Abstract
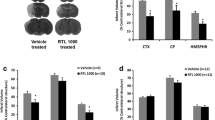
Stroke induces a biphasic effect on the peripheral immune response that involves early activation of peripheral leukocytes followed by severe immunosuppression and atrophy of the spleen. Peripheral immune cells, including T lymphocytes, migrate to the brain and exacerbate the developing infarct. Recombinant T-cell receptor (TCR) Ligand (RTL)551 is designed as a partial TCR agonist for myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG)-reactive T cells and has demonstrated the capacity to limit infarct volume and inflammation in brain when administered to mice undergoing middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO). The goal of this study was to determine if RTL551 could retain protection when given within the therapeutically relevant 4 h time window currently in clinical practice for stroke patients. RTL551 was administered subcutaneously 4 h after MCAO, with repeated doses every 24 h until the time of euthanasia. Cell numbers were assessed in the brain, blood, spleen and lymph nodes and infarct size was measured after 24 and 96 h reperfusion. RTL551 reduced infarct size in both cortex and striatum at 24 h and in cortex at 96 h after MCAO and inhibited the accumulation of inflammatory cells in brain at both time points. At 24 h post-MCAO, RTL551 reduced the frequency of the activation marker, CD44, on T-cells in blood and in the ischemic hemisphere. Moreover, RTL551 reduced expression of the chemokine receptors, CCR5 in lymph nodes and spleen, and CCR7 in the blood and lymph nodes. These data demonstrate effective treatment of experimental stroke with RTL551 within a therapeutically relevant 4 h time window through immune regulation of myelin-reactive inflammatory T-cells.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajmo CT Jr, Vernon DO, Collier L, Hall AA, Garbuzova-Davis S, Willing A, Pennypacker KR (2008) The spleen contributes to stroke-induced neurodegeneration. J Neurosci Res 86:2227–2234
Barr EL, Ouburg S, Igietseme JU, Morre SA, Okwandu E, Eko FO, Ifere G, Belay T, He Q, Lyn D, Nwankwo G, Lillard JW Jr, Black CM, Ananaba GA (2005) Host inflammatory response and development of complications of Chlamydia trachomatis genital infection in CCR5-deficient mice and subfertile women with the CCR5delta32 gene deletion. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 38:244–254
Brait VH, Jackman KA, Walduck AK, Selemidis S, Diep H, Mast AE, Guida E, Broughton BR, Drummond GR, Sobey CG (2010) Mechanisms contributing to cerebral infarct size after stroke: gender, reperfusion, T lymphocytes, and Nox2-derived superoxide. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 30:1306–1317
Brocke S, Piercy C, Steinman L, Weissman IL, Veromaa T (1999) Antibodies to CD44 and integrin alpha4, but not L-selectin, prevent central nervous system inflammation and experimental encephalomyelitis by blocking secondary leukocyte recruitment. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:6896–6901
Burrows GG, Chang JW, Bachinger HP, Bourdette DN, Offner H, Vandenbark AA (1999) Design, engineering and production of functional single-chain T cell receptor ligands. Protein Eng 12:771–778
Burrows GG, Adlard KL, Bebo BF Jr, Chang JW, Tenditnyy K, Vandenbark AA, Offner H (2000) Regulation of encephalitogenic T cells with recombinant TCR ligands. J Immunol 164:6366–6371
Burrows GG, Chou YK, Wang C, Chang JW, Finn TP, Culbertson NE, Kim J, Bourdette DN, Lewinsohn DA, Lewinsohn DM, Ikeda M, Yoshioka T, Allen CN, Offner H, Vandenbark AA (2001) Rudimentary TCR signaling triggers default IL-10 secretion by human Th1 cells. J Immunol 167:4386–4395
Cowell RM, Xu H, Galasso JM, Silverstein FS (2002) Hypoxic-ischemic injury induces macrophage inflammatory protein-1alpha expression in immature rat brain. Stroke 33:795–801
Denes A, Humphreys N, Lane TE, Grencis R, Rothwell N (2010) Chronic systemic infection exacerbates ischemic brain damage via a CCL5 (regulated on activation, normal T-cell expressed and secreted)-mediated proinflammatory response in mice. J Neurosci 30:10086–10095
