Abstract
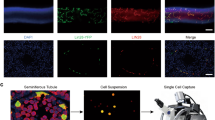
Leucine-rich repeat (LRR) containing proteins play an essential role in signal transduction, cell adhesion, cell development, DNA repair and RNA processing. Here we cloned a novel gene, Spata34, encoding a LRR containing protein of 415 aa. Spata34 gene consisted of 9 exons and 8 introns and mapped to chromosome 3qA3. Spata34 is conserved across species in evolution. The Spata34 gene was expressed at various levels, faintly before first weeks postpartum and strongly from 2 weeks postpartum in adult testes. Western blot analysis showed that Spata34 protein was specially expressed in mouse testis. Immunohistochemical analysis revealed that Spata34 protein was most abundant in the cytoplasm of round spermatids and elongating spermatids within seminiferous tubules of the adult testis. Overexpression of Spata34 in COS7 cells inhibited the transcriptional activity of AP-1, p53 and p21 which suggested that Spata34 protein may act as a transcriptional repressor in p53 and p21 pathway.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kobe B, Kajava AV (2001) The leucine-rich repeat as a protein recognition motif. Curr Opin Struct Biol 11(6):725–732
Boehm T, McCurley N, Sutoh Y, Schorpp M, Kasahara M, Cooper MD (2012) VLR-based adaptive immunity. Annu Rev Immunol 30:203–220
Wang R, Sperry AO (2008) Identification of a novel leucine-rich repeat protein and candidate PP1 regulatory subunit expressed in developing spermatids. BMC Cell Biol 31(9):9
Wang R, Kaul A, Sperry AO (2010) TLRR (lrrc67) interacts with PP1 and is associated with a cytoskeletal complex in the testis. Biol Cell 102(3):173–189
Hoshii T, Takeo T, Nakagata N, Takeya M, Araki K, Yamamura K (2007) LGR4 regulates the postnatal development and integrity of male reproductive tracts in mice. Biol Reprod 76(2):303–313 Epub 2006 Nov 1
Ferlin A, Bogatcheva NV, Gianesello L, Pepe A, Vinanzi C, Agoulnik AI, Foresta C (2006) Insulin-like factor 3 gene mutations in testicular dysgenesis syndrome: clinical and functional characterization. Mol Hum Reprod 12(6):401–406
Scheurle D, de Young MP, Binninger DM, Page H, Jahanzeb M, Narayanan R (2000) Cancer gene discovery using digital differential display. Cancer Res 60(15):4037–4043
Cai ZY, Wang YQ, Yu WS, Xiao J, Li YQ, Liu L, Zhu CB, Tan KR, Deng Y, Yuan WZ, Liu M, Wu X (2006) hnulp1, a basic helix-loop-helix protein with a novel transcriptional repressive domain, inhibits transcriptional activity of serum response factor. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 343:973–981
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Deng Y, Nie DS, Wang J, Tan XJ, Nie ZY, Yang HM, Hu LS, Lu GX (2005) Molecular cloning of MSRG-11 gene related to apoptosis of mouse spermatogenic cells. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 37(3):159–166
Miura M, Sasagawa I, Suzuki Y, Nakada T, Fujii J (2002) Apoptosis and expression of apoptosis related genes in the mouse testis following heat exposure. Fertil Steril 77(4):787–793
Ai J, Wang Y, Tan K, Deng Y, Luo N, Yuan W, Wang Z, Li Y, Wang Y, Mo X, Zhu C, Yin Z, Liu M, Wu X (2008) A human homolog of mouse Lbh gene, hLBH, expresses in heart and activates SRE and AP-1 mediated MAPK signaling pathway. Mol Biol Rep 35(2):179–187
Kobe B, Kajava AV (2001) The leucine-rich repeat as a protein recognition motif. Curr Opin Struct Biol 11(6):725–732
Kajava AV (1998) Structural diversity of leucine-rich repeat proteins. J Mol Biol 277:519–527
Kobe B, Kajava AV (2001) The leucine-rich repeat as a protein recognition motif. Curr Opin Struct Biol 11(6):725–732
Senoo M, Hoshino S, Mochida N, Mochida N, Matsumura Y, Habu S (2002) Identification of a novel protein p59(scr), which is expressed at specific stages of mouse spermatogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 292(4):992–998
Allan DJ, Harmon BV, Roberts SA (1992) Spermatogonial apoptosis has three morphologically recognizable phases and shows no circadian rhythm during normal spermatogenesis in the rat. Cell Prolif 25(3):241–250
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to all members of the Center for Heart Development, College of Life Sciences, in Hunan Normal University, for their excellent technical assistance and encouragement. This study was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 30971570, 31171402, 31071999, 81170088, 31172044, 81170229, 81000035, 31171196), National Basic Research Program of China (2005 CB522505) and the Cooperative Innovation Center of Engineering and New Products for Developmental Biology of Hunan Province (20134486).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Tingfang Chen, Zhigang Jiang and Wei Xu these authors contributed equally to the work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, T., Jiang, Z., Xu, W. et al. Expression and identification of a novel gene Spata34 in mouse spermatogenic cells. Mol Biol Rep 41, 1683–1691 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-013-3017-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-013-3017-1