Abstract
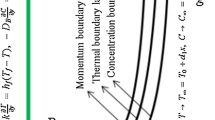
Electrical sensor has been considered in the current attempt. Combination of buoyancy, electric and radiative forces has been included in the governing equations. Convective flow attenuation with insertion of electric field and such force permits to control the style of the flow. Outputs have been illustrated in terms of contours and distributions. The increment of Nu corresponding to increasing permeability is less than that obtained with the rise of voltage. Nu increases with rise of shape factor which is attributed to easier nanoparticles transportation. Growth of radiation term makes Nu to augment, and impact of voltage become stronger.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Manh TD, Nam ND, Abdulrahman GK, Moradi R, Babazadeh H. Impact of MHD on hybrid nanomaterial free convective flow within a permeable region. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-09008-8.
Sheikholeslami M, Rezaeianjouybari B, Darzi M, Shafee A, Li Z, Nguyen TK. Application of nano-refrigerant for boiling heat transfer enhancement employing an experimental study. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2019;141:974–80.
Li Y, Aski FS, Barzinjy AA, Dara RN, Shafee A, Tlili I. Nanomaterial thermal treatment along a permeable cylinder. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08706-7.
Sheikholeslami M, Jafaryar M, Hedayat M, Shafee A, Li Z, Nguyen TK, Bakouri M. Heat transfer and turbulent simulation of nanomaterial due to compound turbulator including irreversibility analysis. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2019;137:1290–300.
Tlili I, Alkanhal TA, Othman M, Dara RN, Shafee A. Water management and desalination in KSA view 2030: case study of solar humidification and dehumidification system. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08700-z.
Sheikholeslami M, Jafaryar M, Shafee A, Li Z, Haq R. Heat transfer of nanoparticles employing innovative turbulator considering entropy generation Int J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019;136:1233–40.
Alrobaian AA, Alsagri AS, Ali JA, Hamad SM, Shafee A, Nguyen TK, Li Z. Investigation of convective nanomaterial flow and exergy drop considering CVFEM within a porous tank. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08564-3.
Sheikholeslami M, Haq R, Shafee A, Li Z. Heat transfer behavior of nanoparticle enhanced PCM solidification through an enclosure with V shaped fins. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2019;130:1322–42.
Manh TD, Nam ND, Abdulrahman GK, Shafee A, Shamlooei M, Babazadeh H, Jilani AK, Tlili I. Effect of radiative source term on the behavior of nanomaterial with considering Lorentz forces. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-09077-9.
Sheikholeslami M, Haq R, Shafee A, Li Z, Elaraki YG, Tlili I. Heat transfer simulation of heat storage unit with nanoparticles and fins through a heat exchanger. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2019;135(2019):470–8.
Shafee A, Sheikholeslami M, Jafaryar M, Babazadeh H. Irreversibility of hybrid nanoparticles within a pipe fitted with turbulator. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-09248-8.
Sheikholeslami M. Effect of uniform suction on nanofluid flow and heat transfer over a cylinder. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng. 2015;37:1623–33.
Sheikholeslami M, Arabkoohsar A, Shafee A, Ismail KAR. Second law analysis of a porous structured enclosure with nano-enhanced phase change material and under magnetic force. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08979-y.
Li F, Sheikholeslami M, Dara RN, Jafaryar M, Shafee A, Nguyen-Thoi T, Li Z. Numerical study for nanofluid behavior inside a storage finned enclosure involving melting process. J Mol Liq. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.111939.
Gao W, Wang WF. The eccentric connectivity polynomial of two classes of nanotubes. Chaos Solitons Fractals. 2016;89:290–4.
Wang R, Sheikholeslami M, Mahmood BS, Shafee A, Nguyen-Thoi T. Simulation of triplex-tube heat storage including nanoparticles, solidification process. J Mol Liq. 2019;296:111731.
Sheikholeslami M, Seyednezhad M. Nanofluid heat transfer in a permeable enclosure in presence of variable magnetic field by means of CVFEM. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;114:1169–80.
Farshad SA, Sheikholeslami M. Numerical examination for entropy generation of turbulent nanomaterial flow using complex turbulator in a solar collector. Phys A Stat Mech Appl. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2019.123951.
Gao W, Yan L, Shi L. Generalized Zagreb index of polyomino chains and nanotubes. Optoelectron Adv Mater Rapid Commun. 2017;11(1–2):119–24.
Sheikholeslami M, Shehzad SA. CVFEM simulation for nanofluid migration in a porous medium using Darcy model. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;122:1264–71.
