Abstract
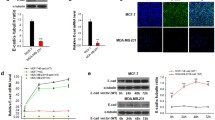
To research the effects of silencing transcription factor SNAI1 on the in vitro biological phenotypes of breast cancer cell line MCF-7, based on the gene sequence of SNAI1, we linked shRNA with the green fluorescent protein-expressing eukaryotic expression vector pGCsilencer™ U6/Neo/GFP, and transfected it into MCF-7 cells. The SNAI1 gene-silencing effect was authenticated by RT-PCR and immunofluorescence. We then examined the effect of gene silencing on the expression of epithelial and mesenchymal markers and on their biological phenotypes of the target cells. Finally, we explained that SNAI1 was bound to E-cadherin in MCF-7 cells by ChIP. Silencing SNAI1 upregulated the expression of epithelial markers claudin-4, claudin-7, and E-cadherin, while expression of the mesenchymal marker matrix metalloproteinase-2 was downregulated. The capacity for proliferation, migration, and invasion was diminished. SNAI1 binds to the E-cadherin gene promoter and inhibits its transcription. We can conclude that silencing gene SNAI1 inhibits expression of properties that are associated with the malignant phenotype of MCF-7 cells and reverses the epithelial–mesenchymal transition process by regulating relevant target gene E-cadherin.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jung KW, Won YJ, Kong HJ, Oh CM, Seo HG, Lee JS (2013) Cancer statistics in Korea: incidence, mortality, survival and prevalence in 2010. Cancer Res Treat 45:1–14. doi:10.4143/crt.2013.45.1.1
Cowin P, Rowlands TM, Hatsell SJ (2005) Cadherins and catenins in breast cancer. Curr Opin Cell Biol 17:499–508. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2005.08.014
May CD, Sphyris N, Evans KW, Werden SJ, Guo W, Mani SA (2011) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cells: a dangerously dynamic duo in breast cancer progression. Breast Cancer Res 13:202. doi:10.1186/bcr2789
Blanco MJ, Moreno-Bueno G, Sarrio D, Locascio A, Cano A, Palacios J, Nieto MA (2002) Correlation of Snail expression with histological grade and lymph node status in breast carcinomas. Oncogene 21:3241–3246. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1205416
Geradts J, de Herreros AG, Su Z, Burchette J, Broadwater G, Bachelder RE (2011) Nuclear Snail1 and nuclear ZEB1 protein expression in invasive and intraductal human breast carcinomas. Hum Pathol 42:1125–1131. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2010.11.004
Peinado H, Ballestar E, Esteller M, Cano A (2003) Snail mediates e-cadherin repression by the recruitment of the Sin3A/histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1)/HDAC2 complex. Mol Cell Biol 24:306–319. doi:10.1128/mcb.24.1.306-319.2004
Foubert E, De Craene B, Berx G (2010) Key signalling nodes in mammary gland development and cancer. The Snail1-Twist1 conspiracy in malignant breast cancer progression. Breast Cancer Res 12:206. doi:10.1186/bcr2585
van der Wurff AA, Vermeulen SJ, van der Linden EP, Mareel MM, Bosman FT, Arends JW (1997) Patterns of alpha- and beta-catenin and E-cadherin expression in colorectal adenomas and carcinomas. J Pathol 182:325–330. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-9896(199707)182:3<325:AID-PATH865>3.0.CO;2-Y
Dang H, Ding W, Emerson D, Rountree CB (2011) Snail1 induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and tumor initiating stem cell characteristics. BMC Cancer 11:396. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-11-396
Schwartz B, Melnikova VO, Tellez C, Mourad-Zeidan A, Blehm K, Zhao YJ, McCarty M, Adam L, Bar-Eli M (2007) Loss of AP-2alpha results in deregulation of E-cadherin and MMP-9 and an increase in tumorigenicity of colon cancer cells in vivo. Oncogene 26:4049–4058. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210193
Mauro L, Catalano S, Bossi G, Pellegrino M, Barone I, Morales S, Giordano C, Bartella V, Casaburi I, Ando S (2007) Evidences that leptin up-regulates E-cadherin expression in breast cancer: effects on tumor growth and progression. Cancer Res 67:3412–3421. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-2890
