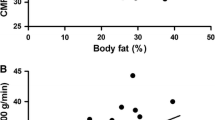
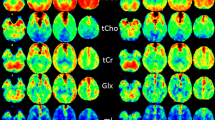
Abstract
Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is a cluster of risk factors associated with significant cardiovascular morbidity and mortality and diminished cognitive function. Given that the cerebral mechanisms mediating the relationship between peripheral metabolic dysfunction and cognitive impairment are unknown, we set out to examine the relationship between diagnosis of metabolic syndrome and cerebral metabolism. Thirteen participants with MetS (aged 48 ± 6 years) and 25 healthy adults (aged 51 ± 6 years) underwent neuropsychological assessment, health screen and proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H MRS) examining N-acetyl-aspartate (NAA), myo-inositol (mI), creatine (Cr), choline (Cho), and glutamate (Glu) concentrations in occipitoparietal grey matter. Cerebral metabolite ratios (NAA/Cr, Cho/Cr, mI/Cr, and Glu/Cr) of participants with MetS, defined by the International Diabetes Federation criteria, were compared with controls matched for age, education, cognition, and emotional function. There were no significant differences in global cognitive function, memory, language, and psychomotor performance between the groups. Diagnosis of MetS was associated with significantly higher mI/Cr (F(1,36) = 5.02, p = 0.031) and Glu/Cr ratio (F(1,36) = 4.81, p = 0.035). Even in cognitively normal adults, MetS is related to cerebral metabolic disturbances, a possible indication of early brain vulnerability. Longitudinal studies that begin in mid-life can help validate the use of 1H MRS markers as indicators of long-term cognitive outcomes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbaraly TN, Kivimaki M, Shipley MJ, Tabak AG, Jokela M, Virtanen M, Marmot MG, Ferrie JE, Singh-Manoux A (2010) Metabolic syndrome over 10 years and cognitive functioning in late midlife: the Whitehall II study. Diab Care 33(1):84–89
Alberti KGMM, Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet PZ, Cleeman JI, Donato KA, Fruchart J-C, James WPT, Loria CM, Smith SC (2009) Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: a joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation 120(16):1640–1645
Angelie E, Bonmartin A, Boudraa A, Gonnaud PM, Mallet JJ, Sappey-Marinier D (2001) Regional differences and metabolic changes in normal aging of the human brain: proton MR spectroscopic imaging study. Am J Neuroradiol 22(1):119–127
Arvanitakis Z, Bennett DA, Wilson RS, Barnes LL (2010) Diabetes and cognitive systems in older black and white persons. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 24(1):37–42
Barker PB, Gillard JH, van Zijl PC, Soher BJ, Hanley DF, Agildere AM, Oppenheimer SM, Bryan RN (1994) Acute stroke: evaluation with serial proton MR spectroscopic imaging. Radiology 192(3):723–732
Beck AT, Steer RA, Brown GK (1996) BDI-II Manual. The Psychological Corporation, Fort Worth
Berry GT, Wang ZJ, Dreha SF, Finucane BM, Zimmerman RA (1999) In vivo brain myo-inositol levels in children with Down syndrome. J Pediatr 135(1):94–97
Brand A, Richter-Landsberg C, Leibfritz D (1993) Multinuclear NMR studies on the energy metabolism of glial and neuronal cells. Dev Neurosci 15(3–5):289–298
Danielsen ER, Ross B (1999) Magnetic resonance spectroscopy diagnosis of neurological diseases. Marcel Dekker, New York
Delis DC, Kramer JH, Kaplan E, Ober BA (2000) California Verbal Learning Test (CVLT-II) Manual. Harcourt Assessment Company, San Antonio
Dik MG, Jonker C, Comijs HC, Deeg DJH, Kok A, Yaffe K, Penninx BW (2007) Contribution of metabolic syndrome components to cognition in older individuals. Diab Care 30(10):2655–2660
Erecińska M, Silver IA (1990) Metabolism and role of glutamate in mammalian brain. Prog Neurobiol 35(4):245–296
Eslinger P (1984) The Iowa screening battery for mental decline. University of Iowa College of Medicine, Iowa
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR (1975) “Mini-mental state”. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res 12(3):189–198
García Santos JM, Fuentes LJ, Vidal JB, Carrillo A, Antequera M, Campoy G, Antúnez C, Torres del Río S, García-Sevilla J, Ortega G (2010) Posterior paralimbic and frontal metabolite impairments in asymptomatic hypertension with different treatment outcomes. Hypertens Res 33(1):67–75
Gatto NM, Henderson VW, St John JA, McCleary C, Hodis HN, Mack WJ (2008) Metabolic syndrome and cognitive function in healthy middle-aged and older adults without diabetes. Neuropsychol Dev Cogn B Aging Neuropsychol Cogn 15(5):627–641
