Abstract
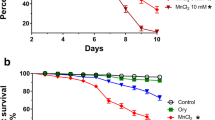
Several experimental and epidemiological reports have associated manganese exposure with induction of oxidative stress and locomotor dysfunctions. Diphenyl diselenide (DPDS) is widely reported to exhibit antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects in in vitro and in vivo studies via multiple biochemical mechanisms. The present study investigated the protective effect of DPDS on manganese-induced toxicity in Drosophila melanogaster. The flies were exposed, in a dietary regimen, to manganese alone (30 mmol per kg) or in combination with DPDS (10 and 20 µmol per kg) for 7 consecutive days. Exposure to manganese significantly (p < 0.05) increased flies mortality, whereas the survivors exhibited significant locomotor deficits with increased acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity. However, dietary supplementation with DPDS caused a significant decrease in mortality, improvement in locomotor activity and restoration of AChE activity in manganese-exposed flies. Additionally, the significant decreases in the total thiol level, activities of catalase and glutathione-S-transferase were accompanied with significant increases in the generation of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species and thiobarbituric acid reactive substances in flies exposed to manganese alone. Dietary supplementation with DPDS significantly augmented the antioxidant status and prevented manganese-induced oxidative stress in the treated flies. Collectively, the present data highlight that DPDS may be a promising chemopreventive drug candidate against neurotoxicity resulting from acute manganese exposure.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
US EPA (2003) Health effects support document for manganese. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water, EPA. EPA-822-R-03-003, Washington, D.C
Dobson AW, Erikson KM, Aschner M (2004) Manganese neurotoxicity. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1012:115–128
Claus Henn B, Schnaas L, Ettinger AS, Schwartz J, Lamadrid-Figueroa H, Hernández-Avila M, Amarasiriwardena C, Hu H, Bellinger DC, Wright RO, Téllez-Rojo MM (2012) Associations of early childhood manganese and lead coexposure with neurodevelopment. Environ Health Perspect 120:126–131
Avila DS, Puntel RL, Aschner M (2013) Manganese in health and disease. Met Ions Life Sci 13:199–227
Zoni S, Lucchini RG (2013) Manganese exposure: cognitive, motor and behavioral effects on children: a review of recent findings. Curr Opin Pediatr 25:255–260
Kim G, Lee HS, Seok Bang J, Kim B, Ko D, Yang M (2015) A current review for biological monitoring of manganese with exposure, susceptibility, and response biomarkers. J Environ Sci Health C Environ Carcinog Ecotoxicol Rev 33:229–254
Burton NC, Guilarte TR (2009) Manganese neurotoxicity: lessons learned from longitudinal studies in nonhuman primates. Environ Health Perspect 117:325–332
Roels HA, Bowler RM, Kim Y, Claus Henn B, Mergler D, Hoet P, Gocheva VV, Bellinger DC, Wright RO, Harris MG, Chang Y, Bouchard MF, Riojas-Rodriguez H, Menezes-Filho JA, Tellez-Rojo MM (2012) Manganese exposure and cognitive deficits: a growing concern for manganese neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicology 33:872–880
Guilarte TR (2013) Manganese neurotoxicity: new perspectives from behavioral, neuroimaging, and neuropathological studies in humans and non-human primates. Front Aging Neurosci 5:23–31
Santos D, Batoreu C, Mateus L, Marreilha Dos Santos AP, Aschner M (2014) Manganese in human parenteral nutrition: considerations for toxicity and biomonitoring. Neurotoxicology 43:36–45
Aschner M, Guilarte TR, Schneider JS, Zheng W (2007) Manganese: recent advances in understanding its transport and neurotoxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 221:131–147
Bellinger FP, Raman AV, Reeves MA, Berry MJ (2009) Regulation and function of selenoproteins in human disease. Biochem J 422:11–22
Sunde RA, Raines AM (2011) Selenium regulation of the selenoprotein and nonselenoprotein transcriptomes in rodents. Adv Nutr 2:138–150
Rosa RM, Roesler R, Braga AL, Saffi J, Henriques JA (2007) Pharmacology and toxicology of diphenyl diselenide in several biological models. Braz J Med Biol Res 40:1287–1304
