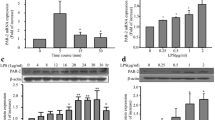
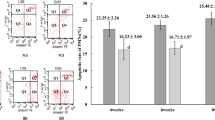
Abstract
As is the case for tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-1β (IL-1β), degranulated substances (DS) released from polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN) and H2O2 cause endothelial cell apoptosis through the phosphorylation of members of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) family. Stimulation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) with IL-1β or TNF-α/cycloheximide (CHX) was found to enhance the phosphorylation of p38 and Jun-N-terminal kinase (JNK) in a time-dependent fashion, but did not affect the time-dependent phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase. In addition, IL-1β and TNF-α/CHX induced the phosphorylation of activating transcription factor-2 (ATF-2), but not c-Jun. Moreover, the p38 in HUVEC was phosphorylated by DS released from PMN and also by H2O2, but not by •O2 − induced by myeloperoxidase (MPO) of PMN. On the other hand, caspase 8 in HUVEC was activated by DS, but not by H2O2 and/or •O2 −. In addition, caspases 3 and 7 were cleaved by the treatment of DS and turned into active forms. DS was concentrated, analyzed by electrophoresis, and revealed to contain precursor and subunits of MPO (90, 60, and 14 kDa) and another peptide with a molecular weight of about 28 kDa. Because SB203580 that was an inhibitor of p38 MAPK did not repress phosphorylation of ATF-2 in HUVEC, it was suggested that JNK was more important than p38 in a series of signaling courses. These results suggest the possibility that not only TNF-α/CHX and IL-1β but also DS released from PMN and the cell-permeable reactive oxygen species H2O2 induce blood vessel injury through endothelial apoptosis.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin-1β
- DS:
-
Degranulated substances
- PMN:
-
Polymorphonuclear leukocytes
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- HUVEC:
-
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells
- CHX:
-
Cycloheximide
- JNK:
-
Jun-N-terminal kinase
- ERK:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- ATF-2:
-
Activating transcription factor-2
- MPO:
-
Myeloperoxidase
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- TNFR:
-
TNF-α receptor
- FMLP:
-
FormylMet-Leu-Phe
- CB:
-
Cytochalasin B
- EGTA:
-
Ethyleneglycol-bis(2-aminoethylether)tetraacetic acid
- PMSF:
-
Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline without calcium and magnesium
- HBSS:
-
Hanks’ balanced salt solution
- SDS:
-
Sodium dodecyl-sulfate
References
Wang CY, Mayo MW, Korneluk RG, Goeddel DV, Baldwin AS Jr (1998) NF-κB antiapoptosis: induction of TRAF1 and TRAF2 and c-IAP1 and c-IAP2 to suppress caspase-8 activation. Science 281:1680–1683
Hoshino A, Nagao T, Ito-Ihara T, Ishida-Okawara A, Uno K, Muso E, Nagi-Miura N, Ohno N, Tokunaka K, Naoe S, Hashimoto H, Yasuhara M, Yamamoto K, Suzuki K (2007) Trafficking of QD-conjugated MPO-ANCA in murine systemic vasculitis and glomerulonephritis model mice. Microbiol Immunol 51:551–566
Yamamoto K, Miyoshi-Koshio T, Utuki Y, Mizuno S, Suzuki K (1991) Virucidal activity and viral protein modification by myeloperoxidase: a candidate for defense factor of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes against Influenza infection. J Infect Dis 164:8–14
Aratani Y, Kura F, Watanabe H, Akagawa H, Takano Y, Suzuki K, Maeda N, Koyama M (2000) Differential host susceptibility to pulmonary infections with bacteria and fungi in mice deficient in myeloperoxidase. J Infect Dis 182:1276–1279
Stehlik C, de Martin R, Kumabashiri I, Schmid JA, Binder BR, Lipp J (1998) Nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB-regulated X-chromosome-linked IAP gene expression protects endothelial cells from tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced apoptosis. J Exp Med 188:211–216
Suzuki K, Okazaki T (2004) Contribution of myeloperoxidase in vasculitis development. Jpn J Infect Dis 57:S2–S3
