Abstract
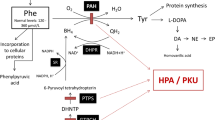
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is a disorder caused by a deficiency in phenylalanine hydroxylase activity, which converts phenylalanine (Phe) to tyrosine, leading to hyperphenylalaninemia (HPA) with accumulation of Phe in tissues of patients. The neuropathophysiology mechanism of disease remains unknown. However, recently the involvement of oxidative stress with decreased glutathione levels in PKU has been reported. Intracellular glutathione (GSH) levels may be maintained by the antioxidant action of lipoic acid (LA). The aim of this study was to evaluate the activity of the enzymes involved in the metabolism and function of GSH, such as glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px), glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD), glutathione reductase (GR), glutamate-cysteine ligase (GCL), glutathione-S-transferase (GST) and GSH content in brain and liver of young rats subjected to a chemically induced model of HPA and the effect of LA for a week. In brain, the administration of Phe reduced the activity of the GSH-Px, GR and G6PD and LA prevented these effects totally or partially. GCL activity was increased by HPA and was not affect by LA antioxidant treatment. GST activity did not differ between groups. GSH content was increased by LA and decreased by HPA treatment in brain samples. Considering the liver, all parameters analyzed were increased in studied HPA animals and LA was able to hinder some effects except for the GCL, GST enzymes and GSH content. These results suggested that HPA model alter the metabolism of GSH in rat brain and liver, which may have an important role in the maintenance of GSH function in PKU although liver is not a directly affected organ in this disease. So, an antioxidant therapy with LA may be useful in the treatment of oxidative stress in HPA.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdin AA, Sarhan NI (2011) Intervention of mitochondrial dysfunction-oxidative stress-dependent apoptosis as a possible neuroprotective mechanism of α-lipoic acid against rotenone-induced parkinsonism and l-dopa toxicity. Neurosci Res 71(4):387–395
Artuch R, Colome C, Vilaseca MA et al (2001) Plasma phenylalanine is associated with decreased serum ubiquinone-10 concentrations in phenylketonuria. J Inherit Metab Dis 24:359–366
Aoyama K, Watabe M, Nakaki T (2008) Regulation of Neuronal Glutathione Synthesis. J Pharmacol Sci 108:227–238
Berti SL, Nasi GM, Garcia C, de Castro FL, Nunes ML, Rojas DB, Moraes TB, Dutra-Filho CS, Wannmacher CMD (2012) Pyruvate and creatine prevent oxidative stress and behavioral alterations caused by phenylalanine administration into hippocampus of rats. Metab Brain Dis 27:79–89
Bilska A, Włodek L (2005) Lipoic acid - the drug of the future? Pharmacol Rep 57(5):570–577
Browne RW, Armstrong D (1998) Reduced glutathione and glutathione disulfide. Methods Mol Biol 108:347–352
Brigelius-Flohe´ R (1999) Tissue-specific functions of individual glutathione peroxidases. Free Radic Biol Med 27:951–965
Calberg I, Manervik B (1985) Glutathione Reductase. Methods Enzymol 113:484–490
Chung PM, Cappel RE, Gilbert HF (1991) Inhibition of glutathione disulfide reductase by glutathione. Arch Biochem Biophys 288(1):48–53
de Souza GF, Saldanha GB, de Freitas RM (2010) Lipoic acid increases glutathione peroxidase, Na+, K + -atpase and acetylcholinesterase activities in rat hippocampus after pilocarpine-induced seizures? Arq Neuropsiquiatr 68(4):586–591
Diamond A, Ciaramitaro V, Donner E, Djali S, Robinson MB (1994) An Animal Model of Early-treated PKU. J Neurosci 14(5):3072–3082
Dickinson DA, Forman HJ (2002) Cellular glutathione and thiols metabolism. Biochem Pharmacol 64:1019–1026
Dickinson DA, Moellering DR, Iles KE et al (2003) Cytoprotection against oxidative stress and the regulation of glutathione synthesis. Biol Chem 384:527–537
