Abstract
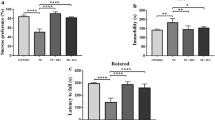
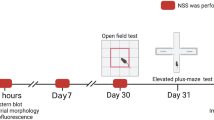
Stroke is one of the main threats to the public health worldwide. Metformin, an anti-diabetic drug, is an activator of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). Metformin plays an important role on improving behavior in neurodegenerative diseases through diverse pathways. In the current study we aimed to investigate the probable effects of metformin on anxiety and autophagy pathway in global cerebral ischemia. Rats were divided into seven groups; Sham, ischemia (I/R), metformin (met), compound c (CC), CC+ischemia, met+ischemia, met+CC+ischemia. Metformin was pretreated for 2 weeks and CC administrated half an hour before global cerebral ischemia. Blood glucose, body weight, sensorimotor scores, elevated plus maze and open field test were evaluated after ischemia. Autophagy related factors were measured by Western blot and immunofluorescent assay in hippocampus of rats. Based on our results, pretreatment of rats by metformin improved sensory motor signs, anxiolytic behavior and locomotion in ischemic rats. CC injection in I/R rats attenuated the therapeutic effects of metformin. Autophagy factors such as light chain 3B, Atg7, Atg5-12 and beclin-1 decreased in ischemic rats compared to the sham group (P < 0.001 in all proteins). Level of autophagic factors increased in metformin pretreated rats compared to global cerebral ischemia (P < 0.001 in all proteins). These data indicated that the beneficial role of metformin in behavior and autophagy flux mediates via AMPK. Our results recommended that metformin therapy could improve psychological disorders and movement disability following I/R and profound understanding of AMPK-dependent autophagy would enhance its development as a promising target for intracellular pathway.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appenrodt E, Schnabel R, Schwarzberg H (1998) Vasopressin administration modulates anxiety-related behavior in rats. Physiol Behav 64:543–547
Ashabi G, Ahmadiani A, Abdi A, Abraki SB, Khodagholi F (2013) Time course study of Abeta formation and neurite outgrowth disruption in differentiated human neuroblastoma cells exposed to H2O2: protective role of autophagy. Toxicol In Vitro 27:1780–1788
Ashabi G, Khalaj L, Khodagholi F, Goudarzvand M, Sarkaki (2014a) A pre-treatment with metformin activates Nrf2 antioxidant pathways and inhibits inflammatory responses through induction of AMPK after transient global cerebral ischemia. Metab Brain Dis
Ashabi G, Khodagholi F, Khalaj L, Goudarzvand M, Nasiri M (2014b) Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase by metformin protects against global cerebral ischemia in male rats: interference of AMPK/PGC-1alpha pathway. Metab Brain Dis 29:47–58
Bowen SE, Wiley JL, Balster RL (1996) The effects of abused inhalants on mouse behavior in an elevated plus-maze. Eur J Pharmacol 312:131–136
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Brown ES, Rush AJ, McEwen BS (1999) Hippocampal remodeling and damage by corticosteroids: implications for mood disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 21:474–484
Calvert JW, Gundewar S, Jha S, Greer JJ, Bestermann WH, Tian R, Lefer DJ (2008) Acute metformin therapy confers cardioprotection against myocardial infarction via AMPK-eNOS-mediated signaling. Diabetes 57:696–705
Carchman EH, Whelan S, Loughran P, Mollen K, Stratamirovic S, Shiva S, Rosengart MR, Zuckerbraun BS (2013) Experimental sepsis-induced mitochondrial biogenesis is dependent on autophagy, TLR4, and TLR9 signaling in liver. FASEB J 27:4703–4711
Chandler MJ, DeLeo J, Carney JM (1985) An unanesthetized-gerbil model of cerebral ischemia-induced behavioral changes. J Pharmacol Methods 14:137–146