Jin S, Ray RM, Johnson LR (2008) TNF-α/cycloheximide-induced apoptosis in intestinal epithelial cells requires Rac1-regulated reactive oxygen species. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 294:G928–G937
Han J, Lee JD, Bibbs L, levitch RJU (1994) A MAP kinase targeted by endotoxin and hyperosmolarity in mammalian cells. Science 265:808–811
Kyriakis JM, Banerjee P, Nikolakaki E, Dai T, Rubie EA, Ahmad MF, Avruch J, Woodgett JR (1994) The stress-activated protein kinase subfamily of c-Jun kinase. Nature 369:156–160
Lechner C, Zahalka MA, Giot JF, Moller NP, Ullrich A (1996) ERK6, a mitogen-activated protein kinase involved in C2C12 myoblast differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:4355–4359
Lee JD, Laydon JT, McDonnell PC, Gallagher TF, Kumar S, Green D, McNulty D, Blumenthal MJ, Heys JR, Landvatter SW et al (1994) A protein kinase involved in the regulation of inflammatory cytokine biosynthesis. Nature 372:739–746
Rouse J, Cohen P, Trigon S, Morange M, Alonso-Llamazares A, Zamanillo D, Hunt T (1994) A novel kinase cascade triggered by stress and heat shock that stimulates MAPKAP kinase-2 and phosphorylation of the small heat shock proteins. Cell 78:1027–1037
Yilmaz A, Kliche S, Mayr-Beyrle U, Fellbrich G, Waltenberger J (2003) p38 MAPK inhibition is critically involved in VEGFR-2-mediated endothelial cell survival. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 306:730–736
Gomes E, Rockwell P (2008) p38 MAPK as a negative regulator of VEGF/VEGFR-2 signaling pathway in serum deprived human SK-N-SH neuroblastoma cells. Neurosci Lett 431:95–100
Cuenda A, Rousseau S (2007) p38 MAP-kinases pathway regulation, function and role in human diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta 1773:1358–1375
Zhang C-L, Song F, Zhang J, Song Q-H (2010) Hypoxia-induced Bcl-2 expression in endothelial cells via p38 MAPK pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 394:976–980
King LA, Toledo AH, Rivera-Chavez FA, Toledo-Pereyra LH (2009) Role of p38 and JNK in liver ischemia and reperfusion. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 16:763–770
Borregaard N, Cowland JB (1997) Granules of the human neutrophilic polymorphonuclear leukocyte. Blood 89:3503–3521
Homma T, Suzuki K, Kudo Y, Inagawa M, Mizuno S, Yamaguchi K, Tagawa M (1989) Preparation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against human myeloperoxidase. Arch Biochem Biophys 273:189–196
Dimmeler S, Haendeler J, Nehls M, Zeiher AM (1997) Suppression of apoptosis by nitric oxide via inhibition of interleukin-1β-converting enzyme (ICE)-like and cysteine protease protein (CPP)-32-like proteases. J Exp Med 185:601–607
de Klaver MJM, Manning L, Palmer LA, Rich GF (2002) Isoflurane pretreatment inhibits cytokine-induced cell death in cultured rat smooth muscle cells and human endothelial cells. Anesthesiology 97:24–32
Kofler S, Nickel T, Weis M (2005) Role of cytokines in cardiovascular diseases: a focus on endothelial responses to inflammation. Clin Sci 108:205–213
Thuret G, Chiquet C, Herrag S, Dumollard J-M, Boudard D, Bednarz J, Campos L, Gain P (2003) Mechanisms of staurosporine induced apoptosis in a human corneal endothelial cell line. Br J Ophthalmol 87:346–352
Sprague AH, Khalil RA (2009) Inflammatory cytokines in vascular dysfunction and vascular disease. Biochem Pharmacol 78:539–552
Gavrieli Y, Sherman Y, Ben-Sasson SA (1992) Identification of programmed cell death in situ via specific labeling of nuclear DNA fragmentation. J Cell Biol 119:493–501
Surapisitchat J, Hoefen RJ, Pi X, Yoshizumi M, Yan C, Berk BC (2001) Fluid shear stress inhibits TNF-α activation of JNK but not ERK1/2 or p38 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells: inhibitory crosstalk among MAPK family members. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:6476–6481
Moriguchi T, Toyoshima F, Masuyama N, Hanafusa H, Gotoh Y, Nishida E (1997) A novel SAPK/JNK kinase, MKK7, stimulated by TNF-α and cellular stresses. EMBO J 16:7045–7053
