Abstract
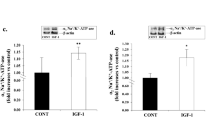
The mechanism of protective action of hyaluronic acid (HA) on collagen metabolism disturbances in tissues during inflammation is not known. Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) receptor and β1-integrin receptor signaling plays an important role in the regulation of collagen biosynthesis at both transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels. The present study was undertaken to evaluate the effect of IL-1β (inductor of experimental inflammation) on the signaling pathways as well as on collagen biosynthesis, gelatinases and prolidase activity in cultured human chondrocytes and the effect of HA on these processes. It was found that IL-1β-dependent inhibition of collagen biosynthesis was accompanied by increase in β1-integrin receptor, NF-kB expressions, and increase in phosphorylation of FAK, that resulted in stimulation of metalloproteinase MMP-2 and MMP-9 activities, but not prolidase activity and expression. Simultaneously, decrease in expression of IGF-I receptor and phosphorylation of Akt and p38 were found. All those processes were counteracted by HA. This suggests that cross talk between β1-integrin and IGF-I receptors is disturbed by IL-1β, and HA recovers their proper signaling in cultured chondrocytes. We propose that IGF-I receptor and β1-integrin signaling may play an important role in protective effect of hyaluronic acid on interleukin-1-induced inhibition of collagen biosynthesis in cultured human chondrocytes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Martel-Pelletier J (1998) Patophysiology of osteoarthritis. Osteoarth Cartil 6:374–376
Benton HP, Tyler JA (1988) Inhibition of cartilage proteoglycan synthesis by interleukin 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 154:421–428
Gowen M, Wood DD, Ihrie EJ, Meats JE, Russel RGG (1984) Stimulation by human interleukin-1 of cartilage breakdown and production of collagenase and proteoglycanase by human chondrocytes but not by human osteoblasts in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta 797:186–193
Matsuno H, Yudoh K, Kondo M, Goto M, Kimura T (1999) Biochemical effect of intra-articular injections of high molecular weight hyaluronate in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Inflamm Res 48:154–159
Hiramitsu T, Yasuda T, Ito H, Shimizu M, Julovi SM, Kakinuma T, Akiyoshi M, Yoshida M, Nakamura T. (2006) Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 mediates the inhibitory effects of hyaluronan on interleukin-1β-induced matrix metalloproteinase production in rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts via down- regulation of NF-kB and p38. Rheumatology 45:824–832
Aruffo A, Stamenkovic I, Melnick M, Underhill CB, Seed B (1990) CD44 is the principal cell surface receptor for hyaluronate. Cell 61:1303–1313
Lisignoli G, Grassi F, Zini N, Toneguzzi S, Piacentini A, Guidolin D, Bevilacqua C, Facchini A (2001) Anti-Fas-induced apoptosis in chondrocytes reduced by hyaluronan: evidence for CD44 and CD54 (intercellular adhesion molecule 1) involvement. Arthritis Rheum 44:1800–1807
Tool BP (1991) Proteoglycans and hyaluronan in morphogenesis and differentiation. In: Hay ED (ed) Cell biology of extracellular matrix, Plenum Press, New York
Altman RD, Moskowitz R (1998) Intra-articular sodium hyaluronate (Hyalgan®) in the treatment of patients with osteoarthritis of the knee: a randomized clinical trial. J Rheumatol 25:2203–2212
Tool BP (1997) Hyaluronan in morphogenesis. J Intern Med 24:35–40
Gumbiner BM, Yamada KM (1995) Cell-to-cell contact and extracellular matrix. Curr Opin Cell Biol 7:615–618
Plow EF, Haas TA, Zhang L, Loftus J, Smith JW (2000) Ligand binding to integrins. J Biol Chem 275:21785–21788
Tyler JA, Bolis S, Dingle JT, Middleson JFS (1992) Mediators of matrix catabolism. In: Kuettner KE, Schleyerbach R, Peyron JG, Hascall VC (eds) Articular cartilage and osteoarthritis, Raven Press, New York
Beekman B, Verzijl N, DeRoos JADM, TeKoppele JM (1998) Matrix degradation by chondrocytes cultured in alginate: IL-1β induces proteoglycan degradation and proMMP synthesis but does not result in collagen degradation. Osteoarth Cartil 6:330–340