Espejo EF (1997) Effects of weekly or daily exposure to the elevated plus-maze in male mice. Behav Brain Res 87:233–238
Forslin Aronsson S, Spulber S, Popescu LM, Winblad B, Post C, Oprica M, Schultzberg M (2006) alpha-Melanocyte-stimulating hormone is neuroprotective in rat global cerebral ischemia. Neuropeptides 40:65–75
Gage WH, Sleik RJ, Polych MA, McKenzie NC, Brown LA (2003) The allocation of attention during locomotion is altered by anxiety. Exp Brain Res 150:385–394
Garcia JH, Wagner S, Liu KF, Hu XJ (1995) Neurological deficit and extent of neuronal necrosis attributable to middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Statistical validation. Stroke 26:627–634, discussion 635
Girbovan C, Morin L, Plamondon H (2012) Repeated resveratrol administration confers lasting protection against neuronal damage but induces dose-related alterations of behavioral impairments after global ischemia. Behav Pharmacol 23:1–13
Grishchuk Y, Ginet V, Truttmann AC, Clarke PG, Puyal J (2011) Beclin 1-independent autophagy contributes to apoptosis in cortical neurons. Autophagy 7:1115–1131
Guo Y, Yu W, Sun D, Wang J, Li C, Zhang R, Babcock SA, Li Y, Liu M, Ma M, Shen M, Zeng C, Li N, He W, Zou Q, Zhang Y, Wang H (2014) A novel protective mechanism for mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH2) in type i diabetes-induced cardiac dysfunction: Role of AMPK-regulated autophagy. Biochim Biophys Acta 1852:319–331
Hadley G, Papadakis M, Buchan AM (2014) A method of inducing global cerebral ischemia. Methods Mol Biol 1135:111–120
Jiang T, Yu JT, Zhu XC, Wang HF, Tan MS, Cao L, Zhang QQ, Gao L, Shi JQ, Zhang YD, Tan L (2014) Acute metformin preconditioning confers neuroprotection against focal cerebral ischaemia by pre-activation of AMPK-dependent autophagy. Br J Pharmacol 171:3146–3157
Khang R, Park C, Shin JH (2014) The biguanide metformin alters phosphoproteomic profiling in mouse brain. Neurosci Lett 579:145–150
Krause GS, Kumar K, White BC, Aust SD, Wiegenstein JG (1986) Ischemia, resuscitation, and reperfusion: mechanisms of tissue injury and prospects for protection. Am Heart J 111:768–780
Lennox R, Porter DW, Flatt PR, Holscher C, Irwin N, Gault VA (2014) Comparison of the independent and combined effects of sub-chronic therapy with metformin and a stable GLP-1 receptor agonist on cognitive function, hippocampal synaptic plasticity and metabolic control in high-fat fed mice. Neuropharmacology 86:22–30
Li J, Benashski SE, Venna VR, McCullough LD (2010) Effects of metformin in experimental stroke. Stroke 41:2645–2652
Li W, Huang R, Shetty RA, Thangthaeng N, Liu R, Chen Z, Sumien N, Rutledge M, Dillon GH, Yuan F, Forster MJ, Simpkins JW, Yang SH (2013) Transient focal cerebral ischemia induces long-term cognitive function deficit in an experimental ischemic stroke model. Neurobiol Dis 59:18–25
Liu Y, Tang G, Li Y, Wang Y, Chen X, Gu X, Zhang Z, Yang GY (2014) Metformin attenuates blood–brain barrier disruption in mice following middle cerebral artery occlusion. J Neuroinflammation 11:177
Ma TC, Buescher JL, Oatis B, Funk JA, Nash AJ, Carrier RL, Hoyt KR (2007) Metformin therapy in a transgenic mouse model of Huntington’s disease. Neurosci Lett 411:98–103
Meijer AJ, Codogno P (2007) AMP-activated protein kinase and autophagy. Autophagy 3:238–240
Menard J, Treit D (1998) The septum and the hippocampus differentially mediate anxiolytic effects of R(+)-8-OH-DPAT. Behav Pharmacol 9:93–101
Miller JL, Linville TD, Dykens EM (2013) Effects of metformin in children and adolescents with Prader-Willi syndrome and early-onset morbid obesity: a pilot study. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 27:23–29
