Abstract
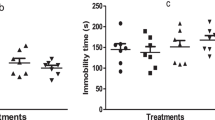
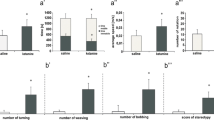
Evidence from the literature indicates that mitochondrial dysfunction occurs in schizophrenia and other psychiatric disorders. To produce an animal model that simulates psychotic symptoms analogous to those seen in schizophrenic patients, sub-anesthetic doses of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonists (such as ketamine) have been used. The aim of this study was to evaluate behavioral changes and mitochondrial dysfunction in rats administered ketamine for 7 consecutive days. Behavioral evaluation was performed using an activity monitor 1, 3 and 6 h after the last injection. The activities of mitochondrial respiratory chain complexes I, II, I-III and IV in multiple brain regions (prefrontal cortex, striatum and hippocampus) were also evaluated. Our results showed that hyperlocomotion occurred in the ketamine group 1 and 3 h after the last injection. Stereotypic movements were elevated only when animals were evaluated 1 h after receiving ketamine. In addition, we found that ketamine administration affects the respiratory chain, altering the activity of respiratory chain complexes in the striatum and hippocampus after 1 h, those in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus after 3 h and those in the prefrontal cortex and striatum 6 h after the last administration of ketamine. These findings suggest that ketamine alters the behavior of rats and changes the activity of respiratory chain complexes in multiple brain regions at different time points.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Battisti JJ, Shreffler CB, Uretsky NJ, Wallace LJ (2000) NMDA antagonists block expression of sensitization of amphetamine-and apomorphuneinduced stereotypy. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 67:241–246. doi:10.1016/S0091-3057(00)00324-5
Becker A, Peters B, Schroeder H, Mann T, Huether G, Grecksch G (2003) Ketamine-induced changes in rat behavior: a possible animal model of schizophrenia. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 27:687–700. doi:10.1016/S0278-5846(03)00080-0
Ben-Shachar D (2002) Mitochondrial dysfunction in schizophrenia: a possible linkage to dopamine. J Neurochem 83:1241–1251. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2002.01263
Ben-Shachar D, Laifenfeld D (2003) Mitochondria, synaptic plasticity, and schizophrenia. Int Rev Neurobiol 59:273–296. doi:10.1016/S0074-7742(04)59011-6
Ben-Shachar D, Bonne O, Chisin R, Klein E, Lester H, Aharon-Peretz J et al (2007) Cerebral glucose utilization and platelet mitochondiral complex I activity in schizophrenia: a FDG-PET study. Prog Neupsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 31:807–813. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2006.12.025
Birch-Machin MA, Briggs HL, Saborido AA, Bindoff LA, Turnbull DM (1994) An evaluation of the measurement of the activities of complexes I–IV in the respiratory chain of human skeletal muscle mitochondria. Biochem Med Metab Biol 51:35–42. doi:0885-4505/94
Boekema EJ, Braun HP (2007) Supramolecular structure of the mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation system. J Biol Chem 282:1–4. doi:10.1074/jbc.R600031200
Bowie CR, Harvey PD (2006) Schizophrenia from a neuropsychiatric perspective. Mt Sinai J Med 73:993–998
Bressan RA, Pilowsky LS (2003) Hipótese glutamatérgica da esquizofrenia. Rev Bras Psiq 25:177–183. doi:10.1590/S1516-44462003000300011
Bubber P, Hartounian V, Gibsin GE, Blass JP (2010) Abnormalities in the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle in the brains of schizophrenia patients. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 21:254–260. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2010.10.007
Bubeníková-Valešová V, Horáček J, Vrajová M, Höschl C (2008) Models of schizophrenia in humans and animals based on inhibition of NMDA receptors. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 38:1014–1023. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2008.03.012
Cassina A, Radi R (1996) Differential inhibitory action of nitric oxide and peroxynitrite on mitochondrial electron transport. Arch Biochem Biophys 328:309–316. doi:10.1006/abbi.1996.0178
Cavelier L, Jazin E, Eriksson I, Prince J, Bave U, Oreland L, Gyllensten U (1995) Decreased cytochrome c oxidase activity and lack of age related accumulation of mtDNA in brain of schizophrenics. Genomics 29:217–228. doi:10.1006/geno.1995.1234
De Padua AC, Gama CS, Lobato MI. Psicofármacos. Artmed POA. 2005.