Shafee A, Sheikholeslami M, Jafaryar M, Babazadeh H. Utilizing copper oxide nanoparticles for expedition of solidification within a storage system. J Mol Liq. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.112371.
Sheikholeslami M, Keshteli AN, Babazadeh H. Nanoparticles favorable effects on performance of thermal storage units. J Mol Liq. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.112329.
Gao W, Wang WF. The vertex version of weighted wiener number for bicyclic molecular structures. Comput Math Methods Med 2015, Article ID 418106, 10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/418106.
Rezaeianjouybari B, Sheikholeslami M, Shafee A, Babazadeh H. A novel bayesian optimization for flow condensation enhancement using nanorefrigerant: a combined analytical and experimental study. Chem Eng Sci. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2019.115465.
Rabbi KM, Sheikholeslami M, Karim A, Shafee A, Li Z, Tlili I. Prediction of MHD flow and entropy generation by Artificial Neural Network in square cavity with heater-sink for nanomaterial. Physica A Stat Mech Appl Physica A. 2020;541:123520.
Keshteli AN, Sheikholeslami M. Effects of Wavy Wall and Y shaped fins on solidification of PCM with dispersion of Al2O3 nanoparticle. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08807-3.
Nguyen TK, Usman M, Sheikholeslami M, Haq R, Shafee A, Jilani AK, Tlili I. Numerical analysis of MHD flow and nanoparticle migration within a permeable space containing non-equilibrium model. Physica A Stat Mech Appl. 2020;537:122459.
Sheikholeslami M, Vajravelu K. Nanofluid flow and heat transfer in a cavity with variable magnetic field. Appl Math Comput. 2017;298:272–82.
Sheikholeslami M, Rokni HB. Magnetic nanofluid flow and convective heat transfer in a porous cavity considering Brownian motion effects. Phys Fluids. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5012517.
Sheikholeslami M, Rokni HB. Influence of EFD viscosity on nanofluid forced convection in a cavity with sinusoidal wall. J Mol Liq. 2017;232:390–5.
Gao W, Zhu LL, Wang KY. Ranking based ontology scheming using eigenpair computation. J Intell Fuzzy Syst. 2016;31(4):2411–9.
Sheikholeslami M, Arabkoohsar A, Khan I, Shafee A, Li Z. Impact of Lorentz forces on Fe3O4–water ferrofluid entropy and exergy treatment within a permeable semi annulus. J Clean Prod. 2019;221:885–98.
Sheikholeslami M, Mahian O. Enhancement of PCM solidification using inorganic nanoparticles and an external magnetic field with application in energy storage systems. J Clean Prod. 2019;215:963–77.
Ma X, Sheikholeslami M, Jafaryar M, Shafee A, Nguyen-Thoi T, Li Z. Solidification inside a clean energy storage unit utilizing phase change material with copper oxide nanoparticles. J Clean Prod. 2020;245:118888. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118888.
Sheikholeslami M, Shehzad SA, Li Z, Shafee A. Numerical modeling for alumina nanofluid magnetohydrodynamic convective heat transfer in a permeable medium using Darcy law. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;127:614–22.
Jouybari BR, Osgouie KG, Meghdari A. Optimization of kinematic redundancy and workspace analysis of a dual-arm cam-lock robot. Robotica. 2016;34(1):23–42.
Gao W, Zhu LL, Wang KY. Ontology sparse vector learning algorithm for ontology similarity measuring and ontology mapping via ADAL technology. Int J Bifurc Chaos. 2015;25(14):1540034. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218127415400349.
Sheikholeslami M, Li Z, Shafee A. Lorentz forces effect on NEPCM heat transfer during solidification in a porous energy storage system. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;127:665–74.
Rezaeianjouybari B, Osgouie BG, Meghdari A. Employing neural networks for manipulability optimization of the dual-arm cam-lock robot. In Proceedings (IMECE) of ASME international mechanical engineering congress and exposition, vol 8.
Gao W, Zhu LL. Gradient learning algorithms for ontology computing. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2014, Article ID 438291, 12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/438291.
Sheikholeslami M, Jafaryar M, Ali JA, Hamad Sm, Divsalar A, Shafee A, Nguyen-Thoi T, Li Z. Simulation of turbulent flow of nanofluid due to existence of new effective turbulator involving entropy generation. J Mol Liq. 2019;291:111283.
Sheikholeslami M, Ghasemi A, Li Z, Shafee A, Saleem S. Influence of CuO nanoparticles on heat transfer behavior of PCM in solidification process considering radiative source term. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;126:1252–64.