de Bem AF, Farina M, Portella RL, Nogueira CW, Dinis TCP, Laranjinha JAN, Almeida LM, Rocha JBT (2008) Diphenyldiselenide, a simple glutathione peroxidase mimetic, inhibits human LDL oxidation in vitro. Atherosclerosis 201:92–100
Kade IJ, Borges VC, Savegnago L, Ibukun EO, Zeni G, Nogueira CW, Rocha JB (2009) Effect of oral administration of diphenyl diselenide on antioxidant status, and activity of delta aminolevulinic acid dehydratase and isoforms of lactate dehydrogenase, in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Cell Biol Toxicol 25:415–424
Posser T, de Paula MT, Franco JL, Leal RB, Rocha JBT (2010) Diphenyl diselenide induces apoptotic cell death and modulates ERK1/2 phosphorylation in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Arch Toxicol 117:645–651
Corte CLD, Soares FAA, Aschner M, Rocha JBT (2012) Diphenyl diselenide prevents methylmercury-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in rat liver slices. Tetrahedron 68:10437–10443
Avila DS, Benedetto A, Au C, Manarin F, Erikson K, Soares FA, Rocha JB, Aschner M (2012) Organotellurium and organoselenium compounds attenuate Mn-induced toxicity in Caenorhabditis elegans by preventing oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med 52:1903–1910
Benford DJ, Hanley AB, Bottrill K, Oehlschlager S, Balls M, Brance F, Castegnara JJ, Descotes J, Hemminiky K, Lindsay D, Schilter B (2000) Biomarkers as predictive tools in toxicity testing. The report and recommendations of ECVAM workshop 40. Alt Lab Anim 28:119–131
Baker KD, Thummel CS (2007) Diabetic larvae and obese flies-emerging studies of metabolism in Drosophila. Cell Metab 6:257–266
Jafari M (2010) Drosophila melanogaster as a model system for the evaluation of anti-aging compounds. Fly (Austin) 4:253–257
Riemensperger T, Issa AR, Pech U, Coulom H, Nguyễn MV, Cassar M, Jacquet M, Fiala A, Birman S (2013) A single dopamine pathway underlies progressive locomotor deficits in a Drosophila model of Parkinson disease. Cell Rep 5:952–960
Nguyen TB, Ida H, Shimamura M, Kitazawa D, Akao S, Yoshida H, Inoue YH, Yamaguchi M (2014) Role of SCOX in determination of Drosophila melanogaster lifespan. Am J Cancer Res 4:325–336
Adedara IA, Klimaczewski CV, Barbosa NB, Farombi EO, Souza DO, Rocha JBT (2015) Influence of diphenyl diselenide on chlorpyrifos-induced toxicity in Drosophila melanogaster. J Trace Elem Med Biol 32:52–59
Bonilla E, Contreras R, Medina-Leendertz S, Mora M, Villalobos V, Bravo Y (2012) Minocycline increases the life span and motor activity and decreases lipid peroxidation in manganese treated Drosophila melanogaster. Toxicology 294:50–53
Mora M, Bonilla E, Medina-Leendertz S, Bravo Y, Arcaya JL (2014) Minocycline increases the activity of superoxide dismutase and reduces the concentration of nitric oxide, hydrogen peroxide and mitochondrial malondialdehyde in manganese treated Drosophila melanogaster. Neurochem Res 39:1270–1278
Le Bourg E, Lints FA (1992) Hypergravity and aging in Drosophila melanogaster. 4. Climbing activity. Gerontology 38:59–64
Lowry OH, Rosenbrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V Jr, Feather-Stone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95
Pérez-Severiano F, Santamaría A, Pedraza-Chaverri J, Medina-Campos ON, Ríos C, Segovia J (2004) Increased formation of reactive oxygen species, but no changes in glutathione peroxidase activity, in striata of mice transgenic for the Huntington’s disease mutation. Neurochem Res 29:729–733
Puntel RL, Roos DH, Grotto D, Garcia SC, Nogueira CW, Rocha JB (2007) Antioxidant properties of Krebs cycle intermediates against malonate pro-oxidant activity in vitro: a comparative study using the colorimetric method and HPLC analysis to determine malondialdehyde in rat brain homogenates. Life Sci 81:51–62
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82:70–77
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Habig WH, Jakoby WB (1981) Assays for differentiation of glutathione S-transferases. Methods Enzymol 77:398–405
Abolaji OA, Kamdem JP, Lugokenski TH, Nascimento TK, Waczuk EP, Farombi EO, Loreto ÉL, Rocha JBT (2014) Involvement of oxidative stress in 4-vinylcyclohexene-induced toxicity in Drosophila melanogaster. Free Radic Biol Med 71:99–108