Gaugler JE, Yu F, Krichbaum K, Wyman JF (2009) Predictors of nursing home admission for persons with dementia. Med Care 47(2):191–198
Geissler A, Fründ R, Schölmerich J, Feuerbach S, Zietz B (2003) Alterations of cerebral metabolism in patients with diabetes mellitus studied by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 111(7):421–427
Han J, Ma L (2010) Study of the features of proton MR spectroscopy ((1)H-MRS) on amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Magn Reson Imaging 31(2):305–308
Heikkilä O, Lundbom N, Timonen M, Groop P-H, Heikkinen S, Mäkimattila S (2008) Risk for metabolic syndrome predisposes to alterations in the thalamic metabolism. Metab Brain Dis 23(3):315–324
Heikkilä O, Lundbom N, Timonen M, Groop PH, Heikkinen S, Mäkimattila S (2009) Hyperglycaemia is associated with changes in the regional concentrations of glucose and myo-inositol within the brain. Diabetologia 52(3):534–540
Helms G, Ciumas C, Kyaga S, Savic I (2006) Increased thalamus levels of glutamate and glutamine (Glx) in patients with idiopathic generalised epilepsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 77(4):489–494
Holub BJ (1986) Metabolism and function of myo-inositol and inositol phospholipids. Annu Rev Nutr 6:563–597
Hurd R, Sailasuta N, Srinivasan R, Vigneron DB, Pelletier D, Nelson SJ (2004) Measurement of brain glutamate using TE-averaged PRESS at 3T. Magn Reson Med 51(3):435–40
Kalmijn S, Foley D, White L, Burchfiel CM, Curb JD, Petrovitch H, Ross GW, Havlik RJ, Launer LJ (2000) Metabolic cardiovascular syndrome and risk of dementia in Japanese-American elderly men. The Honolulu-Asia aging study. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20(10):2255–60
Kantarci K, Jack CR, Xu YC, Campeau NG, O’Brien PC, Smith GE, Ivnik RJ, Boeve BF, Kokmen E, Tangalos EG et al (2000) Regional metabolic patterns in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease: a 1H MRS study. Neurology 55(2):210–217
Kimura T, Ohkubo M, Igarashi H, Kwee IL, Nakada T (2007) Increase in glutamate as a sensitive indicator of extracellular matrix integrity in peritumoral edema: a 3.0-tesla proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. J Neurosurg 106(4):609–613
Kivipelto M, Ngandu T, Fratiglioni L, Viitanen M, Kåreholt I, Winblad B, Helkala E-L, Tuomilehto J, Soininen H, Nissinen A (2005) Obesity and vascular risk factors at midlife and the risk of dementia and Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 62(10):1556–1560
Klove H, Forster FM (1963) Clinical neuropsychology, the medical clinics of North America. Saunders, New York
Kreis R, Ross BD (1992) Cerebral metabolic disturbances in patients with subacute and chronic diabetes mellitus: detection with proton MR spectroscopy. Radiology 184(1):123–130
Kreis R, Ernst T, Ross BD (1993) Absolute quantitation of water and metabolites in the human brain. II. Metabolite concentrations. J Magn Reson Series B 102:9–19
Lau DCW (2009) Metabolic syndrome: perception or reality? Curr Atheroscler Rep 11(4):264–271
Lezak MD (1995) Neuropsychological Assessment. Oxford University Press, New York
Lipton SA, Rosenberg PA (1994) Excitatory amino acids as a final common pathway for neurologic disorders. N Engl J Med 330(9):613–22
Miller BL, Moats RA, Shonk T, Ernst T, Woolley S, Ross BD (1993) Alzheimer disease: depiction of increased cerebral myo-inositol with proton MR spectroscopy. Radiology 187(2):433–437
Moats RA, Ernst T, Shonk TK, Ross BD (1994) Abnormal cerebral metabolite concentrations in patients with probable Alzheimer disease. Magn Reson Med 32(1):110–115
Morris JC, Heyman A, Mohs RC, Hughes JP, van Belle G, Fillenbaum G, Mellits ED, Clark C (1989) The Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer’s Disease (CERAD). Part I. Clinical and neuropsychological assessment of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 39(9):1159–1165
Murata T, Koshino Y, Omori M, Murata I, Nishio M, Horie T, Umezawa Y, Isaki K, Kimura H, Itoh S (1993) In vivo proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study on premature aging in adult Down’s syndrome. Biol Psychiatry 34(5):290–297
Narayana PA (2005) Magnetic resonance spectroscopy in the monitoring of multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimaging 15(4 Suppl):46S–57S
Olson BLB, Holshouser BA, Britt W, Mueller C, Baqai W, Patra S, Petersen F, Kirsch WM (2008) Longitudinal metabolic and cognitive changes in mild cognitive impairment patients. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 22(3):269–277
Parnetti L, Tarducci R, Presciutti O, Lowenthal DT, Pippi M, Palumbo B, Gobbi G, Pelliccioli GP, Senin U (1997) Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy can differentiate Alzheimer’s disease from normal aging. Mech Ageing Dev 97(1):9–14