Wang X, Destrument A, Tournier C (2007) Physiological roles of MKK4 and MKK7: insights from animal models. Biochim Biophys Acta 1773:1349–1357
Brancho D, Tanaka N, Jaeschke A, Ventura JJ, Kelkar N, Tanaka Y, Kyuuma M, Takeshita T, Flavell RA, Davis RJ (2003) Mechanism of p38 MAP kinase activation in vivo. Genes Dev 17:1969–1978
Ge B, Gram H, Di Padova F, Huang B, New L, Ulevitch RJ, Luo Y, Han J (2002) MAPKK-independent activation of p38α-mediated by TAB 1-dependent autophosphorylation of p38α. Science 295:1291–1294
Ge B, Xiong X, Jing Q, Mosley JL, Filose A, Bian D, Huang S, Han J (2003) TAB 1 (transforming growth factor-β-activated protein kinase 1-binding protein 1β), a novel splicing variant of TAB 1 that interacts with p38α but not TAK1. J Biol Chem 278:2286–2293
Kang YJ, Seit-Nebi A, Davis RJ, Han J (2006) Multiple activation mechanisms of p38α mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem 281:26225–26234
Suzuki K, Hino M, Hato F, Kitagawa S (1999) Cytokine-specific activation of distinct mitogen-activated protein kinase subtype cascades in human neutrophils stimulated by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor, and tumor necrosis factor-α. Blood 93:341–349
Suzuki K, Hino M, Kutsuna H, Hato F, Sakamoto C, Takahashi T, Tatsumi N, Kitagawa S (2001) Selective activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade in human neutrophils stimulated by IL-1β. J Immunol 167:5940–5947
Boudreau RT, Conrad DM, Hoskin DW (2007) Apoptosis induced by protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) inhibition in T leukemia cells is negatively regulated by PP2A-associated p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. Cell Signal 19:139–151
Alvarado-Kristensson M, Andersson T (2005) Protein phosphatase 2A regulates apoptosis in neutrophils by dephosphorylating both p38 MAPK and its substrate caspase 3. J Biol Chem 280:6238–6244
Koshio O, Akanuma Y, Kasuga M (1988) Hydrogen peroxide stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of the insulin receptor and its tyrosine kinase activity in intact cells. Biochem J 250:95–101
Goldstein BJ, Mahadev K, Wu X (2005) Redox paradox: insulin action is facilitated by insulin-stimulated reactive oxygen species with multiple potential signaling targets. Diabetes 54:311–321
Junttila MR, Li SP, Westermarck J (2008) Phosphatase-mediated crosstalk between MAPK signaling pathways in the regulation of cell survival. FASEB J 22:954–965
Yang Z, von Ballmoos MW, Faessler D, Voelzmann J, Ortmann J, Diehm N, Kalka-Moll W, Baumgartner I, Di Santo S, Kalka C (2010) Paracrine factors secreted by endothelial progenitor cells prevent oxidative stress-induced apoptosis of mature endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis 211:103–109
Xu ZR, Hu L, Cheng LF, Qian Y, Yang YM (2010) Dihydrotestosterone protects human vascular endothelial cells from H2O2-induced apoptosis through inhibition of caspase-3, caspase-9 and p38 MAPK. Eur J Pharmacol 643:254–259
Kumar S, Jiang MS, Adams JL, Lee JC (1999) Pyridinylimidazole compound SB 203580 inhibits the activity but not the activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 263:825–831
Niu Q-X, Chen HQ, Chen ZY, Fu YL, Lin JL, He S-H (2008) Induction of inflammatory cytokine release from human umbilical vein endothelial cells by agonists of proteinase-activated receptor-2. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 35:89–96
Acknowledgements
We express our sincere thanks to Dr. Yasuo Akanuma (Institute for Diabetes Care and Research, Asahi Life Foundation, Tokyo) and Dr. Akiko Ishida-Okawara (National Institute of Infectious Diseases, Tokyo) for their helpful support and discussions. This study was supported by grants from the Human Science Foundation (Tokyo, Japan).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koshio, O., Nagao, T., Mabuchi, A. et al. Apoptotic signaling in endothelial cells with neutrophil activation. Mol Cell Biochem 363, 269–280 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-1179-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-1179-5