Aschner M, Dorman DC (2006) Manganese: pharmacokinetics and molecular mechanisms of brain uptake. Toxicol Rev 25:147–154
Evren V, Apaydin M, Khalilnezhad A, Erbas O, Taskiran D (2015) Protective effect of edaravone against manganese-induced toxicity in cultured rat astrocytes. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 40:563–567
Farina M, Avila DS, da Rocha JB, Aschner M (2013) Metals, oxidative stress and neurodegeneration: a focus on iron, manganese and mercury. Neurochem Int 62:575–594
Gorojod RM, Alaimo A, Porte Alcon S, Pomilio C, Saravia F, Kotler ML (2015) The autophagic-lysosomal pathway determines the fate of glial cells under manganese- induced oxidative stress conditions. Free Radic Biol Med 87:237–251
de Bem AF, de Lima Portella R, Farina M, Perottoni J, Paixão MW, Nogueira CW, Teixeira Rocha JB (2007) Low toxicity of diphenyldiselenide in rabbits: a long-term study. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 101:47–55
Barbosa NB, Rocha JB, Soares JC, Wondracek DC, Gonçalves JF, Schetinger MR, Nogueira CW (2008) Dietary diphenyl diselenide reduces the STZ-induced toxicity. Food Chem Toxicol 46:186–194
Day J, Damsma G, Fibiger HC (1991) Cholinergic activity in the rat hippocampus, cortex and striatum correlates with locomotor activity: an in vivo microdialysis study. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 38:723–729
Liapi C, Zarros A, Galanopoulou P, Theocharis S, Skandali N, Al-Humadi H, Anifantaki F, Gkrouzman E, Mellios Z, Tsakiris S (2008) Effects of short-term exposure to manganese on the adult rat brain antioxidant status and the activities of acetylcholinesterase, (Na+, K+)-ATPase and Mg2+-ATPase: modulation by l-cysteine. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 103:171–175
Chtourou Y, Fetoui H, Garoui EM, Zeghal N (2012) Improvement of cerebellum redox states and cholinergic functions contribute to the beneficial effects of silymarin against manganese-induced neurotoxicity. Neurochem Res 37:469–479
Lebda MA, El-Newwshy MS, El-Sayed YS (2012) Neurohepatic toxicity of subacute manganese chloride exposure and potential chemoprotective effects of lycopene. Neurotoxicology 33:98–104
Santos D, Milatovic D, Andrade V, Batoreu MC, Aschner M, Marreilha dos Santos AP (2012) The inhibitory effect of manganese on acetylcholinesterase activity enhances oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in the rat brain. Toxicology 292:90–98
Micic D, Micic J, Kaltzo I, Spatz M (1978) Effect of pentobarbital on the synaptosomal activity of acetylcholinesterase in Mongolian gerbils. Experientia 34:169–170
Vernadakis A, Rutledge CO (1973) Effects of ether and pentobarbital anaesthesia on the activities of brain acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase in young adult rats. J Neurochem 20:1503–1504
Santos D, Milatovic D, Andrade V, Batoreu MC, Aschner M, Marreilha dos Santos AP (2012) Comments to the Editor concerning the cholinergic response to manganese-induced neurotoxicity, based on the paper entitled “The inhibitory effect of manganese on acetylcholinesterase activity enhances oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in the brain” by Santos et al. Toxicology 298:59–60
Adedara IA, Rosemberg DB, Souza DO, Kamdem JP, Farombi EO, Aschner M, Rocha JBT (2015) Biochemical and behavioral deficits in lobster cockroach Nauphoeta cinerea model of methylmercury exposure. Toxicol Res 4:442–451
Adedara IA, Rosemberg DB, de Souza D, Farombi EO, Aschner M, Souza DO, Rocha JBT (2016) Neurobehavioral and biochemical changes in Nauphoeta cinerea following dietary exposure to chlorpyrifos. Pesticide Biochem Physiol. doi:10.1016/j.pestbp.2015.12.004
Milatovic D, Gupta RC, Aschner M (2006) Anticholinesterase toxicity and oxidative stress. Sci World J 6:295–310
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the TWAS-CNPq 2013 Postdoctoral Fellowship (FR number: 3240274252) awarded to IAA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adedara, I.A., Abolaji, A.O., Rocha, J.B.T. et al. Diphenyl Diselenide Protects Against Mortality, Locomotor Deficits and Oxidative Stress in Drosophila melanogaster Model of Manganese-Induced Neurotoxicity. Neurochem Res 41, 1430–1438 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-1852-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-1852-x