Di Donato S (2000) Disorders related to mitochondrial membranes: phatology of the respiratory chain and neurodegeneration. J Inheret Metab Dis 23:247–263. doi:10.1023/A:1005684029429
Duncan GE, Leipzig JN, Mailman RB, Lieberman JA (1998) Differential effects of clozapine and haloperidol on ketamine-induced brain metabolic activation. Brain Res 812:65–75. doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(98)00926-3
Farber NB, Wozniak DF, Price MT, Labruyere J, Huss J, Peter HS, Olney JW (1995) Age-specific neurotoxicity in the rat associated with NMDA receptor blockade: potential relevance to schizophrenia? Biol Psychiat 38:788–796. doi:10.1016/0006-3223(95)00046-1
Fattal O, Budur K, Vaughan AJ, Franco K (2006) Review of the literature on major mental disorders in adult patients with mitochondrial diseases. Psychosomat 47:1–7. doi:10.1176/appi.psy.47.1.1
Fischer JC, Ruitenbeek W, Berden JA, Trijbels JM, Veerkamp JH, Stadhouders AM et al (1985) Differential investigation of the capacity of succinate oxidation in human skeletal muscle. Clin Chim Acta 153:23–26
Hitri A, O’Connor DA, Cohen JM, Keuler DJ, Deutsch SI (1993) Differentiation between MK-801-and apomorphine-induced stereotyped behaviors in mice. Clin Neuropharmacol 16:220–236
Hunt MJ, Raynaud B, Garcia R (2006) Ketamine dose-dependently unduces high-frequency oscillations in the nucleus accumbens in freely moving rats. Biol Psychiat 60:1206–1214. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.01.020
Karry R, Klein E, Ben-Shachar D (2004) Mitochondrial complex I subunits expression is altered in schizophrenia: a postmortem study. Biol Psychiatry 55:676–684. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2003.12.012
Krystal JH, Karper LP, Seibyl JP, Freeman GF, Delaney R, Bremner JD (1994) Subanesthetic effects of the noncompetitive NMDA antagonists, ketamine, in humans. Arch Gen Psychiatry 51:199–214
Kung L, Roberts RC (1999) Mitochondrial pathology in human schizophrenic striatum: a postmortem ultrastructural study. Synapse 31:67–75
Lewis DA, Lieberman JA (2000) Catching up on schizophrenia: natural history and neurobiology. Neuron 28:325–334. doi:10.1016/S0896-6273(00)00111-2
Lipska BK, Weinberger DR (2000) To model a psychiatric disorder in animals: schizophrenia as a reality test. Neuropsychopharmacol 23:223–239. doi:10.1038/sj.npp.1395545
Littlewood CL, Jones N, O’Neill MJ, Mitchell SN, Tricklebank M, Williams SCR (2006) Mapping the central effects of ketamine in the rat using pharmacological MRI Psychopharmacol 186:64–81. doi:10.1007/s00213-006-0344-0
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–267
Marcotte ER, Pearson DM, Srivastava LK (2001) Animal models of schizophrenia: a critical review. J Psychiatry Neurosci 26:395–410
Maurer I, Moller HJ (1997) Inhibition of complex I by neuroleptics in normal human brain cortex parallels the extrapyramidal toxicity of neuroleptics. Mol Cell Biochem 174:255–259. doi:10.1023/A:1006872911332
Maurer I, Zierz S, Möller HJ (2001) Evidence for a mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation defect in brains from patients with schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 48:125–136. doi:10.1016/S0920-9964(00)00075-X
Maxwell JC (2005) Party Drugs: properties, prevalence, patterns and problems. Subst Use Misus 40:1203–1240. doi:10.1081/JA-200066736
Meltzer HY, Bastani B, Ramirez L, Matsubara S (1989) Clozapine: new research on efficacy and mechanism of action. Eur Arch Psychiatry Neurol Sci 238:332–339
