Abstract
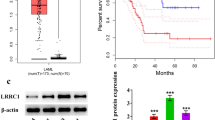
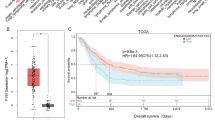
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a type of hematologic diseases, which is related to abnormal genes. The aberrant microtubule actin cross-linking factor 1 (MACF1) is associated with progression of multiple tumors by initiating cell proliferation. Nevertheless, the function and action mechanism of MACF1 in AML cell proliferation remain mostly unknown. Our study aimed to explore the influence of MACF1 on AML cell proliferation by CCK-8 and EdU staining assays. Moreover, we aimed to explore the effect of MACF1 on downstream Runx2 and the PI3K/Akt signaling. MACF1 expression in AML patients was predicted by bioinformatics analysis. Cells were transfected with si-con, si-MACF1 or Runx2 using Lipofectamine 2000. Upregulated MACF1 was found in AML patients and predicted worse overall survival. MACF1 expression was upregulated in AML cells compared with that in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. MACF1 silencing reduced AML cell proliferation. Runx2 level was increased in AML cells, and decreased by silencing MACF1. Runx2 upregulation rescued MACF1 silencing-mediated inhibition of proliferation. MACF1 downregulation inhibited activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway by decreasing Runx2. Activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway abrogated the suppressive role of MACF1 downregulation in AML cell proliferation. In conclusion, MACF1 knockdown decreased AML cell proliferation by reducing Runx2 and inactivating the PI3K/Akt signaling.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Pelcovits A, Niroula R (2020) Acute myeloid leukemia: a review. R I Med J 103(3):38–40
Estey EH (2018) Acute myeloid leukemia: 2019 update on risk-stratification and management. Am J Hematol 93(10):1267–1291
Blackburn LM, Bender S, Brown S (2019) Acute leukemia: diagnosis and treatment. Semin Oncol Nurs 35(6):150950
Prada-Arismendy J, Arroyave JC, Rothlisberger S (2017) Molecular biomarkers in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Rev 31(1):63–76
Cusseddu R, Robert A, Cote JF (2021) Strength through unity: the power of the mega-scaffold MACF1. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:641727
Hu L, Xiao Y, Xiong Z, Zhao F, Yin C, Zhang Y et al (2017) MACF1, versatility in tissue-specific function and in human disease. Semin Cell Dev Biol 69:3–8
Miao Z, Ali A, Hu L, Zhao F, Yin C, Chen C et al (2017) Microtubule actin cross-linking factor 1, a novel potential target in cancer. Cancer Sci 108(10):1953–1958
Zhao W, Yang H, Chai J, Xing L (2021) RUNX2 as a promising therapeutic target for malignant tumors. Cancer Manag Res 13:2539–2548
Schnerch D, Lausch E, Becker H, Felthaus J, Pfeifer D, Mundlos S et al (2014) Up-regulation of RUNX2 in acute myeloid leukemia in a patient with an inherent RUNX2 haploinsufficiency and cleidocranial dysplasia. Leuk Lymphoma 55(8):1930–1932
Sun CC, Li SJ, Chen ZL, Li G, Zhang Q, Li DJ (2019) Expression and prognosis analyses of runt-related transcription factor family in human leukemia. Mol Ther Oncolytics 12:103–111
Qiu WX, Ma XL, Lin X, Zhao F, Li DJ, Chen ZH et al (2020) Deficiency of Macf1 in osterix expressing cells decreases bone formation by Bmp2/Smad/Runx2 pathway. J Cell Mol Med 24(1):317–327
Hu L, Su P, Yin C, Zhang Y, Li R, Yan K et al (2018) Microtubule actin crosslinking factor 1 promotes osteoblast differentiation by promoting beta-catenin/TCF1/Runx2 signaling axis. J Cell Physiol 233(2):1574–1584
Cohen-Solal KA, Boregowda RK, Lasfar A (2015) RUNX2 and the PI3K/AKT axis reciprocal activation as a driving force for tumor progression. Mol Cancer 14:137
Lu H, Jiang T, Ren K, Li ZL, Ren J, Wu G et al (2018) RUNX2 plays an oncogenic role in esophageal carcinoma by activating the PI3K/AKT and ERK signaling pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem 49:217–225
Tandon M, Chen Z, Pratap J (2014) Runx2 activates PI3K/Akt signaling via mTORC2 regulation in invasive breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res 16:R16
Nepstad I, Hatfield KJ, Gronningsaeter IS, Reikvam H (2020) The PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling pathway in human acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells. Int J Mol Sci 21(8):2907
