Abstract
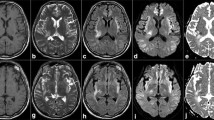
It is not clear whether cerebral edema in fulminant hepatic failure is predominantly vasogenic or cytotoxic, though cytotoxic edema due to astrocyte swelling is more likely. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging can differentiate vasogenic from cytotoxic edema. We performed diffusion-weighted imaging in patients with fulminant hepatic failure to clarify the issue by measuring apparent diffusion coefficient, which quantifies movement of water molecule across cell membrane. Seven patients with fulminant hepatic failure underwent conventional and diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Apparent diffusion coefficient was measured in four cortical areas and 12 deep white and gray matter regions in both cerebral hemispheres. Thirteen healthy subjects served as controls. The apparent diffusion coefficient values in patients and controls were compared using Wilcoxon signed rank test. Two patients who survived underwent repeat imaging using same protocol. Patients with FHF had significantly lower apparent diffusion coefficient in all cortical and deep white and gray matter regions of interest compared to controls (p < 0.001), suggesting cytotoxic cell swelling. In two survivors with repeat imaging, one showed complete resolution while the changes persisted in the other, suggesting ischemic injury. Cerebral edema in fulminant hepatic failure is predominantly due to cytotoxic edema.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acharya, S.K., Dasarathy, S., Kumer, T.L., Sushma, S., Prasanna, K.S., Tandon, A., Sreenivas, V., Nijhawan, S., Panda, S.K., Nanda, S.K., Irshad, M., Joshi, Y.K., Duttagupta, S., Tandon, R.K., and Tandon, B.N. (1996). Fulminant hepatic failure in a tropical population: Clinical course, cause, and early predictors of outcome. Hepatology 23:1448–1455.
Aggarwal, S., Yonas, H., Kang, Y., Martin, M., Kramer, D., Obrist, W.D., and Darby, J. (1991). Relationship of cerebral blood flow and cerebral swelling to outcome in patients with acute fulminant hepatic failure. Transplant Proc. 23:1978–1979.
Albrecht, J., and Dolinska, M. (2001). Glutamine as a pathogenic factor in hepatic encephalopathy. J. Neurosci. Res. 65:1–5.
Alper, G., Jarjour, I.T., Reyes, J.D., Towbin, R.B., Hirsch, W.L., and Bergman, I. (1998). Outcome of children with cerebral edema caused by fulminant hepatic failure. Pediatr. Neurol. 18:299–304.
Arnold, S.M., Els, T., Spreer, J., and Schumacher, M. (2001). Acute hepatic encephalopathy with diffuse cortical lesions. Neuroradiology 43:551–554.
Blei, A.T. (1991). Cerebral edema and intracranial hypertension in acute liver failure: Distinct aspects of the same problem. Hepatology 13:376–379.
Blei, A.T., Olafsson, S., Therrien, G., and Butterworth, R.F. (1994). Ammonia-induced brain edema and intracranial hypertension in rats after portacaval anastomosis. Hepatology 19:1437–1444.
Blei, A.T., and Traber, P.G. (1989). Brain edema in experimental fulminant hepatic failure. In (R.F. Butterworth and G. Pomier-Layrargues, eds.), Hepatic Encephalopathy, Humana, Clifton, NJ, pp. 231–244.
Butterworth, R.F., Giguere, J.F., Michaud, J., Lavoie, J., and Layrargues, G.P. (1987). Ammonia: Key factor in the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy. Neurochem. Pathol. 6:270–274.
Chan, R., Erbay, S., Oljeski, S., Thaler, D., and Bhadelia, R. (2003). Hypoglycemia and diffusion-weighted imaging. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 27:420–423.
Conn, H.O. (1994). The hepatic encephalopathies. In (H.O. Conn and J. Bircher, eds.), Hepatic Encephalopathy Syndromes and Therapies, Medi-Ed, Bloomington, IN, pp. 1–12.
Cordoba, J., Gottstein, J., and Blei, A.T. (1996). Glutamine, myo-inositol, and organic brain osmolytes after portacaval anastomosis in the rat: Implications for ammonia-induced brain edema. Hepatology 24:919–923.
Ede, J.R., and Williams, R.W. (1986). Hepatic encephalopathy and cerebral edema. Semin. Liver Dis. 6:107–118.
Gupta, R.K., Saraswat, V.A., Poptani, H., Dhiman, R.K., Kohli, A., Gujral, R.B., and Naik, S.R. (1993). Magnetic resonance imaging and localized in vivo proton spectroscopy in patients with fulminant hepatic failure. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 88:670–674.
Horowitz, M.E., Schafer, D.F., Molnar, P., Jones, E.A., Blasberg, R.G., Patlak, C.S., Waggoner, J., and Fenstermacher, J.D. (1983). Increased blood brain transfer in a rabbit model of acute liver failure. Gastroenterology 84:1003–1011.
Jalan, R., Damink, S.W., Deutz, N.E., Lee, A., and Hayes, P.C. (1999). Moderate hypothermia for uncontrolled intracranial hypertension in acute liver failure. Lancet 354:1164–1168.