Sheikholeslami M, Jafaryar M, Saleem S, Li Z, Shafee A, Jiang Y. Nanofluid heat transfer augmentation and exergy loss inside a pipe equipped with innovative turbulators. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;126:156–63.
Hedayat M, Sheikholeslami M, Shafee A, Nguyen-Thoi T, Henda MB, Tlili I, Li Z. Investigation of nanofluid conduction heat transfer within a triplex tube considering solidification. J Mol Liq. 2019;290:111232.
Raju CSK, Hoque MM, Anika NN, Mamatha SU, Sharma P. Natural convective heat transfer analysis of MHD unsteady Carreau nanofluid over a cone packed with alloy nanoparticles. Powder Technol. 2017;317:408–16.
Qi C, Wang G, Yang L, Wan Y, Rao Z. Two-phase lattice Boltzmann simulation of the effects of base fluid and nanoparticle size on natural convection heat transfer of nanofluid. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;105:664–72.
Putra N, Roetzel W, Das SK. Natural convection of nano-fluids. Heat Mass Transf. 2003;39:775–84.
Sheikholeslami M, Arabkoohsar A, Babazadeh H. Modeling of nanomaterial treatment through a porous space including magnetic forces. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08878-2.
Sheikholeslami M, Darzi M, Li Z. Experimental investigation for entropy generation and exergy loss of nano-refrigerant condensation process. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;125:1087–95.
Sheikholeslami M, Shehzad SA, Li Z. Water based nanofluid free convection heat transfer in a three dimensional porous cavity with hot sphere obstacle in existence of Lorenz forces. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;125:375–86.
Sheikholeslami M, Gerdroodbary MB, Shafee A, Tlili I. Hybrid nanoparticles dispersion into water inside a porous wavy tank involving magnetic force. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08858-6.
Gao W. Three algorithms for graph locally harmonious colouring. J Differ Equ Appl. 2017;23(1–2):8–20.
Sheikholeslami M, Ghasemi A. Solidification heat transfer of nanofluid in existence of thermal radiation by means of FEM. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;123:418–31.
Sheikholeslami M, Jafaryar M, Li Z. Nanofluid turbulent convective flow in a circular duct with helical turbulators considering CuO nanoparticles. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;124:980–9.
Farshad SA, Sheikholeslami M. FVM modeling of nanofluid forced convection through a solar unit involving MCTT. Int J Mech Sci. 2019;159:126–39.
Qin Y, Zhang M, Hiller JE. Theoretical and experimental studies on the daily accumulative heat gain from cool roofs. Energy. 2017;129:138–47.
Farshad SA, Sheikholeslami M. Nanofluid flow inside a solar collector utilizing twisted tape considering exergy and entropy analysis. Renew Energy. 2019;141:246–58.
Sheikholeslami M, Darzi M, Sadoughi MK. Heat transfer improvement and Pressure Drop during condensation of refrigerant-based Nanofluid: an experimental procedure. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;122:643–50.
Gao W, Liang L, Xu TW, Zhou JX. Degree conditions for fractional (g, f, n’, m)-critical deleted graphs and fractional ID-(g, f, m)-deleted graphs. Bull Malays Math Sci Soc. 2016;39:315–30.
Farshad SA, Sheikholeslami M, Hosseini SH, Shafee A, Li Z. Nanofluid turbulent forced convection through a solar flat plate collector with Al2O3 nanoparticles. Microsyst Technol. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-019-04430-2.
Sheikholeslami M, Shehzad SA. Simulation of water based nanofluid convective flow inside a porous enclosure via Non-equilibrium model. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;120:1200–12.
Farshad SA, Sheikholeslami M. Turbulent nanofluid flow through a solar collector influenced by multi-channel twisted tape considering entropy generation. Eur Phys J Plus. 2019;134:149. https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2019-12606-2.
Qin Y, He Y, Wu B, Ma S, Zhang X. Regulating top albedo and bottom emissivity of concrete roof tiles for reducing building heat gains. Energy Build. 2017;156:218–24.
Gao W, Wang WF. Toughness and fractional critical deleted graph. Util Math. 2015;98:295–310.
Sheikholeslami M. Finite element method for PCM solidification in existence of CuO nanoparticles. J Mol Liq. 2018;265:347–55.
Sheikholeslami M. Solidification of NEPCM under the effect of magnetic field in a porous thermal energy storage enclosure using CuO nanoparticles. J Mol Liq. 2018;263:303–15.
Qin Y. Pavement surface maximum temperature increases linearly with solar absorption and reciprocal thermal inertial. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2016;97:391–9.
