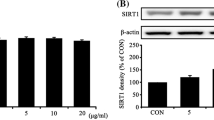
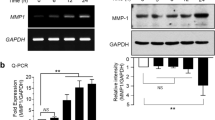
Abstract
Type I collagen is the major constituent of the skin and the reduction of dermal type I collagen content is closely associated with the intrinsic skin aging. We here found that esculetin, 6,7-dihydroxycoumarin, strongly induces type I procollagen expression in human dermal fibroblasts. Esculetin not only increased protein levels of type I procollagen but also increased mRNA levels of COL1A1 but not COL1A2. Esculetin activated the MAPKs (ERK1/2, p38, JNK) and PI3K/Akt pathways, through which it promoted the type I procollagen expression. We also demonstrated that the binding motifs for transcription factor Sp1 occur with the highest frequency in the COL1A1 promoter and that esculetin increases the Sp1 expression through the MAPK and PI3K/Akt pathways. These results suggest that esculetin promotes type I procollagen expression through the MAPK and PI3K/Akt pathways and that Sp1 might be involved in the esculetin-induced type I procollagen expression via activation of the COL1A1 transcription.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rittie L, Fisher GJ (2002) UV-light-induced signal cascades and skin aging. Ageing Res Rev 1:705–720
Shoulders MD, Raines RT (2009) Collagen structure and stability. Annu Rev Biochem 78:929–958
Chung JH, Seo JY, Choi HR et al (2001) Modulation of skin collagen metabolism in aged and photoaged human skin in vivo. J Invest Dermatol 117:1218–1224
Varani J, Warner RL, Gharaee-Kermani M et al (2000) Vitamin A antagonizes decreased cell growth and elevated collagen-degrading matrix metalloproteinases and stimulates collagen accumulation in naturally aged human skin. J Invest Dermatol 114:480–486
Varani J, Dame MK, Rittie L et al (2006) Decreased collagen production in chronologically aged skin: roles of age-dependent alteration in fibroblast function and defective mechanical stimulation. Am J Pathol 168:1861–1868
Takeda K, Gosiewska A, Peterkofsky B (1992) Similar, but not identical, modulation of expression of extracellular matrix components during in vitro and in vivo aging of human skin fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol 153:450–459
Ikeda H, Sunazuka T, Suzuki H et al (2008) EM703, the new derivative of erythromycin, inhibits transcription of type I collagen in normal and scleroderma fibroblasts. J Dermatol Sci 49:195–205
Park WY, Park JS, Cho KA et al (2000) Up-regulation of caveolin attenuates epidermal growth factor signaling in senescent cells. J Biol Chem 275:20847–20852
Kim SR, Park JH, Lee ME et al (2008) Selective COX-2 inhibitors modulate cellular senescence in human dermal fibroblasts in a catalytic activity-independent manner. Mech Ageing Dev 129:706–713
Pearson G, Robinson F, Beers Gibson T et al (2001) Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways: regulation and physiological functions. Endocr Rev 22:153–183
Leevers SJ, Vanhaesebroeck B, Waterfield MD (1999) Signalling through phosphoinositide 3-kinases: the lipids take centre stage. Curr Opin Cell Biol 11:219–225
Kaneko T, Tahara S, Takabayashi F (2003) Suppression of lipid hydroperoxide-induced oxidative damage to cellular DNA by esculetin. Biol Pharm Bull 26:840–844
Kim SH, Kang KA, Zhang R et al (2008) Protective effect of esculetin against oxidative stress-induced cell damage via scavenging reactive oxygen species. Acta Pharmacol Sin 29:1319–1326
Lee BC, Lee SY, Lee HJ et al (2007) Anti-oxidative and photo-protective effects of coumarins isolated from Fraxinus chinensis. Arch Pharm Res 30:1293–1301
Fylaktakidou KC, Hadjipavlou-Litina DJ, Litinas KE et al (2004) Natural and synthetic coumarin derivatives with anti-inflammatory/antioxidant activities. Curr Pharm Des 10:3813–3833