Milot MR, Plamondon H (2009) Time-dependent effects of global cerebral ischemia on anxiety, locomotion, and habituation in rats. Behav Brain Res 200:173–180
Mrsulja BB, Mrsulja BJ, Ito U, Walker JT Jr, Spatz M, Klatzo I (1975) Experimental cerebral ischemia in Mongolian gerbils. II. Changes in carbohydrates. Acta Neuropathol 33:91–103
Niimura M, Takagi N, Takagi K, Mizutani R, Ishihara N, Matsumoto K, Funakoshi H, Nakamura T, Takeo S (2006) Prevention of apoptosis-inducing factor translocation is a possible mechanism for protective effects of hepatocyte growth factor against neuronal cell death in the hippocampus after transient forebrain ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26:1354–1365
Paiva MA, Goncalves LM, Providencia LA, Davidson SM, Yellon DM, Mocanu MM (2010) Transitory activation of AMPK at reperfusion protects the ischaemic-reperfused rat myocardium against infarction. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 24:25–32
Paiva MA, Rutter-Locher Z, Goncalves LM, Providencia LA, Davidson SM, Yellon DM, Mocanu MM (2011) Enhancing AMPK activation during ischemia protects the diabetic heart against reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 300:H2123–H2134
Patil SP, Jain PD, Ghumatkar PJ, Tambe R, Sathaye S (2014) Neuroprotective effect of metformin in MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease in mice. Neuroscience 277:747–754
Paul SL, Srikanth VK, Thrift AG (2007) The large and growing burden of stroke. Curr Drug Targets 8:786–793
Pietrelli A, Lopez-Costa J, Goni R, Brusco A, Basso N (2011) Aerobic exercise prevents age-dependent cognitive decline and reduces anxiety-related behaviors in middle-aged and old rats. Neuroscience 202:252–266
Pillow BH, Flavell JH (1985) Intellectual realism: the role of children’s interpretations of pictures and perceptual verbs. Child Dev 56:664–670
Pintana H, Apaijai N, Pratchayasakul W, Chattipakorn N, Chattipakorn SC (2012) Effects of metformin on learning and memory behaviors and brain mitochondrial functions in high fat diet induced insulin resistant rats. Life Sci 91:409–414
Poels J, Spasic MR, Callaerts P, Norga KK (2009) Expanding roles for AMP-activated protein kinase in neuronal survival and autophagy. Bioessays 31:944–952
Polajnar M, Zerovnik E (2014) Impaired autophagy: a link between neurodegenerative and neuropsychiatric diseases. J Cell Mol Med 18:1705–1711
Prakash R, Li W, Qu Z, Johnson MA, Fagan SC, Ergul A (2013) Vascularization pattern after ischemic stroke is different in control versus diabetic rats: relevance to stroke recovery. Stroke 44:2875–2882
Preitner F, Muzzin P, Revelli JP, Seydoux J, Galitzky J, Berlan M, Lafontan M, Giacobino JP (1998) Metabolic response to various beta-adrenoceptor agonists in beta3-adrenoceptor knockout mice: evidence for a new beta-adrenergic receptor in brown adipose tissue. Br J Pharmacol 124:1684–1688
Pulsinelli WA, Brierley JB (1979) A new model of bilateral hemispheric ischemia in the unanesthetized rat. Stroke 10:267–272
Rami A, Kogel D (2008) Apoptosis meets autophagy-like cell death in the ischemic penumbra: Two sides of the same coin? Autophagy 4:422–426
Rodriguez-Navarro JA, Rodriguez L, Casarejos MJ, Solano RM, Gomez A, Perucho J, Cuervo AM, Garcia de Yebenes J, Mena MA (2010) Trehalose ameliorates dopaminergic and tau pathology in parkin deleted/tau overexpressing mice through autophagy activation. Neurobiol Dis 39:423–438
Sarti C, Pantoni L, Bartolini L, Inzitari D (2002) Persistent impairment of gait performances and working memory after bilateral common carotid artery occlusion in the adult Wistar rat. Behav Brain Res 136:13–20
Shaerzadeh F, Motamedi F, Minai-Tehrani D, Khodagholi F (2014) Monitoring of neuronal loss in the hippocampus of Abeta-injected rat: autophagy, mitophagy, and mitochondrial biogenesis stand against apoptosis. Neuromol Med 16:175–190