dos Reis EA, Rieger E, de Souza SS, Rasia-Filho AA, Wannmacher CMD (2013) Effects of a co-treatment with pyruvate and creatine on dendritic spines in rat hippocampus and posterodorsal medial amygdala in a phenylketonuria animal model. Metab Brain Dis 28:509–517
Ercal N, Aykin-Burns N, Gurer-Orhan H, Mcdonald JD (2002) Oxidative stress in a phenylketonuria animal model. Free Radic Biol Med 32:906–911
Favilli F, Marraccini P, Iantomasi T, Vincenzini MT (1997) Effect of orally administered glutathione on glutathione levels in some organs of rats: role of specific transporters. Br J Nutr 78:293–300
Fonseca RR, Johnson WE, O’Brien SJ et al (2010) Molecular evolution and the role of oxidative stress in the expansion and functional diversification of cytosolic glutathione transferases. BMC Evol Biol 10:281
Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jacoby WB (1974) Glutathione S-Transferase: the first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem 249:7130–7139
Hagen TM, Ingersoll RT, Lykkesfeldt J et al (1999) (R)-α-lipoic acid-supplemented old rats have improved mitochondrial function, decreased oxidative damage, and increased metabolic rate. Faseb J 13:411–418
Huerta-Olvera SG, Macías-Barragán J, Ramos-Márquez ME et al (2010) Alpha-lipoic acid regulates heme oxygenase gene expression and nuclear Nrf2 activation as a mechanism of protection against arsenic exposure in HepG2 cells. Envir Toxicol Pharmacol 29:144–149
Järvinen K, Soini Y, Kinnula VL (2003) γ-Glutamylcysteine Synthetase in Lung Cancer. Effect on Cell Viability. Methods Mol Med 74:211–222
Johnson WM, Wilson-Delfosse AL, Mieyal JJ (2012) Dysregulation of Glutathione Homeostasis in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Nutrients 4:1399–1440
Kienzle-Hagen ME, Pederzolli CD, Sgaravatti AM et al (2002) Experimental hyperphenylalaninemia provokes oxidative stress in rat brain. Biochim Biophys Acta 1586(3):344–352
Kretzschmar M (1996) Regulation of hepatic glutathione metabolism and its role in hepatotoxicity. Exp Toxic Pathol 48:439–446
Leong SF, Clark JB (1984) Regional enzyme development in rat brain. Enzymes associated with glucose utilization. Biochem J 218:131–138
Lissi EA, Cáceres T, Videla LA (1986) Visible chemiluminescence from rat brain homogenates undergoing autoxidation. I. Effect of additives and products accumulation. Free Radic Biol Med 2(1):63–69
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL et al (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Lu SC (1999) Regulation of hepatic glutathione synthesis: current concepts and controversies. FASEB J 13(10):1169–1183
Lu SC (2009) Regulation of glutathione synthesis. Mol Aspects Med 30(1–2):42–59
Luttges MW, Gerren RA (1979) Postnatal alpha-methylphenylalanine treatment effects on adult mouse locomotor activity and avoidance learning. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 11(5):493–498
Mazzola PN, Karikas GA, Schulpis KH, Dutra-Filho CS (2013) Antioxidant treatment strategies for hyperphenylalaninemia. Metab Brain Dis. doi:10.1007/s11011-013-9414-2
Ookhtens O, Kaplowitz N (1998) Role of the liver in intergorgan homeostasis of glutathione and cyst(e)ine. Semin Liver Dis 18:313–329
Packer L, Tritschler HJ, Wessel K (1997) Neuroprotection by the metabolic antioxidant α-lipoic acid. Free Rad Biol and Med 22:359–378
Pietz J (1998) Neurological aspects of adult phenylketonuria. Curr Opin Neurol 11:679–688
Reed MC, Thomas RL, Pavisic J, James SJ, Ulrich CM, Nijhon HF (2008) A mathematical model of glutathione metabolism. Theor Biol Med Model 5:8. doi:10.1186/1742-4682-5-8
Samuel S, Kathirvel R, Jayavelu T, Chinnakkannu P (2005) Protein oxidative damage in arsenic induced rat brain: influence of DL-α-lipoic acid. Toxicol Lett 155:27–34
Sanayama Y, Nagasaka H, Takayanagi M et al (2011) Experimental evidence that phenylalanine is strongly associated to oxidative stress in adolescents and adults with phenylketonuria. Mol Genet Metab 103(3):220–225