Meyer JM (2007) Antipsychotic safety and efficacy concerns. J Clin Psychiatry 68:20–26
Nikam SS, Awasthi AK (2008) Evolution of schizophrenia drugs: a focus on dopaminergic systems. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 9:37–46
Park S, Holzman PS (1992) Schizophrenics show spatial working memory deficits. Arch Gen Psychiatry 49:975–982
Prabakaran S, Swatton JE, Ryan MM, Huffaker SJ, Huang JTJ, Griffin JL (2004) Mitochondrial dysfunction in schizophrenia: evidence for compromised brain metabolism and oxidative stress. Mol Psychiatry 9:684–697. doi:10.1038/sj.mp.4001511
Prince JA, Blennow K, Gottfries CG, Karlsson I, Oreland L (1997) Mitochondrial function in differentially altered in the basal ganglia of chronic schizophrenics. Neuropsychopharmacol 21:372–379. doi:S0893-133X(99)00016-0
Reddy PH (2008) Mitochondrial medicine for aging and neurodegenerative diseases. Neuromolecular Med 10:291–315
Reddy PH (2009) Role of mitochondria in neurodegenerative diseases: mitochondria as a therapeutic target in Alzheimer’s disease. CNS Spectr 14:8–13
Rezin GT, Amboni G, Zugno AI, Quevedo J, Streck EL (2008) Mitchondrial dysfunction and psychiatric disorders. Neurochem Res 34:1021–1029. doi:10.1007/s11064-008-9865-8
Robertson GS, Hori SE, Powell KJ (2006) Schizophrenia: an integrative approach to modelling a complex disorder. J Psyc Neurosci 31:157–167
Rustin P, Chretien D, Bourgeron T, Gérard B, Rötig A, Saudubray JM, Munnich A (1994) Biochemical and molecular investigations in respiratory chain deficiencies. Clin Chim Acta 228:35–51
Strazielle C, Sturchler-Pierrat C, Staufenbiel M, Lalonde R (2003) Regional brain cytochrome oxidase activity in beta-amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice with the Swedish mutation. Neurosc 118:1151–1163. doi:10.1016/S0306-4522(03)00037-X
Swerdlow NR, Bakshi V, Waikar M, Taad N, Geyer MA (1998) Seroquel, clozapine and chlorpromazine restore sensorimotor gating in ketamine-treated rats. Psychopharmacol 140:75–80. doi:10.1007/s002130050741
Takeyama K, Yoshikawa M, Oka T, Kawaguchi M, Suzuki T, Hashimoto A (2006) Ketamine enhances the expression of serine racemase and D-amino acid oxidase mRNAs in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 540:82–86. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.04.021
Tien AY, Eaton WW (1992) Psychopathologic precursors and sociodemographic risk factors for the schizophrenia syndrome. Arch Gen Psychiatry 49:37–46
Uranova N, Orlovskaya D, Vikhreva O, Zimina I, Kolomeets N, Vostrikov V et al (2001) Electron microscopy of oligodendroglia in severe mental illness. Brain Res Bull 55:597–610. doi:10.1016/S0361-9230(01)00528-7
Van Den Buuse M, Garner B, Gogos A, Kusljic S (2005) Importance of animal models in schizophrenia research. Aust N Z J Psychiatry 39:550–557
Wood SJ, Yücel M, Pantelis C, Berk M (2009) Neurobiology of schizophrenia spectrum disorders: the role of oxidative stress. Ann Acad Med Singapore 38:396–401
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by grants from CNPq, Instituto Cérebro e Mente, INCT and UNESC to AIZ, ELS, and JQ (CNPq Research Fellows).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Oliveira, L., Fraga, D.B., De Luca, R.D. et al. Behavioral changes and mitochondrial dysfunction in a rat model of schizophrenia induced by ketamine. Metab Brain Dis 26, 69–77 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-011-9234-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-011-9234-1