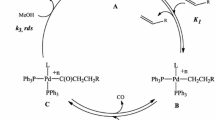
Abstract
Excess aryl halide and a reducing agent admixture extend the lifetime of a catalyst in the Heck reaction. In the presence of a simple catalytic system without any ligands, the reaction between an unactivated aryl bromide and styrene in dimethyl formamide yields a stoichiometric amount of the product when the starting mixture contains 0.04–1.6 mol % PdCl2 , 18% HCOONa, 112% AcONa, and a sixfold excess of the aryl bromide (with respect to the initial amount of styrene). It is possible to raise the turnover number of the catalyst by conducting the reaction in several successive runs without regenerating or separating the catalyst. The data obtained confirm the earlier hypothesis that colloidal palladium particles formed during the reaction serve as a main “reservoir” accumulating catalytically active, homogeneous Pd(0) complexes.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Whitcombe, N.J., King Luik (Mimi) Hii, and Gibson, S.E., Tetrahedron, 2001, vol. 57, no. 35, p. 7449.
Beletskaya, I.P. and Chepracov, A.V., Chem. Rev., 2000, vol. 100, no. 8, p. 3009.
Kohler, K., Heidenreich, R.G., Krauter, J.G.E., and Pietsch, J., Chem.—Eur. J., 2002, vol. 8, no. 3, p. 622.
Biffis, A., Zecca, M., and Basato, M., Eur. J. Inorg. Chem., 2001, vol. 421, no. 5, p. 1131.
Reetz, M.T., Lohmer, G., and Schwickardi, R., Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl., 1998, vol. 37, no. 4, p. 481.
Shmidt, A.F., Mametova, L.V., Tkach, V.S., and Dmit-rieva, T.V., Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Ser. Khim., 1991, no. 1, p. 208.
Shmidt, A.F., Halaiqa, A., Nindakova, L.O., and Skripina, O.S., React. Kinet. Catal. Lett., 1999, vol. 67, no. 2, p. 301.
Reetz, M.T. and Westermann, E., Angew. Chem., 2000, vol. 39, no. 1, p. 165.
Shmidt, A.F. and Mametova, L.V., Kinet. Katal., 1996, vol. 37, no. 3, p. 431.
Shmidt, A.F., Smirnov, V.V., Starikova, O.V., and Elaev, A.V., Kinet. Katal., 2001, vol. 42, p. 223.
Biffis, A., Zecca, M., and Basato, M., J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem., 2001, vol. 173, nos. 1–2, p. 249.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Kinetika i Kataliz, Vol. 46, No. 1, 2005, pp. 54–58.
Original Russian Text Copyright © 2005 by Shmidt, Smirnov.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shimdt, A.F., Smirnov, V.V. Role of catalyst deactivation and regeneration in the heck reaction involving unactivated aryl bromides. Kinet Catal 46, 47–51 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10975-005-0039-2
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10975-005-0039-2