Shehata M, Inokuchi K (2014) Does autophagy work in synaptic plasticity and memory? Rev Neurosci 25:543–557
Skutella T, Probst JC, Renner U, Holsboer F, Behl C (1998) Corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor (type I) antisense targeting reduces anxiety. Neuroscience 85:795–805
Spencer SJ, Auer RN, Pittman QJ (2006) Rat neonatal immune challenge alters adult responses to cerebral ischaemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26:456–467
Takahashi N, Shibata R, Ouchi N, Sugimoto M, Murohara T, Komori K (2015) Metformin stimulates ischemia-induced revascularization through an eNOS dependent pathway in the ischemic hindlimb mice model. J Vasc Surg 61:489–496
Tang P, Hou H, Zhang L, Lan X, Mao Z, Liu D, He C, Du H (2013) Autophagy reduces neuronal damage and promotes locomotor recovery via inhibition of apoptosis after spinal cord injury in rats. Mol Neurobiol 49:276–287
Taylor TN, Davis PH, Torner JC, Holmes J, Meyer JW, Jacobson MF (1996) Lifetime cost of stroke in the United States. Stroke 27:1459–1466
Viollet B, Guigas B, Sanz Garcia N, Leclerc J, Foretz M, Andreelli F (2011) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of metformin: an overview. Clin Sci (Lond) 122:253–270
Wang D, Corbett D (1990) Cerebral ischemia, locomotor activity and spatial mapping. Brain Res 533:78–82
Wang P, Guan YF, Du H, Zhai QW, Su DF, Miao CY (2011) Induction of autophagy contributes to the neuroprotection of nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase in cerebral ischemia. Autophagy 8:77–87
Wang PR, Wang JS, Zhang C, Song XF, Tian N, Kong LY (2013) Huang-Lian-Jie-Du-Decotion induced protective autophagy against the injury of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion via MAPK-mTOR signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol 149:270–280
Wen YD, Sheng R, Zhang LS, Han R, Zhang X, Zhang XD, Han F, Fukunaga K, Qin ZH (2008) Neuronal injury in rat model of permanent focal cerebral ischemia is associated with activation of autophagic and lysosomal pathways. Autophagy 4:762–769
Winter B, Juckel G, Viktorov I, Katchanov J, Gietz A, Sohr R, Balkaya M, Hortnagl H, Endres M (2005) Anxious and hyperactive phenotype following brief ischemic episodes in mice. Biol Psychiatry 57:1166–1175
Xia DY, Li W, Qian HR, Yao S, Liu JG, Qi XK (2013) Ischemia preconditioning is neuroprotective in a rat cerebral ischemic injury model through autophagy activation and apoptosis inhibition. Braz J Med Biol Res 46:580–588
Yu OH, Yin H, Azoulay L (2015) The combination of DPP-4 inhibitors versus sulfonylureas with metformin after failure of first-line treatment in the risk for major cardiovascular events and death. Can J Diabetes. doi:10.1016/j.jcjd.2015.02.002
Zhao Z, Han F, Yang S, Wu J, Zhan W (2014) Oxamate-mediated inhibition of lactate dehydrogenase induces protective autophagy in gastric cancer cells: involvement of the Akt-mTOR signaling pathway. Cancer Lett 358:17–26
Acknowledgments
This paper was extracted as a part of Ghorbangol Ashabi’s Ph.D thesis. The study was financially supported by research affairs of Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences (grant No. APRC-93-05) and was performed in Ahvaz Physiology Research Center. Authors have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarkaki, A., Farbood, Y., Badavi, M. et al. Metformin improves anxiety-like behaviors through AMPK-dependent regulation of autophagy following transient forebrain ischemia. Metab Brain Dis 30, 1139–1150 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-015-9677-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-015-9677-x