Dirnagl U, Klehmet J, Braun JS, Harms H, Meisel C, Ziemssen T, Prass K, Meisel A (2007) Stroke-induced immunodepression: experimental evidence and clinical relevance. Stroke 38:770–773
Ebert LM, Schaerli P, Moser B (2005) Chemokine-mediated control of T cell traffic in lymphoid and peripheral tissues. Mol Immunol 42:799–809
Frenkel D, Huang Z, Maron R, Koldzic DN, Hancock WW, Moskowitz MA, Weiner HL (2003) Nasal vaccination with myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein reduces stroke size by inducing IL-10-producing CD4+ T cells. J Immunol 171:6549–6555
Gelderblom M, Leypoldt F, Steinbach K, Behrens D, Choe CU, Siler DA, Arumugam TV, Orthey E, Gerloff C, Tolosa E, Magnus T (2009) Temporal and spatial dynamics of cerebral immune cell accumulation in stroke. Stroke 40:1849–1857
Hardison JL, Wrightsman RA, Carpenter PM, Kuziel WA, Lane TE, Manning JE (2006) The CC chemokine receptor 5 is important in control of parasite replication and acute cardiac inflammation following infection with Trypanosoma cruzi. Infect Immun 74:135–143
Jauch EC, Lindsell C, Broderick J, Fagan SC, Tilley BC, Levine SR (2006) Association of serial biochemical markers with acute ischemic stroke: the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke recombinant tissue plasminogen activator Stroke Study. Stroke 37:2508–2513
Jin R, Yang G, Li G (2010) Inflammatory mechanisms in ischemic stroke: role of inflammatory cells. J Leukoc Biol 87:779–789
Khan IA, Thomas SY, Moretto MM, Lee FS, Islam SA, Combe C, Schwartzman JD, Luster AD (2006) CCR5 is essential for NK cell trafficking and host survival following Toxoplasma gondii infection. PLoS Pathog 2:e49
Kremlev SG, Roberts RL, Palmer C (2007) Minocycline modulates chemokine receptors but not interleukin-10 mRNA expression in hypoxic-ischemic neonatal rat brain. J Neurosci Res 85:2450–2459
Kuwabara T, Ishikawa F, Yasuda T, Aritomi K, Nakano H, Tanaka Y, Okada Y, Lipp M, Kakiuchi T (2009) CCR7 ligands are required for development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis through generating IL-23-dependent Th17 cells. J Immunol 183:2513–2521
Liesz A, Hagmann S, Zschoche C, Adamek J, Zhou W, Sun L, Hug A, Zorn M, Dalpke A, Nawroth P, Veltkamp R (2009) The Spectrum of Systemic Immune Alterations After Murine Focal Ischemia. Immunodepression Versus Immunomodulation. Stroke
Offner H, Subramanian S, Parker SM, Afentoulis ME, Vandenbark AA, Hurn PD (2006a) Experimental stroke induces massive, rapid activation of the peripheral immune system. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26:654–665
Offner H, Subramanian S, Parker SM, Wang C, Afentoulis ME, Lewis A, Vandenbark AA, Hurn PD (2006b) Splenic atrophy in experimental stroke is accompanied by increased regulatory T cells and circulating macrophages. J Immunol 176:6523–6531
Offner H, Sinha S, Wang C, Burrows GG, Vandenbark AA (2008) Recombinant T cell receptor ligands: immunomodulatory, neuroprotective and neuroregenerative effects suggest application as therapy for multiple sclerosis. Rev Neurosci 19:327–339
Offner H, Sinha S, Burrows GG, Ferro AJ, Vandenbark AA (2010) RTL therapy for multiple sclerosis: a phase I clinical study. J Neuroimmunol
Prass K, Meisel C, Hoflich C, Braun J, Halle E, Wolf T, Ruscher K, Victorov IV, Priller J, Dirnagl U, Volk HD, Meisel A (2003) Stroke-induced immunodeficiency promotes spontaneous bacterial infections and is mediated by sympathetic activation reversal by poststroke T helper cell type 1-like immunostimulation. J Exp Med 198:725–736
Pure E, Cuff CA (2001) A crucial role for CD44 in inflammation. Trends Mol Med 7:213–221
Sallusto F, Geginat J, Lanzavecchia A (2004) Central memory and effector memory T cell subsets: function, generation, and maintenance. Annu Rev Immunol 22:745–763