Potenza MV, Mechanick JI (2009) The metabolic syndrome: definition, global impact, and pathophysiology. Nutr Clin Pract 24(5):560–577
Provencher SW (1993) Estimation of metabolite concentrations from localized in vivo proton NMR spectra. Magn Reson Med 30(6):672–679
Pu Y, Li QF, Zeng CM, Gao J, Qi J, Luo DX, Mahankali S, Fox PT, Gao JH (2000) Increased detectability of alpha brain glutamate/glutamine in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Am J Neuroradiol 21(1):203–212
Raffaitin C, Gin H, Empana J-P, Helmer C, Berr C, Tzourio C, Portet F, Dartigues J-F, Alperovitch A, Barberger-Gateau P (2009) Metabolic syndrome and risk for incident Alzheimer’s disease or vascular dementia: the Three-City Study. Diab Care 32(1):169–174
Reitan R (1958) Validity of the Trail Making Test as an indicator of organic brain damage. Percept Mot Skills 8:271–276
Riedel G, Platt B, Micheau J (2003) Glutamate receptor function in learning and memory. Behav Brain Res 140(1–2):1–47
Ross BD (1991) Biochemical considerations in 1H spectroscopy. Glutamate and glutamine; myo-inositol and related metabolites. NMR Biomed 4(2):59–63
Ross BD, Bluml S, Cowan R, Danielsen E, Farrow N, Gruetter R (1997) In vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy of human brain: the biophysical basis of dementia. Biophys Chem 68(1–3):161–172
Skoog I, Lernfelt B, Landahl S, Palmertz B, Andreasson LA, Nilsson L, Persson G, Odén A, Svanborg A (1996) 15-year longitudinal study of blood pressure and dementia. Lancet 347(9009):1141–1145
Srinivasan R, Sailasuta N, Hurd R, Nelson S, Pelletier D (2005) Evidence of elevated glutamate in multiple sclerosis using magnetic resonance spectroscopy at 3 T. Brain 128(Pt 5):1016–1025
Valenzuela MJ, Sachdev P (2001) Magnetic resonance spectroscopy in AD. Neurology 56(5):592–598
Vanhanen M, Koivisto K, Moilanen L, Helkala EL, Hänninen T, Soininen H, Kervinen K, Kesäniemi YA, Laakso M, Kuusisto J (2006) Association of metabolic syndrome with Alzheimer disease: a population-based study. Neurology 67(5):843–847
Waldstein SR, Brown JRP, Maier KJ, Katzel LI (2005) Diagnosis of hypertension and high blood pressure levels negatively affect cognitive function in older adults. Ann Behav Med 29(3):174–180
Wechsler D (1979) Manual for the Wechsler adult intelligence scale, 3rd edn. The Psychological Corporation, San Antonio
Wechsler D (1999) Wechsler abbreviated scale of intelligence manual. Harcourt Assessment Company, San Antonio
Whitmer RA, Gunderson EP, Barrett-Connor E, Quesenberry CP, Yaffe K (2005) Obesity in middle age and future risk of dementia: a 27 year longitudinal population based study. BMJ 330(7504):1360
Yaffe K (2007) Metabolic syndrome and cognitive disorders: is the sum greater than its parts? Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 21(2):167–171
Yaffe K, Blackwell T, Kanaya AM, Davidowitz N, Barrett-Connor E, Krueger K (2004) Diabetes, impaired fasting glucose, and development of cognitive impairment in older women. Neurology 63(4):658–663
Yaffe K, Haan M, Blackwell T, Cherkasova E, Whitmer RA, West N (2007) Metabolic syndrome and cognitive decline in elderly Latinos: findings from the Sacramento Area Latino Study of Aging study. J Am Geriatr Soc 55(5):758–762
Yaffe K, Weston AL, Blackwell T, Krueger KA (2009) The metabolic syndrome and development of cognitive impairment among older women. Arch Neurol 66(3):324–328
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by American Heart Association grant 09BGIA2060722 (APH) and the University of Texas at Austin (APH). The authors thank the UT Imaging Center staff for their help with the participants.
Conflict of interest disclosure
Dr. Haley is funded by American Heart Association grant #09BGIA2060722 and received research support from the University of Texas at Austin and NINR Center Grant P30 NR005051.
Dr. Tanaka serves on the scientific advisory board for Endothelix, is funded by NIH grants #AG20966 and DA018431, and received research support from the American Heart Association and the Yoga Care Foundation.
Ms. Gonzales, Mr. Tarumi, Mr. Miles and Dr. Goudarzi have no disclosures to report.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haley, A.P., Gonzales, M.M., Tarumi, T. et al. Elevated cerebral glutamate and myo-inositol levels in cognitively normal middle-aged adults with metabolic syndrome. Metab Brain Dis 25, 397–405 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-010-9221-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-010-9221-y