Abstract
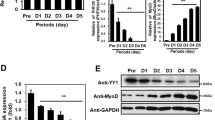
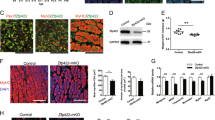
CXXC5 is a member of the CXXC-type zinc-finger domain containing protein family, which is suggested to function in gene transcription, cell adhesion and cytoskeleton organization. Previous studies have revealed that CXXC5 is expressed in skeletal muscle, but whether it regulates skeletal myogenesis is yet unknown. Here, we screened for the possible signaling pathways in which CXXC5 might participate using luciferase gene reporters. The results indicated that CXXC5 significantly increased the activities of the promoters of genes involved in skeletal muscle differentiation. We therefore studied the role of CXXC5 during skeletal myogenesis in C2C12 myoblasts. Our findings suggest that overexpression of CXXC5 in C2C12 myoblasts facilitated myocyte differentiation, while RNAi interference of CXXC5 significantly inhibited the differentiation of C2C12 myoblasts. This study suggests that CXXC5 plays a significant role in regulating skeletal myogenesis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson T, Södersten E, Duckworth JK, Cascante A, Fritz N, Sacchetti P, Cervenka I, Bryja V, Hermanson O (2009) CXXC5 is a novel BMP4-regulated modulator of Wnt signaling in neural stem cells. J Biol Chem 284:3672–3681
Aras S, Pak O, Sommer N, Finley R Jr, Hüttemann M, Weissmann N, Grossman LI (2013a) Oxygen-dependent expression of cytochrome c oxidase subunit 4-2 gene expression is mediated by transcription factors RBPJ, CXXC5 and CHCHD2. Nucleic Acids Res 41:2255–2266
Aras S, Pak O, Sommer N, Finley R Jr, Hüttemann M, Weissmann N, Grossman LI (2013b) Krüppel-like factor 6 (KLF6) promotes cell proliferation in skeletal myoblasts in response to TGFβ/Smad3 signaling. Skelet Muscle 3:7
Chen T, Jiang Z, Xu W, Wang Y, Li Y, Wan Y, Yuan W, Mo X, Wu X, Deng Y, Fan X, Nie D (2014) Expression and identification of a novel gene Spata34 in mouse spermatogenic cells. Mol Biol Rep 41:1683–1691
Devaney JM, Wang S, Funda S, Long J, Taghipour DJ, Tbaishat R, Furbert-Harris P, Ittmann M, Kwabi-Addo B (2013) Identification of novel DNA-methylated genes that correlate with human prostate cancer and high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 16:292–300
Dias P, Dilling M, Houghton P (1994) The molecular basis of skeletal muscle differentiation. Semin Diagn Pathol 11:3–14
Girgis CM, Clifton-Bligh RJ, Mokbel N, Cheng K, Gunton JE (2014) Vitamin D signaling regulates proliferation, differentiation and myotube size in C2C12 skeletal muscle cells. Endocrinology 155:347–357
Hu J, Yuan W, Tang M, Wang Y, Fan X, Mo X, Li Y, Ying Z, Wan Y, Ocorr K, Bodmer R, Deng Y, Wu X (2010) KBTBD7, a novel human BTB-kelch protein, activates transcriptional activities of SRE and AP-1. BMB Rep 43:17–22
Jara E, Hidalgo MA, Hancke JL, Hidalgo AI, Hidalgo A, Brauchi S, Nuñez L, Villalobos C, Burgos R (2014) Delphinidin activates NFAT and induces IL-2 production through SOCE in T cells. Cell Biochem Biophys 68:497–509
Kim MS, Yoon SK, Bollig F, Kitagaki J, Hur W, Whye NJ, Wu YP, Rivera MN, Park JY, Kim HS, Malik K, Bell DW, Englert C, Perantoni AO, Lee SB (2010) A novel Wilmstumor 1 (WT1) target gene negatively regulates the WNT signaling pathway. J Biol Chem 285:14585–14593
Kim HY, Yang DH, Shin SW, Kim MY, Yoon JH, Kim S, Park HC, Kang DW, Min D, Hur MW, Choi KY (2014) CXXC5 is a transcriptional activator of Flk-1 and mediates bone morphogenic protein-induced endothelial cell differentiation and vessel formation. FASEB J 28:615–626
Knappskog S, Myklebust LM, Busch C, Aloysius T, Varhaug JE, Lønning PE, Lillehaug JR, Pendino F (2011) RINF (CXXC5) is overexpressed in solid tumors and is an unfavorable prognostic factor in breast cancer. Ann Oncol 22:2208–2215
L’Hôte D, Georges A, Todeschini AL, Kim JH, Benayoun BA, Bae J, Veitia RA (2012) Discovery of novel protein partners of the transcription factor FOXL2 provides insights into its physiopathological roles. Hum Mol Genet 21:3264–3274
Li DL, Niu Z, Yu W, Qian Y, Wang Q, Li Q, Yi Z, Luo J, Wu X, Wang Y, Schwartz RJ, Liu M (2009) SMYD1, the myogenic activator, is a direct target of serum response factor and myogenin. Nucleic Acids Res 37:7059–7071
Lin JR, Qin HH, Wu WY, He SJ, Xu JH (2014)Vitamin C protects against UV irradiation-induced apoptosis through reactivating silenced tumor suppressor genes p21 and p16 in a Tet-dependent DNA demethylation manner in human skin cancer cells. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 29:257–264