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao G, Li C, Zhang Z (2017) GEPIA: a web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res 45(W1):W98–W102
Klegeris A, Bissonnette CJ, McGeer PL (2003) Reduction of human monocytic cell neurotoxicity and cytokine secretion by ligands of the cannabinoid-type CB2 receptor. Br J Pharmacol 139(4):775–786
Kayser S, Levis MJ (2018) Advances in targeted therapy for acute myeloid leukaemia. Br J Haematol 180(4):484–500
Quick QA (2018) Microtubule-actin crosslinking factor 1 and plakins as therapeutic drug targets. Int J Mol Sci 19(2):368
Wang X, Jian X, Dou J, Wei Z, Zhao F (2020) Decreasing microtubule actin cross-linking factor 1 inhibits melanoma metastasis by decreasing epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Cancer Manag Res 12:663–673
Li Q, Luan Q, Zhu H, Zhao Y, Ji J, Wu F et al (2021) Circular RNA circ_0005774 contributes to proliferation and suppresses apoptosis of acute myeloid leukemia cells via circ_0005774/miR-192-5p/ULK1 ceRNA pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 551:78–85
Wu F, Yin C, Qi J, Duan D, Jiang X, Yu J et al (2020) miR-362-5p promotes cell proliferation and cell cycle progression by targeting GAS7 in acute myeloid leukemia. Hum Cell 33(2):405–415
Hu L, Su P, Li R, Yan K, Chen Z, Shang P et al (2015) Knockdown of microtubule actin crosslinking factor 1 inhibits cell proliferation in MC3T3-E1 osteoblastic cells. BMB Rep 48(10):583–588
Jing GY, Zheng XZ, Ji XX (2021) lncRNA HAND2-AS1 overexpression inhibits cancer cell proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma by downregulating RUNX2 expression. J Clin Lab Anal 35(4):e23717
Zhou M, Zhang P, Zhao Y, Liu R, Zhang Y (2021) Overexpressed circRANBP17 acts as an oncogene to facilitate nasopharyngeal carcinoma via the miR-635/RUNX2 axis. J Cancer 12(14):4322–4331
Guo Z, Zhou K, Wang Q, Huang Y, Ji J, Peng Y et al (2021) The transcription factor RUNX2 fuels YAP1 signaling and gastric cancer tumorigenesis. Cancer Sci 112:3533–3544
Darici S, Alkhaldi H, Horne G, Jorgensen HG, Marmiroli S, Huang X (2020) Targeting PI3K/Akt/mTOR in AML: rationale and clinical evidence. J Clin Med 9(9):2934
Annageldiyev C, Tan SF, Thakur S, Dhanyamraju PK, Ramisetti SR, Bhadauria P et al (2020) The PI3K/AKT pathway inhibitor ISC-4 induces apoptosis and inhibits growth of leukemia in preclinical models of acute myeloid leukemia. Front Oncol 10:393
Qu Y, Wang Y, Wang P, Lin N, Yan X, Li Y (2020) Overexpression of long noncoding RNA HOXA-AS2 predicts an adverse prognosis and promotes tumorigenesis via SOX4/PI3K/AKT pathway in acute myeloid leukemia. Cell Biol Int 44(8):1745–1759
Shi M, Yang R, Lin J, Wei QI, Chen L, Gong W et al (2021) LncRNA-SNHG16 promotes proliferation and migration of acute myeloid leukemia cells via PTEN/PI3K/AKT axis through suppressing CELF2 protein. J Biosci 46:4
Han M, Chen L, Wang Y (2018) miR-218 overexpression suppresses tumorigenesis of papillary thyroid cancer via inactivation of PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway by targeting Runx2. Onco Targets Ther 11:6305–6316
Pranavkrishna S, Sanjeev G, Akshaya RL, Rohini M, Selvamurugan N (2021) Regulation of Runx2 and its signaling pathways by microRNAs in breast cancer metastasis. Curr Protein Pept Sci 22:534–547
Lin X, Xiao Y, Chen Z, Ma J, Qiu W, Zhang K et al (2019) Microtubule actin crosslinking factor 1 (MACF1) knockdown inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis via Akt/GSK3beta/NFATc1 signalling pathway. Mol Cell Endocrinol 494:110494
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PW and JZ conducted the experiments and wrote the manuscript. HZ collected and analyzed the data. FZ collected the data and designed and supervised the study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, P., Zhang, J., Zhang, H. et al. The role of MACF1 on acute myeloid leukemia cell proliferation is involved in Runx2-targeted PI3K/Akt signaling. Mol Cell Biochem 478, 433–441 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-022-04517-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-022-04517-x