 686–692
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1978) Reaction of linoleic acid hydroperoxide with thiobarbituric acid. J Lipid Res 19(8):1053–1057
Pandey UB, Nichols CD (2011) Human disease models in Drosophila melanogaster and the role of the fly in therapeutic drug discovery. Pharmacol Rev 63(2):411–436. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.110.003293
Paul BT, Manz DH, Torti FM, Torti SV (2017) Mitochondria and Iron: current questions. Expert Rev Hematol 10(1):65–79
Pesta D, Gnaiger E (2012) High-resolution respirometry: OXPHOS protocols for human cells and permeabilized fibers from small biopsies of human muscle. In: Mitochondrial bioenergetics. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 25–58
Piñero DJ, Li NQ, Connor JR, Beard JL (2000) Variations in dietary iron alter brain iron metabolism in developing rats. J Nutr 130(2):254–263
Poetini MR, Araujo SM, de Paula MT, Bortolotto VC, Meichtry LB, de Almeida FP, Jesse CR, Kunz SN (2018) Prigol. “Hesperidin attenuates iron-induced oxidative damage and dopamine depletion in Drosophila melanogaster model of Parkinson’s disease. Chemico-Biol Interact 279:177–186
Salim S (2017) Oxidative stress and the central nervous system. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 360(1):201–205
Sarter M, Lustig C (2020) Forebrain cholinergic signaling: wired and phasic, not tonic, and causing behavior. J Neurosci 40(4):712–719
Schapira AH, Jenner P (2011) Etiology and pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 26(6):1049–1055
Schneider SA, Obeso JA (2014) Clinical and pathological features of Parkinson’s disease. Behavioral Neurobiology of Huntington’s disease and Parkinson’s disease, pp 205–220
Sian-Hülsmann J, Mandel S, Youdim MB, Riederer P (2011) The relevance of iron in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 118:6
Siddique YH, Naz F, Rashid M, Mian S (2021) Effect of Itrifal Muqawwi-e-Dimagh (a polyherbal drug) on the transgenic Drosophila model of Parkinson’s Disease. Phytomed Plus 1(4):100131
Siima AA, Stephano F, Munissi JJ, Nyandoro SS (2020) Ameliorative effects of flavonoids and polyketides on the rotenone induced Drosophila model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurotoxicology 81:209–215
Sousa S, Maia ML, Correira-Sá L, Fernandes VC, Delerue-Matos C, Calhau C, Domingues VF (2020) Chemistry and toxicology behind insecticides and herbicides. Controlled release of pesticides for sustainable agriculture. Springer, Cham, pp 59–109
Stephano F, Nolte S, Hoffmann J, El-Kholy S, von Frieling J, Bruchhaus I, Fink C, Roeder T (2018) Impaired Wnt signaling in dopamine containing neurons is associated with pathogenesis in a rotenone triggered Drosophila Parkinson’s disease model. Sci Rep 8(1):1–11
Uddin MS, Hossain MF, Al Mamun A, Shah MA, Hasana S, Bulbul IJ, Sarwar MS, Mansouri RA, Rauf GM, Abdel-Daim MM (2020) Exploring the multimodal role of phytochemicals in the modulation of cellular signaling pathways to combat age-related neurodegeneration. Sci Total Environ 725:138313
US EPA (United States Enviornmental Protection Agency) (2007) https://archive.epa.gov/pesticides/reregistration/web/pdf/rotenone_red.pdf. Accessed 7 July 2016
Wolff SP (1994) Ferrous ion oxidation in presence of ferric ion indicator xylenol orange for measurement of hydroperoxides. Methods Enzymol 233:182–189. Academic
Xue J, Wang HLi, Xiao G (2020) Transferrin1 modulates rotenone-induced Parkinson’s disease through affecting iron homeostasis in Drosophila melanogaster. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 531(3):305–311
Zhang S, Tang MB, Luo HY, Shi CH, Xu YM (2017) Necroptosis in neurodegenerative diseases: a potential therapeutic target. Cell Death Dis 8:6
Zhou L, Chen L, Zeng X, Liao J, Ouyang D (2020) Ginsenoside compound K alleviates sodium valproate-induced hepatotoxicity in rats via antioxidant effect, regulation of peroxisome pathway and iron homeostasis. Toxicol Appl Pharmcol 386:114829
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.O. Adedara: Conceptualization, Investigation, Data curation, Writing – Original Draft. T.A. Otenaike: Investigation, Data curation. A.A. Olabiyi: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. I.A. Adedara: Writing – review & editing. A.O. Abolaji: Conceptualization, Data curation, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The use of Drosophila melanogaster requires no formal ethical approval; however, all experiments were performed in the most conducive environment and humane form as possible.
Conflict of interest
All authors have contributed to the success of this work, read and agree to submit it for consideration in your noble journal. Therefore, we declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Adedara, A.O., Otenaike, T.A., Olabiyi, A.A. et al. Neurotoxic and behavioral deficit in Drosophila melanogaster co-exposed to rotenone and iron. Metab Brain Dis 38, 349–360 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-01104-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-01104-3