Abstract
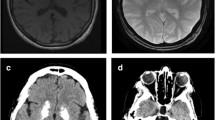
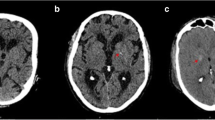
Though basal ganglia calcification (BGC) has been recognized as a feature of mitochondriopathy, little is known about its frequency in a larger cohort. The aim of this work was to assess the frequency of BGC, type and frequency of clinical and additional imaging central-nervous-system (CNS) abnormalities and of non-CNS abnormalities in mitochondriopathy patients with BGC. Retrospectively reviewed were the records of all mitochondriopathy patients in whom BGC was found on cerebral CT during 10 years. Among those who underwent cerebral CT, thirty-six, 24 women, 12 men, aged 33–93 years, showed BGC. The most frequent clinical CNS manifestations in these patients were epilepsy (n = 9), Parkinson syndrome (n = 9), dementia (n = 7), dysarthria (n = 5), spasticity (n = 4), tremor (n = 4), or stroke (n = 4). Additional cerebral CT-findings were atrophy (n = 10), lacunas (n = 6), leucaraiosis (n = 6), focal gliosis (n = 4), or stroke (n = 1). MR imaging, carried out in 12 patients, confirmed BGC in one. The 36 patients presented with involvement of the CNS (n = 32), endocrine system (n = 29), peripheral nervous system (n = 28), heart (n = 23), inner ear (n = 16), eyes (n = 15), guts (n = 11), blood (n = 9), kidney (n = 2), or dermis (n = 2). BGC occurs in one sixth of non-selected patients with mitochondriopathy and is associated with clinical and imaging CNS abnormalities and multisystem disease in the majority of them.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn, J.H., Yoo, C.I., Lee, C.R., Lee, J.H., Lee, H., Kim, C.Y., Park, J.K., Sakai, T., Yoon, C.S., and Kim, Y. (2003). Calcification mimicking manganese-induced increased signal intensities in T1-weighted MR images in a patient taking herbal medicine: Case report. Neurotoxicology 24:835–838.
Avrahami, E., Cohn, D.F., Feibel, M., and Tadmor, R. (1994). MRI demonstration and CT correlation of the brain in patients with idiopathic intracerebral calcification. J. Neurol. 241:381–384.
Castello, E., and Pallestrini, E.A. (1997). Otoneurological manifestations in Fahr’s disease. A case report. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 17:430–435.
Finsterer, J., Jarius, C., Eichberger, H., and Jaksch, M. (2001). Phenotype variability in 130 adult patients with respiratory chain disorder. J. Inher. Metab. Dis. 24:560–576.
Gomille, T., Meyer, R.A., Falkai, P., Gaebel, W., Konigshausen, T., and Christ, F. (2001). Prevalence and clinical significance of computerized tomography verified idiopathic calcinosis of the basal ganglia. Radiologe. 41:205–210.
Guo, Y., Guo, Z., Chen, L., Zhang, J., Wang, W., Liu, X., Ren, H., and Gao, S. (1997). Clinical, pathologic and genetic studies on mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis and stroke-like episodes. Chin. Med. J. (Engl.) 110:851–855.
Harvey, J.N., and Barnett, D. (1992). Endocrine dysfunction in Kearns-Sayre syndrome. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxford) 37:97–103.
Kim, I.O., Kim, J.H., Kim, W.S., Hwang, Y.S., Yeon, K.M., and Han, M.C. (1996). Mitochondrial myopathy encephalopathy lactic acidosis and strokelike episodes (MELAS) syndrome: CT and MR findings in seven children. Am. J. Roentgenol. 166:641–645.
Nardin, R.A., and Johns, D.R. (2001). Mitochondrial dysfunction and neuromuscular disease. Muscle Nerve. 24:170–191.
Ostling, S., Andreasson, L.A., and Skoog, I. (2003). Basal ganglia calcification and psychotic symptoms in the very old. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry. 18:983–987.
Robeck, S., Stefan, H., Engelhardt, A., and Neundorfer, B. (1996). Follow-up studies and disorders of endocrinologic function in MELAS syndrome. Nervenarzt 67:465–470.
Sanchetee, P., Venkataraman, S., Mohan, C., Shetty, D.D., and Iyengar, G. (1999). Basal ganglia calcification. J. Assoc. Physic. India 47:507–509.
Schäfer, M., and Ferbert, A. (1998). Basal ganglia calcification and hypoparathyroidism. Nervenarzt 69:873–878.
Schmiedel, J., Jackson, S., Schafer, J., and Reichmann, H. (2003). Mitochondrial cytopathies. J. Neurol. 250:267–277.
Sue, C.M., Crimmins, D.S., Soo, Y.S., Pamphlett, R., Presgrave, C.M., Kotsimbos, N., Jean-Francois, M.J., Byrne, E., and Morris, J.G. (1998). Neuroradiological features of six kindreds with MELAS tRNA(Leu) A2343G point mutation: Implications for pathogenesis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 65:233–240.
Terada, H., Barkovich, A.J., Edwards, M.S., and Ciricillo, S.M. (1996). Evolution of high-intensity basal ganglia lesions on T1-weighted MR in neurofibromatosis type 1. Am. J. Neuroradiol 17:755–760.
Walker, U.A., Collins, S., and Byrne, E. (1996). Respiratory chain encephalomyopathies: A diagnostic classification. Eur Neurol 36:260–267.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Finsterer, J., Kopsa, W. Basal Ganglia Calcification in Mitochondrial Disorders. Metab Brain Dis 20, 219–226 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-005-7209-9
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-005-7209-9