Schroeter M, Jander S, Witte OW, Stoll G (1994) Local immune responses in the rat cerebral cortex after middle cerebral artery occlusion. J Neuroimmunol 55:195–203
Sinha S, Subramanian S, Proctor TM, Kaler LJ, Grafe M, Dahan R, Huan J, Vandenbark AA, Burrows GG, Offner H (2007) A promising therapeutic approach for multiple sclerosis: recombinant T-cell receptor ligands modulate experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by reducing interleukin-17 production and inhibiting migration of encephalitogenic cells into the CNS. J Neurosci 27:12531–12539
Sinha S, Miller L, Subramanian S, McCarty OJ, Proctor T, Meza-Romero R, Huan J, Burrows GG, Vandenbark AA, Offner H (2010) Binding of recombinant T cell receptor ligands (RTL) to antigen presenting cells prevents upregulation of CD11b and inhibits T cell activation and transfer of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol 225:52–61
Sorce S, Bonnefont J, Julien S, Marq-Lin N, Rodriguez I, Dubois-Dauphin M, Krause KH (2010) Increased brain damage after ischaemic stroke in mice lacking the chemokine receptor CCR5. Br J Pharmacol 160:311–321
Spleiss O, Gourmala N, Boddeke HW, Sauter A, Fiebich BL, Berger M, Gebicke-Haerter PJ (1998) Cloning of rat HIV-1-chemokine coreceptor CKR5 from microglia and upregulation of its mRNA in ischemic and endotoxinemic rat brain. J Neurosci Res 53:16–28
Stevens SL, Bao J, Hollis J, Lessov NS, Clark WM, Stenzel-Poore MP (2002) The use of flow cytometry to evaluate temporal changes in inflammatory cells following focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Brain Res 932:110–119
Subramanian S, Zhang B, Kosaka Y, Burrows GG, Grafe MR, Vandenbark AA, Hurn PD, Offner H (2009) Recombinant T Cell Receptor Ligand Treats Experimental Stroke. Stroke
Wang PY, Kao CH, Mui MY, Wang SJ (1993) Leukocyte infiltration in acute hemispheric ischemic stroke. Stroke 24:236–240
Wang X, Xu L, Wang H, Zhan Y, Pure E, Feuerstein GZ (2002) CD44 deficiency in mice protects brain from cerebral ischemia injury. J Neurochem 83:1172–1179
Wang C, Mooney JL, Meza-Romero R, Chou YK, Huan J, Vandenbark AA, Offner H, Burrows GG (2003) Recombinant TCR ligand induces early TCR signaling and a unique pattern of downstream activation. J Immunol 171:1934–1940
Yan J, Greer JM, Etherington K, Cadigan GP, Cavanagh H, Henderson RD, O’Sullivan JD, Pandian JD, Read SJ, McCombe PA (2009) Immune activation in the peripheral blood of patients with acute ischemic stroke. J Neuroimmunol 206:112–117
Yilmaz G, Arumugam TV, Stokes KY, Granger DN (2006) Role of T lymphocytes and interferon-gamma in ischemic stroke. Circulation 113:2105–2112
Yilmaz G, Vital S, Yilmaz CE, Stokes KY, Alexander JS, Granger DN (2011) Selectin-mediated recruitment of bone marrow stromal cells in the postischemic cerebral microvasculature. Stroke 42:806–811
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Dr. Sushmita Sinha and Ms. Sandhya Subramanian for helpful discussions and Ms. Eva Niehaus for assistance in preparing the manuscript. This work was supported by NIH Grant NR003521 (PDH), NIH Grant NS047661 (AAV), the Collins Medical Trust (SD), AHA grant 09POST2190040 (SD), and the Biomedical Laboratory R&D Service, Department of Veterans’ Affairs.
Conflict of interest
Drs. Offner, Burrows, Vandenbark, and OHSU have a significant financial interest in Artielle ImmunoTherapeutics, Inc., a company that may have a commercial interest in the results of this research and technology. This potential conflict of interest has been reviewed and managed by the OHSU and VAMC Conflict of Interest in Research Committees.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dziennis, S., Mader, S., Akiyoshi, K. et al. Therapy with recombinant T-cell receptor ligand reduces infarct size and infiltrating inflammatory cells in brain after middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice. Metab Brain Dis 26, 123–133 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-011-9241-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-011-9241-2