Abstract
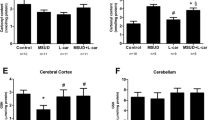
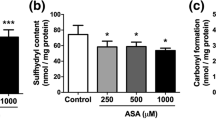
N-Acetylaspartic acid accumulates in Canavan Disease, a severe inherited neurometabolic disease clinically characterized by severe mental retardation, hypotonia, macrocephaly and generalized tonic and clonic type seizures. Considering that the mechanisms of brain damage in this disease remain poorly understood, in the present study we investigated the in vitro and in vivo effects of N-acetylaspartic acid on the activities of catalase, superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase, as well as on hydrogen peroxide concentration in cerebral cortex of 14-day-old rats. Catalase and glutathione peroxidase activities were significantly inhibited, while hydrogen peroxide concentration was significantly enhanced by N-acetylaspartic acid both in vitro and in vivo. In contrast, superoxide dismutase activity was not altered by N-acetylaspartic acid. Our results clearly show that N-acetylaspartic acid impairs the enzymatic antioxidant defenses in rat brain. This could be involved in the pathophysiological mechanisms responsible for the brain damage observed in patients affected by Canavan Disease.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi M, Torii J, Schneck L, Volk BW (1972) Electron microscopy and enzyme histochemical studies of the cerebellum in spongy degeneration (van Bogaert and Bertrand type). Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 20:22
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Meth Enzymol 105:121–126
Akimitsu T, Kurisu K, Hanaya R, Iida K, Kiura Y, Arita K, Matsubayashi H, Ishihara K, Kitada K, Serikawa T, Sasa M (2000) Epileptic seizures induced by N-aspartate in rats: in vivo and in vitro studies. Brain Res 861:143–150
Baslow MH (2002) Evidence supporting a role for N-acetyl-L-aspartate as a molecular water pump in myelinated neurons in the central nervous system—An analytical review. Neurochem Int 40:295–300
Baslow MH (2003) N-acetylaspartate in the vertebrate brain: metabolism and function. Neurochem Res 28:941–953
Beaudet A (2001) Aspartoacylase deficiency (Canavan Disease). In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D (eds) The metabolic and molecular bases of inherited disease. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 5799–5805
Bruce AJ, Baudry M (1995) Oxygen free radicals in rat limbic structures after kainate-induced seizures. Free Radic Biol Med 18:993–100
Gordon N (2000) Canavan disease: a review of recent developments. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 5:65–69
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC (2007a) Cellular responses to oxidative stress: Adaptation, damage, repair, senescence and death. In: Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC (eds) Free Radicals in biology and medicine. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 351–425
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC (2007b) The chemistry of free radicals and related ‘reactive species’. In: Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC (eds) Free radicals in biology and medicine. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 37–104
Janson CG, McPhee SWJ, Francis J, Shera D, Assadi M, Freese A, Hurh P, Haselgrove J, Wang DJ, Bilaniuk L, Leone P (2006) Natural history of Canavan Disease revealed by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS) and diffusion-weighted MRI. Neuropediatrics 37:209–221
Kitada K, Akimitsu T, Shigematsu Y, Kondo A, Maihara T, Yokoi N, Kuramoto T, Sasa M, Serikawa T (2000) Accumulation of N-acetylaspartate in the brain of the tremor rat, a mutant exhibiting absence-like seizure and spongiform degeneration in the central nervous system. J Neurochem 74:2512–2519
Klugmann M, Leichtlein CB, Wymond Symes C, Serikawa T, Young D, During MJ (2005) Restoration of aspartoacylase activity in CNS neurons does not ameliorate motor deficits and demyelination in a model of Canavan Disease. Mol Ther 11:745–753
Kumar S, Mattan NS, de Vellis J (2006) Canavan disease: a white matter disorder. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev 12:157–65
