Abstract
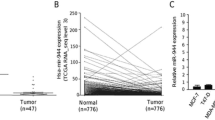
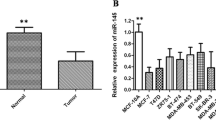
microRNAs (miRNAs) are short non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression by targeting mRNAs, inhibiting the expression of the associated proteins. Although a role for aberrant miRNA expression in cancer has been postulated, the pathophysiologic role and relevance of aberrantly expressed miRNAs in tumor biology has not been established. We evaluated the expression pattern of miRNAs in human breast cancer cells by qPCR, finding out an up-regulated miRNA miR-29b and studying its biological effect by migration assay. We defined a target gene PTEN by bioinformatics approach and western blot. In breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231 cell, which migrate faster than MCF-7, we observed that miR-29b was highly over-expressed. Inhibition of miR-29b in cultured cells increased the expression of the phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) tumor suppressor, promoting apoptosis, decreasing migration, and decreasing invasion. In contrast, enhanced miR-29b expression by transfection with pre-miR-29b decreased the expression of PTEN and impaired apoptosis, increasing tumor cell migration and invasion. Moreover, PTEN was shown to be a direct target of miR-29b and was also shown to contribute to the miR-29b-mediated effects on cell invasion. Modulation of miR-29b altered the role of PTEN involved in cell migration and invasion. Aberrant expression of miR-29b, which modulates PTEN expression, can contribute to migration, invasion, and anti-apoptosis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Iorio MV, Casalini P, Tagliabue E, Ménard S, Croce CM (2008) MicroRNA profiling as a tool to understand prognosis, therapy response and resistance in breast cancer. Eur J Cancer 44(18):2753–2759
Meng F, Henson R, Wehbe-Janek H, Ghoshal K, Jacob ST, Patel T (2007) MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer. Gastroenterology 133(2):647–658
Shi M, Guo N (2009) MicroRNA expression and its implications for the diagnosis and therapeutic strategies of breast cancer. Cancer Treat Rev 35(4):328–334
Li T, Li D, Sha J, Sun P, Huang Y (2009) MicroRNA-21 directly targets MARCKS and promotes apoptosis resistance and invasion in prostate cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 383(3):280–285
Liang Z, Wu H, Reddy S, Zhu A, Wang S, Blevins D, Yoon Y, Zhang Y, Shim H (2007) Blockade of invasion and metastasis of breast cancer cells via targeting CXCR4 with an artificial microRNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 363(3):542–546
Heering J, Erlmann P, Olayioye MA (2009) Simultaneous loss of the DLC1 and PTEN tumor suppressors enhances breast cancer cell migration. Exp Cell Res 315(15):2505–2514
Maurer M, Su T, Saal LH, Koujak S, Hopkins BD, Barkley CR, Wu J, Nandula S, Dutta B, Xie Y, Chin YR, Kim DI, Ferris JS, Gruvberger-Saal SK, Laakso M, Wang X, Memeo L, Rojtman A, Matos T, Yu JS, Cordon-Cardo C, Isola J, Terry MB, Toker A, Mills GB, Zhao JJ, Murty VV, Hibshoosh H, Parsons R (2009) 3-Phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1 potentiates upstream lesions on the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway in breast carcinoma. Cancer Res 69(15):6299–6306
Saal LH, Holm K, Maurer M, Memeo L, Su T, Wang X, Yu JS, Malmström PO, Mansukhani M, Enoksson J, Hibshoosh H, Borg A, Parsons R (2005) PIK3CA mutations correlate with hormone receptors, node metastasis, and ERBB2, and are mutually exclusive with PTEN loss in human breast carcinoma. Cancer Res 65(7):2554–2559
Li G, Robinson GW, Lesche R, Martinez-Diaz H, Jiang Z, Rozengurt N, Wagner KU, Wu DC, Lane TF, Liu X, Hennighausen L, Wu H (2002) Conditional loss of PTEN leads to precocious development and neoplasia in the mammary gland. Development 129(17):4159–4170
Yan LX, Huang XF, Shao Q, Huang MY, Deng L, Wu QL, Zeng YX, Shao JY (2008) MicroRNA miR-21 overexpression in human breast cancer is associated with advanced clinical stage, lymph node metastasis and patient poor prognosis. RNA 14(11):2348–2360
Tavazoie SF, Alarcón C, Oskarsson T, Padua D, Wang Q, Bos PD, Gerald WL, Massagué J (2008) Endogenous human microRNAs that suppress breast cancer metastasis. Nature 451(7175):147–152
