Abstract
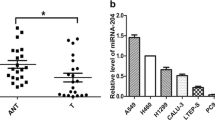
MicroRNAs play critical roles in the development and progression of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). miR-96 acts as an oncogene in some malignancies, while its role in NSCLC is unclear. Here, we validated that miR-96 was significantly increased in both human NSCLC tissues and cell lines. Inhibition of miR-96 expression remarkably reduced cell proliferation, colony formation, migration, and invasion of NSCLC cells. Reversion-inducing-cysteine-rich protein with kazal motifs (RECK) was identified as a target of miR-96 in NSCLC cells. In addition, the expression of RECK was found to be negatively correlated with the expression of miR-96 in NSCLC tissues. Our data suggest that miR-96 might promote the growth and motility of NSCLC cells partially by targeting RECK.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Subramaniam S, Thakur RK, Yadav VK, Nanda R, Chowdhury S, Agrawal A (2013) Lung cancer biomarkers: state of the art. J Carcinog 12:3. doi:10.4103/1477-3163.107958
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A (2012) Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 62:10–29. doi:10.3322/caac.20138
Verdecchia A, Francisci S, Brenner H, Gatta G, Micheli A, Mangone L, Kunkler I, EUROCARE-4 Working Group (2007) Recent cancer survival in Europe: a 2000–02 period analysis of EUROCARE-4 data. Lancet Oncol 8:784–796. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(07)70246-2
Graves P, Zeng Y (2012) Biogenesis of mammalian microRNAs: a global view. Genomics Proteomics Bioinform 10:239–245. doi:10.1016/j.gpb.2012.06.004
Sittka A, Schmeck B (2013) MicroRNAs in the lung. Adv Exp Med Biol 774:121–134. doi:10.1007/978-94-007-5590-1_7
Zhao H, Wang Y, Yang L, Jiang R, Li W (2013) miR-25 promotes gastric cancer cells growth and motility by targeting RECK. Mol Cell Biochem. doi:10.1007/s11010-013-1829-x
Chai ZT, Kong J, Zhu XD, Zhang YY, Lu L, Zhou JM, Wang LR, Zhang KZ, Zhang QB, Ao JY, Wang M, Wu WZ, Wang L, Tang ZY, Sun HC (2013) MicroRNA-26a inhibits angiogenesis by down-regulating VEGFA through the PIK3C2alpha/Akt/HIF-1alpha pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One 8:e77957. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0077957
Ke Y, Zhao W, Xiong J, Cao R (2013) Downregulation of miR-16 promotes growth and motility by targeting HDGF in non-small cell lung cancer cells. FEBS Lett 587:3153–3157. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2013.08.010
Zhao B, Han H, Chen J, Zhang Z, Li S, Fang F, Zheng Q, Ma Y, Zhang J, Wu N, Yang Y (2013) MicroRNA let-7c inhibits migration and invasion of human non-small cell lung cancer by targeting ITGB3 and MAP4K3. Cancer Lett. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2013.08.030
Ma Q, Jiang Q, Pu Q, Zhang X, Yang W, Wang Y, Ye S, Wu S, Zhong G, Ren J, Zhang Y, Liu L, Zhu W (2013) MicroRNA-143 inhibits migration and invasion of human non-small-cell lung cancer and its relative mechanism. Int J Biol Sci 9:680–692. doi:10.7150/ijbs.6623
Zhang N, Wei X, Xu L (2013) miR-150 promotes the proliferation of lung cancer cells by targeting P53. FEBS Lett 587:2346–2351. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2013.05.059
Lei L, Huang Y, Gong W (2013) Inhibition of miR-92b suppresses nonsmall cell lung cancer cells growth and motility by targeting RECK. Mol Cell Biochem. doi:10.1007/s11010-013-1882-5
Chen Y, Peng W, Lu Y, Chen J, Zhu YY, Xi T (2013) MiR-200a enhances the migrations of A549 and SK-MES-1 cells by regulating the expression of TSPAN1. J Biosci 38:523–532
Haflidadottir BS, Larne O, Martin M, Persson M, Edsjo A, Bjartell A, Ceder Y (2013) Upregulation of miR-96 enhances cellular proliferation of prostate cancer cells through FOXO1. PLoS One 8:e72400. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0072400