Liang LP, Patel M (2004) Mitochondrial oxidative stress and increased seizure susceptibility in Sod2(−/+) mice. Free Radic Biol Med 36:542–554
Liang LP, Ho YS, Patel M (2000) Mitochondrial superoxide production in kainate-induced hippocampal damage. Neuroscience 101:563–570
Lissi E, Caceres T, Videla LA (1986) Visible chemiluminescence from rat brain homogenates undergoing autoxidation. I. Effect of additives and products accumulation. Free Radic Biol Med 2:63–69
Llesuy SF, Milei J, Molina H (1985) Comparison of lipid peroxidation and myocardial damage induced by adriamycin and 4′-epiadriamycin in mice. Tumori 71:241–249
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Lewis-Farr A, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Madhavarao CN, Arun P, Moffett JR, Szucs S, Surendran S, Matalon R, Garbern J, Hristova D, Johnson A, Jiang W, Namboodiri MAA (2005) Defective N-acetylaspartate catabolism reduces brain acetate levels and myelin lipid synthesis in Canavan`s disease. PNAS 102:5221–5226
Matalon R, Michals-Matalon K (1999) Biochemistry and molecular biology of Canavan disease. Neurochem Res 24:507–513
Matalon R, Michals-Matalon K (2000) Spongy degeneration of the brain, Canavan Disease: biochemical and molecular findings. Front Biosci 5:d307–d311
Moffett JR, Ross B, Arun P, Madhavarao CN, Namboodiri AMA (2007) N-acetylaspartate in the CNS: from neurodiagnostics to neurobiology. Prog Neurobiol 81:89–131
Namboodiri AMA, Peethambaran A, Mathew R, Sambhu PA, Hershfield J, Moffett JR, Madhavarao CN (2006) Canavan disease and the role of N-acetylaspartate in myelin synthesis. Mol Cell Endocrinol 252:216–223
Patel M (2004) Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress: cause and consequence of epileptic seizures. Free Radic Biol Med 37:1951–1962
Pederzolli CD, Mescka CP, Scapin F, Rockenbach FJ, Sgaravatti AM, Sgarbi MB, Wyse ATS, Wannmacher CMD, Wajner M, Dutra-Filho CS (2007) N-acetylaspartic acid promotes oxidative stress in cerebral cortex of rats. Int J Devl Neurosci 25:317–324
Pick E, Keisari Y (1980) A simple colorimetric method for the measurement of hydrogen peroxide produced by cells in culture. J Immunol Meth 38:161–170
Rice ME, Russo-Menna I (1998) Differential compartmentalization of brain ascorbate and glutathione between neurons and glia. Neuroscience 82:1213–1223
Skiranth SG, Chandrashekar HS, Nagarajan K, Jayakumar PN (2007) Restricted diffusion in Canavan Disease. Childs Nerv Syst 23:465–468
Somani SM, Husain K (1996) Exercise training alters kinetics of antioxidant enzymes in rat tissues. Biochem Mol Biol Int 38:587–595
Surendran S, Michals-Matalon K, Quast MJ, Tyring SK, Wei J, Ezell EL, Matalon R (2003) Canavan disease: a monogenic trait with complex genomic interaction. Mol Genet Metab 80:74–80
Traeger EC, Rapin I (1998) The clinical course of Canavan Disease. Pediatr Neurol 18:207–212
Trotti D, Danbolt NC, Volterra A (1998) Glutamate transporters are oxidant-vulnerable: a molecular link between oxidative stress and excitotoxic neurodegeneration? Trend Pharmacol Sci 19:328–334
Tsai G, Coyle JT (1995) N-acetylaspartate in neuropsychiatric disorders. Prog Neurobiol 46:531–540
Wendel A (1981) Glutathione peroxidase. Meth Enzymol 77:325–332
Yan HD, Ishihara K, Serikawa T, Sasa M (2003) Activation by N-acetyl-L-aspartate of acutely dissociated hippocampal neurons in rats via metabotropic glutamate receptors. Epilepsia 44:1153–1159
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the research grants from Programa de Núcleos de Excelência (PRONEX), Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES), Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio Grande do Sul (FAPERGS) and FINEP Rede Instituto Brasileiro de Neurociência (IBN-Net #01.06.0842-00).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pederzolli, C.D., Mescka, C.P., Magnusson, A.S. et al. N-acetylaspartic acid impairs enzymatic antioxidant defenses and enhances hydrogen peroxide concentration in rat brain. Metab Brain Dis 25, 251–259 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-010-9202-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-010-9202-1