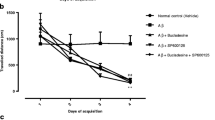
Abstract
Neurodegenerative disorders are generally characterized by abnormal aggregation and deposition of specific proteins. Amyloid beta (Aβ)-associated neurodegenerative disorder is characterized by an oxidative damage that, in turn, leads to some behavioral changes before the establishment of dementia such as depression and anxiety. In the current study, we investigated the effect of heat shock protein 90 inhibitor geldanamycin (GA) administration 24 h before Aβ injection. In our experiment, 7 days after Aβ injection, elevated plus maze and forced swimming test were conducted to assess anxiety and depression-like behaviors. Levels of autophagy markers and malondialdehyde (MDA) and also activity of catalase in the hippocampus of rats were evaluated. Our behavioral analyses demonstrated that GA pretreatment can significantly decrease anxiety- and depression-like behaviors in Aβ-injected rats. Also, levels of autophagy markers including Atg12, Atg7, and LC3-II increased, while MDA level decreased and the activity of catalase increased in rats pretreated with GA compared to Aβ-injected rats. Thus, we assumed that GA, at least in part, ameliorated Aβ-mediated anxiety and depression by inducing autophagy and improving antioxidant defense system.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Barth S, Glick D, Macleod KF (2010) Autophagy: assays and artifacts. J Pathol 221(2):117–124
Bilici M, Efe H, Köroğlu MA, Uydu HA, Bekaroğlu M, Değer O (2001) Antioxidative enzyme activities and lipid peroxidation in major depression: alterations by antidepressant treatments. J Affect Disord 64(1):43–51
Borsini F, Meli A (1988) Is the forced swimming test a suitable model for revealing antidepressant activity? Psychopharmacology 94(2):147–160
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72(1):248–254
Crews F, Nixon K, Kim D, Joseph J, Shukitt‐Hale B, Qin L, Zou J (2006) BHT blocks NF‐κB activation and ethanol‐induced brain damage. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 30(11):1938–1949
Dawson GR, Tricklebank MD (1995) Use of the elevated plus maze in the search for novel anxiolytic agents. Trends Pharmacol Sci 16(2):33–36
Dou F, Netzer WJ, Tanemura K, Li F, Hartl FU, Takashima A, Xu H (2003) Chaperones increase association of tau protein with microtubules. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100(2):721–726
Draper HH, Hadley M (1989) Malondialdehyde determination as index of lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol 186:421–431
Einat H, Yuan P, Manji HK (2005) Increased anxiety-like behaviors and mitochondrial dysfunction in mice with targeted mutation of the Bcl-2 gene: further support for the involvement of mitochondrial function in anxiety disorders. Behav Brain Res 165(2):172–180
Eren İ, Nazıroğlu M, Demirdaş A (2007) Protective effects of lamotrigine, aripiprazole and escitalopram on depression-induced oxidative stress in rat brain. Neurochem Res 32(7):1188–1195
Hara T, Nakamura K, Matsui M, Yamamoto A, Nakahara Y, Suzuki-Migishima R, Mizushima N (2006) Suppression of basal autophagy in neural cells causes neurodegenerative disease in mice. Nature 441(7095):885–889
Harkany T, O’Mahony S, Keijser J, Kelly JP, Kónya C, Borostyánkői ZA, Luiten PG (2001) β-Amyloid (1-42)-induced cholinergic lesions in rat nucleus basalis bidirectionally modulate serotonergic innervation of the basal forebrain and cerebral cortex. Neurobiol Dis 8(4):667–678
He C, Klionsky DJ (2006) Autophagy and neurodegeneration. ACS Chem Biol 1(4):211–213