Valastyan S, Reinhardt F, Benaich N, Calogrias D, Szász AM, Wang ZC, Brock JE, Richardson AL, Weinberg RA (2009) A pleiotropically acting microRNA, miR-31, inhibits breast cancer metastasis. Cell 137(6):1032–1046
Li XF, Yan PJ, Shao ZM (2009) Downregulation of miR-193b contributes to enhance urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) expression and tumor progression and invasion in human breast cancer. Oncogene 28(44):3937–3948
Lowery AJ, Miller N, McNeill RE, Kerin MJ (2008) MicroRNAs as prognostic indicators and therapeutic targets: potential effect on breast cancer management. Clin Cancer Res 14(2):360–365
Meng F, Yamagiwa Y, Ueno Y, Patel T (2006) Over-expression of interleukin-6 enhances cell survival and transformed cell growth in human malignant cholangiocytes. J Hepatol 44(6):1055–1065
Boren T, Xiong Y, Hakam A, Wenham R, Apte S, Wei Z, Kamath S, Chen DT, Dressman H, Lancaster JM (2008) MicroRNAs and their target messenger RNAs associated with endometrial carcinogenesis. Gynecol Oncol 110(2):206–215
Liu B, Peng XC, Zheng XL, Wang J, Qin YW (2009) MiR-126 restoration down-regulate VEGF and inhibit the growth of lung cancer cell lines in vitro and in vivo. Lung Cancer 66(2):169–175
Fujita Y, Kojima K, Hamada N, Ohhashi R, Akao Y, Nozawa Y, Deguchi T, Ito M (2008) Effects of miR-34a on cell growth and chemoresistance in prostate cancer PC3 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 377(1):114–119
Selcuklu SD, Yakicier MC, Erson AE (2009) An investigation of microRNAs mapping to breast cancer related genomic gain and loss regions. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 189(1):15–23
Murakami Y, Yasuda T, Saigo K, Urashima T, Toyoda H, Okanoue T, Shimotohno K (2006) Comprehensive analysis of microRNA expression patterns in hepatocellular carcinoma and non-tumorous tissues. Oncogene 25(17):2537–2545
Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J, Weinberg RA (2007) Tumour invasion and metastasis initiated by microRNA-10b in breast cancer. Nature 449(7163):682–688
Huang Q, Gumireddy K, Schrier M, le Sage C, Nagel R, Nair S, Egan DA, Li A, Huang G, Klein-Szanto AJ, Gimotty PA, Katsaros D, Coukos G, Zhang L, Puré E, Agami R (2008) The microRNAs miR-373 and miR-520c promote tumour invasion and metastasis. Nat Cell Biol 10(2):202–210
Wu H, Wang S, Weng D, Xing H, Song X, Zhu T, Xia X, Weng Y, Xu G, Meng L, Zhou J, Ma D (2008) Reversal of the malignant phenotype of ovarian cancer A2780 cells through transfection with wild-type PTEN gene. Cancer Lett 271(2):205–214
Ghosh AK, Grigorieva I, Steele R, Hoover RG, Ray RB (1999) PTEN transcriptionally modulates c-myc gene expression in human breast carcinoma cells and is involved in cell growth regulation. Gene 235(1–2):85–91
Kölsch V, Charest PG, Firtel RA (2008) The regulation of cell motility and chemotaxis by phospholipid signaling. J Cell Sci 121(Pt 5):551–559
Leslie NR, Yang X, Downes CP, Weijer CJ (2005) The regulation of cell migration by PTEN. Biochem Soc Trans 33(Pt 6):1507–1508
Wan W, Zou H, Sun R, Liu Y, Wang J, Ma D, Zhang N (2007) Investigate the role of PTEN in chemotaxis of human breast cancer cells. Cell Signal 19(11):2227–2236
Li Z, Wang L, Zhang W, Fu Y, Zhao H, Hu Y, Prins BP, Zha X (2007) Restoring E-cadherin-mediated cell–cell adhesion increases PTEN protein level and stability in human breast carcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 363(1):165–170
Zhu L, Loo WT, Louis WC (2007) PTEN and VEGF: Possible predictors for sentinel lymph node micro-metastasis in breast cancer. Biomed Pharmacother 61(9):558–561
Capodanno A, Camerini A, Orlandini C, Baldini E, Resta ML, Bevilacqua G, Collecchi P (2009) Dysregulated PI3 K/Akt/PTEN pathway is a marker of a short disease-free survival in node-negative breast carcinoma. Hum Pathol 40(10):1408–1417
Acknowledgment
We thank professor Ke Zen (School of Life Science, Nanjing University) for technical and financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Bian, Z., Wei, D. et al. miR-29b regulates migration of human breast cancer cells. Mol Cell Biochem 352, 197–207 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-0755-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-0755-z