Lark MW, Gordy JT, Weidner JR, Ayala J, Kimura JH, Williams HR (1995) Cell-mediated catabolism of aggrecan. J Biol Chem 270:2550–2556
Mock WL, Green PC, Boyer KD (1990) Specificity and pH dependence for acylproline cleavage by prolidase. J Biol Chem 265:19600–19605
Jackson SH, Dennis AW, Greenberg M (1975) Iminopeptiduria: a genetic defect in recycling of collagen; a method for determining prolidase in erythrocytes. Can Med Assoc J 113:759–763
Phang JM, Scriver CR (1989) Disorders of proline and hydroxyproline metabolism. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D (eds) The metabolic basis of inherited disease, Mc Graw Hill, New York
Pałka JA, Phang JM (1997) Prolidase activity in fibroblasts is regulated by interaction of extracellular matrix with cell surface integrin receptors. J Cell Biochem 67:166–175
Hanks SK, Calalb MB, Harper MC, Patel SK (1992) Focal adhesion protein-tyrosine kinase phosphorylated in response to cell attachment to fibronectin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:8487–8491
Juliano R (1996) Cooperation between soluble factors and integrin––mediated cell anchorage in the control of cell growth and differentiation. Bioassays 18:911–917
Seger R, Krebs EG (1995) The MAPK signaling cascade. FASEB J 9:726–735
Labat-Robert J, Robert L (2000) Interaction between cells and extracellular matrix: signaling by integrins and the elastin-laminin receptor. Prog Mol Subcell Biol 25:57–70
Goldstein RH, Poliks CF, Plich PF, Smith BD, Fine A (1989) Stimulation of collagen formation by insulin-like growth factor-I in cultures of human lung fibroblasts. Endocrinology 124:964–970
Le Roith D, Werner H, Beitner-Johnson D, Roberts Jr CT (1995) Molecular and cellular aspects of the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor. Endocr Rev 16:143–164
Butler AA, Yakar S, Gewolb IH, Karas M, Okubo Y, LeRoith D (1998) Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signal transduction: at the interface between physiology and cell biology. Comp Biochem Physiol B 121:19–26
Tanaka H, Wakisaka A, Ogasa H, Kawai S, Liang CT (2002) Effect of IGF-I and PDGF administered in vivo on the expression of osteoblast-related genes in old rats. J Endocrinol 174:63–70
Miltyk W, Karna E, Wołczyński S, Pałka J (1998) Insulin-like growth factor I- dependent regulation of prolidase activity in cultured human skin fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biochem 189:177–184
Baserga R, Hongo A, Rubini M, Prisco M, Valentinis B (1997) The IGF-I receptor in cell growth, transformation and apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 1332:105–106
Myara I, Charpentier C, Lemonnier A (1982) Optimal conditions for prolidase assay by proline colorimetric determination: application to imidopeptiduria. Clin Chim Acta 125:193–205
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NI, Far AL, Randall IR (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Oyamada I, Pałka J, Schalk EM, Takeda K, Peterkofsky B (1990) Scorbutic and fasted guinea pig sera contain an insulin-like growth factor I reversible inhibitor of proteoglycan and collagen synthesis in chick embryo chondrocytes and adult human skin fibroblasts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 276:85–93
Peterkofsky B, Chojkier M, Bateman J (1982) Determination of collagen synthesis in tissue and cell culture system. In: Furthmay M (ed) Immunochemistry of the Extracellular Matrix, CRC Press, Boca Raton
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of baceriophage T4. Nature (London) 227:680–685
Karna E, Miltyk W, Pałka JA, Jarząbek K, Wołczyński S (2006) Hyaluronic acid counteracts interleukin-1-induced inhibition of collagen biosynthesis in cultured human chondrocytes. Pharmacol Res 54:275–281
Aydelotte M, Raiss R, Caterson B, Kuettner K (1992) Influence of interleukin-1 on the metabolism of proteoglycans and morphology of cultured bovine articular chondrocytes. Connect Tissue Res 28:143–159