Kadiiska MB, Gladen BC, Baird DD, Germolec D, Graham LB, Parker CE, Barrett JC (2005) Biomarkers of oxidative stress study ii: are oxidation products of lipids, proteins, and DNA markers of CCl 4 poisoning? Free Radic Biol Med 38(6):698–710
Kamper EF, Chatzigeorgiou A, Tsimpoukidi O, Kamper M, Dalla C, Pitychoutis PΜ, Papadopoulou-Daifoti Z (2009) Sex differences in oxidant/antioxidant balance under a chronic mild stress regime. Physiol Behav 98(1):215–222
Kara NZ, Toker L, Agam G, Anderson GW, Belmaker RH, Einat H (2013) Trehalose induced antidepressant-like effects and autophagy enhancement in mice. Psychopharmacology 229(2):367–375
Kelly BL, Ferreira A (2006) β-Amyloid-induced dynamin 1 degradation is mediated by N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in hippocampal neurons. J Biol Chem 281(38):28079–28089
Khalifeh S, Oryan S, Digaleh H, Shaerzadeh F, Khodagholi F, Maghsoudi N, Zarrindast MR (2015) Involvement of Nrf2 in development of anxiety-like behavior by linking Bcl2 to oxidative phosphorylation: estimation in rat hippocampus, amygdala, and prefrontal cortex. J Mol Neurosci 55(2):492–499
Kundu M, Thompson CB (2008) Autophagy: basic principles and relevance to disease. Annu Rev Pathmechdis Mech Dis 3:427–455
Leliveld SR, Bader V, Hendriks P, Prikulis I, Sajnani G, Requena JR, Korth C (2008) Insolubility of disrupted-in-schizophrenia 1 disrupts oligomer-dependent interactions with nuclear distribution element 1 and is associated with sporadic mental disease. J Neurosci 28(15):3839–3845
Lemasters JJ (2005) Selective mitochondrial autophagy, or mitophagy, as a targeted defense against oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and aging. Rejuvenation Res 8(1):3–5
Lu A, Ran R, Parmentier‐Batteur S, Nee A, Sharp FR (2002) Geldanamycin induces heat shock proteins in brain and protects against focal cerebral ischemia. J Neurochem 81(2):355–364
Maccioni RB, Muñoz JP, Barbeito L (2001) The molecular bases of Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. Arch Med Res 32(5):367–381
McLean PJ, Klucken J, Shin Y, Hyman BT (2004) Geldanamycin induces Hsp70 and prevents α-synuclein aggregation and toxicity in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 321(3):665–669
Merenlender-Wagner A, Malishkevich A, Shemer Z, Udawela M, Gibbons A, Scarr E, Gozes I (2013) Autophagy has a key role in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatr
Mirakhur A, Craig D, Hart DJ, McLlroy SP, Passmore AP (2004) Behavioural and psychological syndromes in Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Geriatr Psychiatr 19(11):1035–1039
Nakatogawa H, Suzuki K, Kamada Y, Ohsumi Y (2009) Dynamics and diversity in autophagy mechanisms: lessons from yeast. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10(7):458–467
Namekawa Y, Baba H, Maeshima H, Nakano Y, Satomura E, Takebayashi N, Arai H (2013) Heterogeneity of elderly depression: increased risk of Alzheimer’s disease and Aβ protein metabolism. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatr 43:203–208
Paxinos G, Watson CR (2007) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Elsevier Academic Press, San Diego
Pellow S, Chopin P, File SE, Briley M (1985) Validation of open: closed arm entries in an elevated plus-maze as a measure of anxiety in the rat. J Neurosci Methods 14(3):149–167
Pickford F, Masliah E, Britschgi M, Lucin K, Narasimhan R, Jaeger PA, Wyss-Coray T (2008) The autophagy-related protein beclin 1 shows reduced expression in early Alzheimer disease and regulates amyloid β accumulation in mice. J Clin Invest 118(6):2190