Witaicenis A, Seito LN, Di Stasi LC (2010) Intestinal anti-inflammatory activity of esculetin and 4-methylesculetin in the trinitrobenzenesulphonic acid model of rat colitis. Chem Biol Interact 186:211–218
Kawase M, Sakagami H, Hashimoto K et al (2003) Structure-cytotoxic activity relationships of simple hydroxylated coumarins. Anticancer Res 23:3243–3246
Kuo HC, Lee HJ, Hu CC et al (2006) Enhancement of esculetin on Taxol-induced apoptosis in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 210:55–62
Park C, Jin CY, Kim GY et al (2008) Induction of apoptosis by esculetin in human leukemia U937 cells through activation of JNK and ERK. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 227:219–228
Wang CJ, Hsieh YJ, Chu CY et al (2002) Inhibition of cell cycle progression in human leukemia HL-60 cells by esculetin. Cancer Lett 183:163–168
Asano Y, Ihn H, Yamane K et al (2004) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase is involved in alpha2(I) collagen gene expression in normal and scleroderma fibroblasts. J Immunol 172:7123–7135
Sato M, Shegogue D, Gore EA et al (2002) Role of p38 MAPK in transforming growth factor beta stimulation of collagen production by scleroderma and healthy dermal fibroblasts. J Invest Dermatol 118:704–711
Chetty A, Cao GJ, Nielsen HC (2006) Insulin-like growth factor-I signaling mechanisms, type I collagen and alpha smooth muscle actin in human fetal lung fibroblasts. Pediatr Res 60:389–394
Jinnin M, Ihn H, Yamane K et al (2004) Interleukin-13 stimulates the transcription of the human alpha2(I) collagen gene in human dermal fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 279:41783–41791
Lee J, Jung E, Yu H et al (2008) Mechanisms of carvacrol-induced expression of type I collagen gene. J Dermatol Sci 52:160–169
Jimenez SA, Gaidarova S, Saitta B et al (2001) Role of protein kinase C-delta in the regulation of collagen gene expression in scleroderma fibroblasts. J Clin Invest 108:1395–1403
Wierstra I (2008) Sp1: emerging roles—beyond constitutive activation of TATA-less housekeeping genes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 372:1–13
Sysa P, Potter JJ, Liu X et al (2009) Transforming growth factor-beta1 up-regulation of human alpha(1)(I) collagen is mediated by Sp1 and Smad2 transacting factors. DNA Cell Biol 28:425–434
Kypriotou M, Beauchef G, Chadjichristos C et al (2007) Human collagen Krox up-regulates type I collagen expression in normal and scleroderma fibroblasts through interaction with Sp1 and Sp3 transcription factors. J Biol Chem 282:32000–32014
Chuang JY, Wang YT, Yeh SH et al (2008) Phosphorylation by c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase 1 regulates the stability of transcription factor Sp1 during mitosis. Mol Biol Cell 19:1139–1151
Kanda N, Koike S, Watanabe S (2005) Prostaglandin E2 enhances neurotrophin-4 production via EP3 receptor in human keratinocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 315:796–804
Trisciuoglio D, Iervolino A, Candiloro A et al (2004) bcl-2 induction of urokinase plasminogen activator receptor expression in human cancer cells through Sp1 activation: involvement of ERK1/ERK2 activity. J Biol Chem 279:6737–6745
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2010-0007188), a grant from the National R&D Program for Cancer Control, Ministry for Health and welfare, Republic of Korea (1020420), and the Nutraceutical Bio Brain Korea 21 Project and Well-being Bioproducts Regional Innovation Center Project of Kangwon National University in 2011. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, J.H., Kim, S.R., An, H.J. et al. Esculetin promotes type I procollagen expression in human dermal fibroblasts through MAPK and PI3K/Akt pathways. Mol Cell Biochem 368, 61–67 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-012-1342-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-012-1342-7