Guo Y, Liu H, Zhang H, Shang C, Song Y (2012) miR-96 regulates FOXO1-mediated cell apoptosis in bladder cancer. Oncol Lett 4:561–565. doi:10.3892/ol.2012.775
Xu D, He X, Chang Y, Xu C, Jiang X, Sun S, Lin J (2013) Inhibition of miR-96 expression reduces cell proliferation and clonogenicity of HepG2 hepatoma cells. Oncol Rep 29:653–661. doi:10.3892/or2012.2138
Ma L, Huang Y, Zhu W, Zhou S, Zhou J, Zeng F, Liu X, Zhang Y, Yu J (2011) An integrated analysis of miRNA and mRNA expressions in non-small cell lung cancers. PLoS One 6:e26502. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0026502
Chen RX, Xia YH, Xue TC, Ye SL (2012) Suppression of microRNA-96 expression inhibits the invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Mol Med Rep 5:800–804. doi:10.3892/mmr.2011.695
Yu S, Lu Z, Liu C, Meng Y, Ma Y, Zhao W, Liu J, Yu J, Chen J (2010) miRNA-96 suppresses KRAS and functions as a tumor suppressor gene in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res 70:6015–6025. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4531
Wang L, Wang Q, Li HL, Han LY (2013) Expression of MiR200a, miR93, metastasis-related gene RECK and MMP2/MMP9 in human cervical carcinoma—relationship with prognosis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 14:2113–2118
Wang N, Zhang CQ, He JH, Duan XF, Wang YY, Ji X, Zang WQ, Li M, Ma YY, Wang T, Zhao GQ (2013) MiR-21 down-regulation suppresses cell growth, invasion and induces cell apoptosis by targeting FASL, TIMP3, and RECK genes in esophageal carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci 58:1863–1870. doi:10.1007/s10620-013-2612-2
Chiang CH, Hou MF, Hung WC (2013) Up-regulation of miR-182 by beta-catenin in breast cancer increases tumorigenicity and invasiveness by targeting the matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor RECK. Biochim Biophys Acta 1830:3067–3076. doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.01.009
Hirata H, Ueno K, Shahryari V, Tanaka Y, Tabatabai ZL, Hinoda Y, Dahiya R (2012) Oncogenic miRNA-182-5p targets Smad4 and RECK in human bladder cancer. PLoS One 7:e51056. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0051056
Chandana EP, Maeda Y, Ueda A, Kiyonari H, Oshima N, Yamamoto M, Kondo S, Oh J, Takahashi R, Yoshida Y, Kawashima S, Alexander DB, Kitayama H, Takahashi C, Tabata Y, Matsuzaki T, Noda M (2010) Involvement of the Reck tumor suppressor protein in maternal and embryonic vascular remodeling in mice. BMC Dev Biol 10:84. doi:10.1186/1471-213X-10-84
Welm B, Mott J, Werb Z (2002) Developmental biology: vasculogenesis is a wreck without RECK. Curr Biol 12:R209–R211
Xin C, Buhe B, Hongting L, Chuanmin Y, Xiwei H, Hong Z, Lulu H, Qian D, Renjie W (2013) MicroRNA-15a promotes neuroblastoma migration by targeting reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs (RECK) and regulating matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression. FEBS J 280:855–866. doi:10.1111/febs.12074
Li N, Tang B, Zhu ED, Li BS, Zhuang Y, Yu S, Lu DS, Zou QM, Xiao B, Mao XH (2012) Increased miR-222 in H. pylori-associated gastric cancer correlated with tumor progression by promoting cancer cell proliferation and targeting RECK. FEBS Lett 586:722–728. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2012.01.025
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Haizhou Guo and Qianping Li have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, H., Li, Q., Li, W. et al. miR-96 downregulates RECK to promote growth and motility of non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mol Cell Biochem 390, 155–160 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-1966-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-1966-x