Pomara N, Bruno D, Sarreal AS, Hernando RT, Nierenberg J, Petkova E, Blennow K (2014) Lower CSF amyloid beta peptides and higher F2-isoprostanes in cognitively intact elderly individuals with major depressive disorder. Am J Psychiatr
Porsolt RD, Le Pichon M, Jalfre ML (1977) Depression: a new animal model sensitive to antidepressant treatments. Nature 266(5604):730–732
Potter GG, Steffens DC (2007) Contribution of depression to cognitive impairment and dementia in older adults. Neurologist 13(3):105–117
Rodrigues R, Petersen RB, Perry G (2014) Parallels between major depressive disorder and Alzheimer’s disease: role of oxidative stress and genetic vulnerability. Cell Mol Neurobiol 34(7):925–949
Salam JN, Fox JH, DeTroy EM, Guignon MH, Wohl DF, Falls WA (2009) Voluntary exercise in C57 mice is anxiolytic across several measures of anxiety. Behav Brain Res 197(1):31–40
Sarkaki A, Farbood Y, Badavi M, Khalaj L, Khodagholi F, Ashabi G (2015) Metformin improves anxiety-like behaviors through AMPK-dependent regulation of autophagy following transient forebrain ischemia. Metab Brain Dis 1–12
Sarkar S, Korolchuk VI, Renna M, Imarisio S, Fleming A, Williams A, Rubinsztein DC (2011) Complex inhibitory effects of nitric oxide on autophagy. Mol Cell 43(1):19–32
Shaerzadeh F, Motamedi F, Minai-Tehrani D, Khodagholi F (2014) Monitoring of neuronal loss in the hippocampus of Aβ-injected rat: autophagy, mitophagy, and mitochondrial biogenesis stand against apoptosis. Neruomol Med 16(1):175–190
Shankar GM, Li S, Mehta TH, Garcia-Munoz A, Shepardson NE, Smith I, Selkoe DJ (2008) Amyloid-β protein dimers isolated directly from Alzheimer’s brains impair synaptic plasticity and memory. Nat Med 14(8):837–842
Shehata M, Matsumura H, Okubo-Suzuki R, Ohkawa N, Inokuchi K (2012) Neuronal stimulation induces autophagy in hippocampal neurons that is involved in AMPA receptor degradation after chemical long-term depression. J Neurosci 32(30):10413–10422
Shen HY, He JC, Wang Y, Huang QY, Chen JF (2005) Geldanamycin induces heat shock protein 70 and protects against MPTP-induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity in mice. J Biol Chem 280(48):39962–39969
Stebbins CE, Russo AA, Schneider C, Rosen N, Hartl FU, Pavletich NP (1997) Crystal structure of an Hsp90–geldanamycin complex: targeting of a protein chaperone by an antitumor agent. Cell 89(2):239–250
Sun X, Steffens DC, Au R, Folstein M, Summergrad P, Yee J, Qiu WQ (2008) Amyloid-associated depression: a prodromal depression of Alzheimer disease? Arch Gen Psychiatry 65(5):542–550
Taylor JP, Hardy J, Fischbeck KH (2002) Toxic proteins in neurodegenerative disease. Science 296(5575):1991–1995
Teri L, Ferretti LE, Gibbons LE, Logsdon RG, McCurry SM, Kukull WA, Larson EB (1999) Anxiety in Alzheimer’s disease: prevalence and comorbidity. J Gerontol A: Biol Med Sci 54(7):M348–M352
Wong E, Cuervo AM (2010) Autophagy gone awry in neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Neurosci 13(7):805–811
Zare N, Motamedi F, Digaleh H, Khodagholi F, Maghsoudi N (2015) Collaboration of geldanamycin-activated P70S6K and Hsp70 against beta-amyloid-induced hippocampal apoptosis: an approach to long-term memory and learning. Cell Stress Chaperones 20(2):309–319
Acknowledgments
This work is part of the PhD student’s thesis of N. Zare at the Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of Interest
The author declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zare, N., Khalifeh, S., Khodagholi, F. et al. Geldanamycin Reduces Aβ-Associated Anxiety and Depression, Concurrent with Autophagy Provocation. J Mol Neurosci 57, 317–324 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-015-0619-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-015-0619-1