Satoh T, McKercher SR, Lipton SA (2013) NrF2/ARE-mediated antioxidant actions of pro-electrophilic drugs. Free Radic Biol Med. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.07.022
Scriver CR, Kaufman S (2001) Hyperphenylalaninemia: phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D (eds) The metabolic and molecular bases of inherited disease. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 1667–1724
Seybolt SEJ (2010) Is it time to reassess alpha lipoic acid and niacinamide therapy in schizophrenia? Med Hypotheses 75(6):572–575
Singh S, Anand A, Srivastava PK (2012) Regulation and properties of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase: A review. Int J Plant Physiol Biochem 4(1):1–19
Sirtori LR, Dutra-Filho CS, Fitarelli D et al (2005) Oxidative stress in patients with phenylketonuria. Biochim Biophys Acta 1740(1):68–73
Sitta A, Barschak AG, Deon M et al (2006) Investigation of oxidative stress parameters in treated phenylketonuric patients. Metab Brain Dis 21(4):287–296
Sitta A, Barschak AG, Deon M et al (2009) Effect of short- and long-term exposition to high phenylalanine blood levels on oxidative damage in phenylketonuric patients. Int J Dev Neurosci 27:243–247
Sitta A, Vanzin CS, Biancini GB, Manfredini V, de Oliveira AB, Wayhs CA, Ribas GO, Giugliani L, Schwartz IV, Bohrer D, Garcia SC, Wajner M, Vargas CR (2011) Evidence that Lcarnitine and selenium supplementation reduces oxidative stress in phenylketonuric patients. Cell Mol Neurobiol 31(3):429–436
Suh JH, Shenvi SV, Dixon BM et al (2004) Decline in transcriptional activity of Nrf2 causes age related loss of glutathione synthesis, which is reversible with lipoic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci 101:3381–3386
Tateishi N, Higashi T, Naruse A, Nakashima K, Shiozaki H (1977) Rat liver glutathione: possible role as a reservoir of cysteine. J Nutr 107:51–60
Townsend DM, Manevich Y, He L, Hutchens S, Pazoles CJ, Tew KD (2008) Novel Role for Glutathione S-Transferase: Regulator of protein S-glutathionylation following oxidative and nitrosative stress. J Biol Chem 284(1):436–445
Valdovinos-Flores C, Gosenbatt ME (2012) The role of amino acids transporters in GSH synthesis in the blood brain barrier and central nervous system. Neurochem Intern 61:405–414
Vargas CR, Wajner M, Sitta A (2011) Oxidative stress in phenylketonuric patients. Mol Genet Metab 104:S97–S99
Vilaseca MA, Lambruschini N, Gómez-López L et al (2010) Quality of dietary control in phenylketonuric patients and its relationship with general intelligence. Nutr Hosp 25:60–66
Wagner AE, Ernst IMA, Birringer M, Sancak Ö, Barella L, Rimbach G (2012) A Combination of Lipoic Acid Plus Coenzyme Q10 Induces PGC1α, a Master Switch of Energy Metabolism, Improves Stress Response, and Increases Cellular Glutathione Levels in Cultured C2C12 Skeletal Muscle Cells. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. doi:10.1155/2012/835970
Wendel A (1981) Glutathione peroxidase. Meth Enzymol 77:325–332
White CC, Viernes H, Krejsa CM et al (2003) Fluorescence-based microtiter plate assay for glutamate–cysteine ligase activity. Anal Biochem 318:175–180
Wojtkowiak-Giera A, Wandurska-Nowak E, Michalak M (2011) Changes in the activity and kinetics of mouse intestinal glutathione transferase during experimental trichinellosis. Parasitol Res 108:1309–1313
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the research grants from Brazilian National Research Council (CNPq), Programa de Núcleos de Excelência (PRONEX), CAPES, PROPESQ/UFRGS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moraes, T.B., Dalazen, G.R., Jacques, C.E. et al. Glutathione metabolism enzymes in brain and liver of hyperphenylalaninemic rats and the effect of lipoic acid treatment. Metab Brain Dis 29, 609–615 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-014-9491-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-014-9491-x