Thiery JP, Sleeman JP (2006) Complex networks orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:131–142. doi:10.1038/nrm1835
Peinado H, Olmeda D, Cano A (2007) Snail, Zeb and bHLH factors in tumour progression: an alliance against the epithelial phenotype? Nat Rev Cancer 7:415–428. doi:10.1038/nrc2131
Singh A, Settleman J (2010) EMT, cancer stem cells and drug resistance: an emerging axis of evil in the war on cancer. Oncogene 29:4741–4751. doi:10.1038/onc.2010.215
Ding JX, Feng YJ, Yao LQ, Yu M, Jin HY, Yin LH (2006) The reinforcement of invasion in epithelial ovarian cancer cells by 17 beta-Estradiol is associated with up-regulation of Snail. Gynecol Oncol 103:623–630. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2006.04.023
Peng X, Mehta R, Wang S, Chellappan S, Mehta RG (2006) Prohibitin is a novel target gene of vitamin D involved in its antiproliferative action in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 66:7361–7369. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-1004
Moreno-Bueno G, Portillo F, Cano A (2008) Transcriptional regulation of cell polarity in EMT and cancer. Oncogene 27:6958–6969. doi:10.1038/onc.2008.346
Ferrari-Amorotti G, Fragliasso V, Esteki R, Prudente Z, Soliera AR, Cattelani S, Manzotti G, Grisendi G, Dominici M, Pieraccioli M, Raschella G, Chiodoni C, Colombo MP, Calabretta B (2013) Inhibiting interactions of lysine demethylase LSD1 with snail/slug blocks cancer cell invasion. Cancer Res 73:235–245. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-1739
Peinado H, Ballestar E, Esteller M, Cano A (2004) Snail mediates E-cadherin repression by the recruitment of the Sin3A/histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1)/HDAC2 complex. Mol Cell Biol 24:306–319
Shimokawa M, Haraguchi M, Kobayashi W, Higashi Y, Matsushita S, Kawai K, Kanekura T, Ozawa M (2013) The transcription factor Snail expressed in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and down-regulates COX-2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 430:1078–1082. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.12.035
Wang H, Wang HS, Zhou BH, Li CL, Zhang F, Wang XF, Zhang G, Bu XZ, Cai SH, Du J (2013) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) induced by TNF-alpha requires AKT/GSK-3beta-mediated stabilization of snail in colorectal cancer. PLoS ONE 8:e56664. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0056664
Micalizzi DS, Ford HL (2009) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in development and cancer. Future Oncol 5:1129–1143. doi:10.2217/fon.09.94
Batlle E, Sancho E, Franci C, Dominguez D, Monfar M, Baulida J, Garcia De Herreros A (2000) The transcription factor snail is a repressor of E-cadherin gene expression in epithelial tumour cells. Nat Cell Biol 2:84–89. doi:10.1038/35000034
Olmeda D, Moreno-Bueno G, Flores JM, Fabra A, Portillo F, Cano A (2007) SNAI1 is required for tumor growth and lymph node metastasis of human breast carcinoma MDA-MB-231 cells. Cancer Res 67:11721-11731. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-2318
St Croix B, Sheehan C, Rak JW, Florenes VA, Slingerland JM, Kerbel RS (1998) E-Cadherin-dependent growth suppression is mediated by the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27(KIP1). J Cell Biol 142:557–571
Wang Z, Gong Q, Fan Q (2012) Expression of E-cadherin in angiomyolipoma. Hum Pathol 43:2348–2353. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2012.04.011
Kitase Y, Shuler CF (2013) Microtubule disassembly prevents palatal fusion and alters regulation of the E-cadherin/catenin complex. Int J Dev Biol 57:55–60. doi:10.1387/ijdb.120117yk
Chen D, Wang Y, Zhang K, Jiao X, Yan B, Liang J (2012) Antisense oligonucleotide against clusterin regulates human hepatocellular carcinoma invasion through transcriptional regulation of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and e-cadherin. Int J Mol Sci 13:10594–10607. doi:10.3390/ijms130810594