Pujol JP, Brisset M, Jourdan C, Bocquet J, Jouis V (1984) Effect of a mononuclear cell factor (MCF) on collagen production in cultured articular chondrocytes: role of prostaglandin E2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 119:499–508
Dingle JT (1993) Mechanism of cartilage destruction and repair: the outlook for therapeutic interventions. Clinique Rheum 3:1–5
Rippe RA, Schrum LW, Stefanovic B, Solis-Herruzo JA, Brenner DA (1999) NF-kappaB inhibits expression of the alpha1(I) collagen gene. DNA Cell Biol 10:751–761
Kouba DJ, Chung KY, Nishiyama T, Vindevoghel L, Kon A, Klement JF, Uitto J, Mauviel A (1999) Nuclear factor-kappa B mediates TNF-alpha inhibitory effect on alpha 2(I) collagen (COL1A2) gene transcription in human dermal fibroblasts. J Immunol 162:4226–4234
Fan Z, Yang H, Bau B, Soder S, Aigner T (2006) Role of mitogen activated protein kinases and NF-kappaB on IL-1beta-induced effects on collagen type II, MMP-1 and 13 mRNA expression in normal articular human chondrocytes. Rheumatol Int 26:900–903
Li G, Lubin FD, McGee DW (2004) α3β1 integrin induced suppression of the Caco-2 epithelial cell IL-1 signaling pathway leading to NF-κB activation. Cell Immunol 231:30–39
O’Neill LAJ, Greene C (1998) Signal transduction pathways activated by the IL-1 receptor family: ancient signaling machinery in mammals, insects, and plants. J Leukoc Biol 63:650–657
Qwarnstrom EE, Ostberg CO, Turk GL, Richardson A, Bomsztyk K (1994) Fibronectin attachment activated the NF-κB p50/p65 heterodimer in fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem 269:30765–30768
Klein S, de Fougerolles AR, Blaikie P, Kahn L, Pepe A, Green CD, Koteliansky V, Giancotti FG (2002) α5β1 integrin activates an NF-κB-dependent program of gene expression important for angiogenesis and inflammation. Mol Cell Biol 22:5912–5922
Huang D, Khoe M, Befekadu M, Chung S, Takata Y, Ilic D, Bryer-Ash M (2007) Focal adhesion kinase mediates cell survival via NF-kB and ERK signalling pathways. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 292:1339–1352
Gonzales M, Haan K, Baker SE, Fitchmun M, Todorov I, Weitzman S, Jones JCR (1999) A cell signal pathway involving laminin-5, α3β1 integrin, and mitogen activated protein kinase can regulate epithelial cell proliferation. Mol Biol Cell 10:259–270
Reyes-Reyes M, Mora N, Zentella A, Rosales C (2001) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase mediates integrin-dependent NF-κB and MAPK activation through separate signaling pathways. J Cell Sci 114:1579–1598
Watanabe H, De Caestecker MP, Yamada Y (2001) Transcriptional cross-talk between Smad, ERK1/2, and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways regulates transforming growth factor-β-induced aggrecan gene expression in chondrogenic ATDC5 cells. J Biol Chem 276:14466–14473
Phornphutkul Ch, Wu K, Xu Y, Chen Q, Gruppuso PA (2004) Insulin-like growth factor-I signaling is modified during chondrocyte differentiation. J Endocrinol 183:477–486
Kim SJ, Ju JW, Oh CD, Yoon YM, Song WK, Kim JH, Yoo YJ, Bang OS, Kang SS, Chun JS (2002) ERK-1/2 and p38 kinase oppositely regulate nitric oxide-induced apoptosis of chondrocytes in association with p53, caspase-3, and differentiation status. J Biol Chem 277:1332–1339
Cosaceanu D, Budin RA, Carapancea M, Castro J, Lewensohn R, Dricu A (2007) Ionizing radiation activates IGF-1R triggering a cytoprotective signaling by interfering with Ku-DNA binding and by modulating Ku86 expression via a p38 kinase-dependent mechanism. Oncogene 26:2423–2434
Knudson W, Leser RF (2002) CD44 and integrin matrix receptors participate in cartilage homeostasis. Cell Mol Life Sci 59:36–44
Acknowledgments
The present study was supported by Grant No. 2 PO5F 003 28 from the Committee for Scientific Research (KBN, Poland).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karna, E., Miltyk, W., Surażyński, A. et al. Protective effect of hyaluronic acid on interleukin-1-induced deregulation of β1-integrin and insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling and collagen biosynthesis in cultured human chondrocytes. Mol Cell Biochem 308, 57–64 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-007-9612-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-007-9612-5