Luwor RB, Wang B, Nheu TV, Iaria J, Tsantikos E, Hibbs ML, Sieber OM, Zhu HJ (2011) New reagents for improved in vitro and in vivo examination of TGF-β signaling. Growth Factors 29:211–218
Marshall PA, Hernandez Z, Kaneko I, Widener T, Tabacaru C, Aguayo I, Jurutka PW (2012) Discovery of novel vitamin D receptor interacting proteins that modulate 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 signaling. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 132:147–159
May-Panloup P, Ferré-L’Hôtellier V, Morinière C, Marcaillou C, Lemerle S, Malinge MC, Coutolleau A, Lucas N, Reynier P, Descamps P, Guardiola P (2012) Molecular characterization of corona radiata cells from patients with diminished ovarian reserve using microarray and microfluidic-based gene expression profiling. Hum Reprod 27:829–843
McLeish MJ, Kenyon GL (2005) Relating structure to mechanism in creatine kinase. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 40:1–20
Moncaut N, Rigby PW, Carvajal JJ (2013) Dial M(RF) for myogenesis. FEBS J 280:3980–3990
Park CY, Son JY, Jin CH, Nam JS, Kim DK, Sheen YY (2011) EW-7195, a novel inhibitor of ALK5 kinase inhibits EMT and breast cancer metastasis to lung. Eur J Cancer 47:2253–2642
Riazi Ali M, Lee Haeyul, Hsu Christina, Van Arsdell Glen (2005) CSX/Nkx2.5 modulates differentiation of skeletal myoblasts and promotes differentiation into neuronal cells in vitro. J Biol Chem 280:10716–10720
Sartori R, Gregorevic P, Sandri M (2014) TGFβ and BMP signaling in skeletal muscle: potential significance for muscle-related disease. Trends Endocrinol Metab 25:464–471
Srikuea R, Zhang X, Park-Sarge OK, Esser KA (2012) VDR and CYP27B1 are expressed in C2C12 cells and regenerating skeletal muscle: potential role in suppression of myoblast proliferation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 303:C396–C405
Starkey JD (2014) Triennial growth symposium—a role for vitamin D in skeletal muscle development and growth. J Anim Sci 92:887–892
Treppendahl MB, Möllgård L, Hellström-Lindberg E, Cloos P, Grønbaek K (2013) Downregulation but lack of promoter hypermethylation or somatic mutations of the potential tumor suppressor CXXC5 in MDS and AML with deletion 5q. Eur J Haematol 90:259–260
Villeneuve C, Caudrillier A, Ordener C, Pizzinat N, Parini A, Mialet-Perez J (2009) Dose-dependent activation of distinct hypertrophic pathways by serotonin in cardiac cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 297:H821–H828
von Maltzahn J, Natasha Chang C, Florian Bentzinger C, Michael Rudnicki A (2012) Wnt signaling in myogenesis. Trends Cell Biol 22:602–609
Wang X, Liao P, Fan X, Wan Y, Wang Y, Li Y, Jiang Z, Ye X, Mo X, Ocorr K, Deng Y, Wu X, Yuan W (2013) CXXC5 associates with Smads to mediate TNF-α induced apoptosis. Curr Mol Med 13:1385–1396
Wang N, Zhu M, Wang X, Tan HY, Tsao SW, Feng Y (2014) Berberine-induced tumor suppressor p53 up-regulation gets involved in the regulatory network of MIR-23a in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochim Biophys Acta 1839:849–857
Winter B, Braun T, Arnold HH (1993) cAMP-dependent protein kinase represses myogenic differentiation and the activity of the muscle-specific helix-loop-helix transcription factors Myf-5 and MyoD. J Biol Chem 268:9869–9878
Acknowledgments
We thank all the members of the Center for Heart Development in Hunan Normal University for their assistance. This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (30930054, 81170229, 31171402, 81170088, 31172044, 31071999, 30970425, 31272396, 81270156, 81270291,81370451,81400304,31472060, 81470377, 81470449), Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (12JJ3117, 2015JJ3087), Hunan Provincial Innovation Foundation For Postgraduate (CX2014B200, CX2012B213), the Cooperative Innovation Center of Engineering and New Products for Developmental Biology of Hunan Province 2013-448-6, and the Scientific Research Fund of Hunan Provincial Education Department (No. 14A093).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Guangming Li, Xiangli Ye and Xiyang Peng have contributed equally to this paper.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, G., Ye, X., Peng, X. et al. CXXC5 regulates differentiation of C2C12 myoblasts into myocytes. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 35, 259–265 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10974-014-9400-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10974-014-9400-2