Matter K, Aijaz S, Tsapara A, Balda MS (2005) Mammalian tight junctions in the regulation of epithelial differentiation and proliferation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 17:453–458. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2005.08.003
Fabre-Guillevin E, Malo M, Cartier-Michaud A, Peinado H, Moreno-Bueno G, Vallee B, Lawrence DA, Palacios J, Cano A, Barlovatz-Meimon G, Charriere-Bertrand C (2008) PAI-1 and functional blockade of SNAI1 in breast cancer cell migration. Breast Cancer Res 10:R100. doi:10.1186/bcr2203
Fan F, Samuel S, Evans KW, Lu J, Xia L, Zhou Y, Sceusi E, Tozzi F, Ye XC, Mani SA, Ellis LM (2012) Overexpression of Snail induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and a cancer stem cell-like phenotype in human colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Med 1:5–16. doi:10.1002/cam4.4
Hu CT, Wu JR, Chang TY, Cheng CC, Wu WS (2008) The transcriptional factor Snail simultaneously triggers cell cycle arrest and migration of human hepatoma HepG2. J Biomed Sci 15:343–355. doi:10.1007/s11373-007-9230-y
Kevans D, Wang LM, Sheahan K, Hyland J, O’Donoghue D, Mulcahy H, O’Sullivan J (2011) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) protein expression in a cohort of stage II colorectal cancer patients with characterized tumor budding and mismatch repair protein status. Int J Surg Pathol 19:751–760. doi:10.1177/1066896911414566
Jiao Y, Feng X, Zhan Y, Wang R, Zheng S, Liu W, Zeng X (2012) Matrix metalloproteinase-2 promotes alphavbeta3 integrin-mediated adhesion and migration of human melanoma cells by cleaving fibronectin. PLoS ONE 7:e41591. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0041591
Nagase H, Woessner JF Jr (1999) Matrix metalloproteinases. J Biol Chem 274:21491–21494
Rosivatz E, Becker I, Specht K, Fricke E, Luber B, Busch R, Hofler H, Becker KF (2002) Differential expression of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition regulators snail, SIP1, and twist in gastric cancer. Am J Pathol 161:1881–1891. doi:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64464-1
Ikenouchi J, Matsuda M, Furuse M, Tsukita S (2003) Regulation of tight junctions during the epithelium-mesenchyme transition: direct repression of the gene expression of claudins/occludin by Snail. J Cell Sci 116:1959–1967. doi:10.1242/jcs.00389
Ohkubo T, Ozawa M (2004) The transcription factor Snail downregulates the tight junction components independently of E-cadherin downregulation. J Cell Sci 117:1675–1685. doi:10.1242/jcs.01004
Jorda M, Olmeda D, Vinyals A, Valero E, Cubillo E, Llorens A, Cano A, Fabra A (2005) Upregulation of MMP-9 in MDCK epithelial cell line in response to expression of the Snail transcription factor. J Cell Sci 118:3371–3385. doi:10.1242/jcs.02465
Miyoshi A, Kitajima Y, Sumi K, Sato K, Hagiwara A, Koga Y, Miyazaki K (2004) Snail and SIP1 increase cancer invasion by upregulating MMP family in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Br J Cancer 90:1265–1273. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6601685
Ikenouchi J, Matsuda M, Furuse M, Tsukita S (2003) Regulation of tight junctions during the epithelium-mesenchyme transition: direct repression of the gene expression of claudins/occludin by Snail. J Cell Sci 116:1959–1967. doi:10.1242/jcs.00389
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Code: 81172499) and Science and Technology Development Plan of the Office of Science and Technology Project in Jilin Province (Code: 201115113). We thank Dr. William Orr, Department of Pathology, University of Manitoba, Canada, for his help in the preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yan Lu and Lina Yu have contributed equally to this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, Y., Yu, L., Yang, M. et al. The effects of shRNA-mediated gene silencing of transcription factor SNAI1 on the biological phenotypes of breast cancer cell line MCF-7. Mol Cell Biochem 388, 113–121 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1903-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1903-4