Larsen, S. (1996). Cerebral circulation in liver failure: Ohm’s law in force. Semin. Liver Dis. 16:281–292.
Livingstone, A.S., Potvin, M., Goresky, C.A., Finlayson, M.H., and Hinchey, E.J. (1977). Changes in the blood brain barrier in hepatic coma after hepatectomy in the rat. Gastroenterology 73:697–704.
Lodi, R., Tonon, C., Stracciari, A., Weiger, M., Camaggi, V., Iotti, S., Donati, G., Guarino, M., Bolondi, L., and Barbiroli, B. (2004). Diffusion MRI shows increased water apparent diffusion coefficient in the brains of cirrhotics. Neurology 62:762–766.
Master, S., Gottstein, J., and Blei, A.T. (1999). Cerebral blood flow and the development of ammonia-induced brain edema in rats after portacaval anastomosis. Hepatology 30:876–880.
McManus, M.L., Churchwell, K.B., and Strange, K. (1995). Regulation of cell volume in health and disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 333:1260–1266.
Morgan, M.Y. (1996). Noninvasive neuroinvestigation in liver disease. Semin. Liver Dis. 16:293–314.
Norenberg, M.D. (1998). Astroglial dysfunction in hepatic encephalopathy. Metab. Brain Dis. 13:319–335.
O’Grady, J.G., Alexander, G.J., Hayllar, K.M., and Williams, R. (1989). Early indicators of prognosis in fulminant hepatic failure. Gastroenterology 97:439–445.
Rajasekar, D., Datta, N.R., Gupta, R.K., and Rao, S.B. (2004). A graphical user interface for automatic image registration software designed for radiotherapy treatment planning. Med. Dosim. 29:239–246.
Rose, C., Michalak, A., Rao, K.V., Quack, G., Kircheis, G., and Butterworth, R.F. (1999). L-Ornithine-L-Aspartate lowers plasma and cerebrospinal fluid ammonia and prevents brain edema in rats with acute liver failure. Hepatology 30:636–640.
Rovira, A., Grive, E., Pedraza, S., Rovira, A., and Alonso, J. (2001). Magnetization transfer ratio values and proton MR spectroscopy of normal appearing cerebral white matter in patients with liver cirrhosis. Am. J. Neruroradiol. 22:1137–1142.
Rovira, A., Cordoba, J., Raguer, N., and Alonso, J. (2002). Magnetic resonance imaging measurement of brain edema in patients with liver disease: Resolution after liver transplantation. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 15:731–737.
Schaefer, P.W., Grant, P.E., and Gonzalez, R.G. (2000). Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the brain. Radiology 217:331–345.
Strauss, G.I., Hogh, P., Moller, K., Knudsen, G.M., Hansen, B.A., and Larsen, F.S. (1999). Regional cerebral blood flow during mechanical hyperventilation in patients with fulminant hepatic failure. Hepatology 30:1368–1373.
Tandon, B.N., Bernauau, J., O’Grady, J., Gupta, S.D., Krisch, R.E., Liaw, Y.F., Okuda, K., and Acharya, S.K. (1999). Recommendations of the International Association for the study of the Liver Subcommittee on nomenclature of acute and subacute liver failure. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 14:403–404.
Tominaga, S., Watanabe, A., and Tsuji, T. (1991). Synergistic effect of bile acid, endotoxin, and ammonia on brain edema. Metab. Brain Dis. 6:93–105.
Traber, P.G., Dal Canto, M., Ganger, D.R., and Blei, A.T. (1987). Electron microscopic evaluation of brain edema in rabbits with galactosamine-induced fulminant hepatic failure: Ultrastructure and integrity of blood–brain barrier. Hepatology 7:1272–1277.
Ware, A.J., D’Agostino, A.M., and Combes, B. (1971). Cerebral edema: A major complication of massive hepatic necrosis. Gastroenterology 61:877–884.
Wendon, J.A., Harrison, P.M., Keays, R., and Williams, R. (1994). Cerebral blood flow and metabolism in fulminant liver failure. Hepatology 19:1407–1413.
Willard-Mack, C.L., Koehler, R.C., Hirata, T., Cork, L.C., Takahashi, H., Traystman, R.J., and Brusilow, S.W. (1996). Inhibition of glutamine synthase reduces ammonia-induced astrocyte swelling in rats. Neuroscience 71:589–599.
Woods, R.P., Grafton, S.T., Holmes, C.J., Cherry, S.R., and Mazziotta, J.C. (1998). Automated image registration: I. General methods and intrasubject, intramodality validation. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 22:139–152.
Zwingmann, C., Chatauret, N., Rose, C., Leibfritz, D., and Butterworth, R.F. (2004). Selective alterations of brain osmolyte in acute liver failure: Protective effects of mild hypothermia. Brain Res. 999:118–123.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ranjan, P., Mishra, A.M., Kale, R. et al. Cytotoxic Edema Is Responsible for Raised Intracranial Pressure in Fulminant Hepatic Failure: In Vivo Demonstration Using Diffusion-Weighted MRI in Human Subjects. Metab Brain Dis 20, 181–192 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-005-7206-z
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-005-7206-z