Sheikholeslami M. Influence of magnetic field on Al2O3–H2O nanofluid forced convection heat transfer in a porous lid driven cavity with hot sphere obstacle by means of LBM. J Mol Liq. 2018;263:472–88.
Sheikholeslami M. Investigation of Coulomb forces effects on Ethylene glycol based nanofluid laminar flow in a porous enclosure. Appl Math Mech. 2018;39(9):1341–52.
Gao W. A sufficient condition for a graph to be fractional (a, b, n)-critical deleted graph. ARS Combin. 2015;119:377–90.
Rafatijo H, Monge-Palacios M, Thompson DL. Identifying collisions of various molecularities in molecular dynamics simulations. J Phys Chem A. 2019;123(6):1131–9. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpca.8b11686.
Rafatijo H, Thompson DL. General application of Tolman’s concept of activation energy. J Chem Phys. 2017;147:224111017. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5009751.
Qin Y, Liang J, Tan K, Li F. A side by side comparison of the cooling effect of building blocks with retro-reflective and diffuse-reflective walls. Sol Energy. 2016;133:172–9.
Gao W, Gao Y. Toughness condition for a graph to be a fractional (g,f,n)-critical deleted graph. Sci World J. 2014, Article ID 369798, 7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/369798.
Sheikholeslami M. Numerical simulation for solidification in a LHTESS by means of Nano-enhanced PCM. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng. 2018;86:25–41.
Sheikholeslami M. Numerical modeling of Nano enhanced PCM solidification in an enclosure with metallic fin. J Mol Liq. 2018;259:424–38.
Qin Y, Liang J, Yang H, Deng Z. Gas permeability of pervious concrete and its implications on the application of pervious pavements. Measurement. 2016;78:104–10.
Sheikholeslami M. CuO-water nanofluid flow due to magnetic field inside a porous media considering Brownian motion. J Mol Liq. 2018;249:921–9.
Qin Y, Hiller JE. Understanding pavement-surface energy balance and its implications on cool pavement development. Energy Build. 2014;85:389–99.
Sheikholeslami M. Numerical investigation for CuO–H2O nanofluid flow in a porous channel with magnetic field using mesoscopic method. J Mol Liq. 2018;249:739–46.
Gao W, Liang L, Xu TW, Zhou JX. Tight toughness condition for fractional (g, f, n)-critical graphs. J Korean Math Soc. 2014;51(1):55–65.
Sheikholeslami M. Magnetic field influence on CuO–H2O nanofluid convective flow in a permeable cavity considering various shapes for nanoparticles. Int J Hydrogen Energy. 2017;42:19611–21.
Qin Y. Urban canyon albedo and its implication on the use of reflective cool pavements. Energy Build. 2015;96:86–94.
Sheikholeslami M. Lattice Boltzmann Method simulation of MHD non-Darcy nanofluid free convection. Phys B. 2017;516:55–71.
Qin Y, He H. A new simplified method for measuring the albedo of limited extent targets. Sol Energy. 2017;157(Supplement C):1047–55.
Sheikholeslami M. Influence of magnetic field on nanofluid free convection in an open porous cavity by means of Lattice Boltzmann Method. J Mol Liq. 2017;234:364–74.
Qin Y, Zhang M, Mei G. A new simplified method for measuring the permeability characteristics of highly porous media. J Hydrol. 2018;562:725–32.
Sheikholeslami M. Magnetohydrodynamic nanofluid forced convection in a porous lid driven cubic cavity using Lattice Boltzmann Method. J Mol Liq. 2017;231:555–65.
Sheikholeslami M. CuO-water nanofluid free convection in a porous cavity considering Darcy law. Eur Phys J Plus. 2017;132:55. https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2017-11330-3.
Sheikholeslami M, Arabkoohsar A, Jafaryar M. Impact of a helical-twisting device on nanofluid thermal hydraulic performance of a tube. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08683-x.
Sheikholeslami M. Magnetic field influence on nanofluid thermal radiation in a cavity with tilted elliptic inner cylinder. J Mol Liq. 2017;229:137–47.
Seyednezhad M, Sheikholeslami M, Ali JA, Shafee A, Nguyen TK. Nanoparticles for water desalination in solar heat exchanger. Rev J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08634-6.
Yang L, Mao M, Huang JN, Ji W. Enhancing the thermal conductivity of SAE 50 engine oil by adding zinc oxide nano-powder: an experimental study. Powder Technol. 2019;356:335–41.
Sheikholeslami M. Influence of Lorentz forces on nanofluid flow in a porous cylinder considering Darcy model. J Mol Liq. 2017;225:903–12.
Sheikholeslami M, Sheremet MA, Shafee A, Li Z. CVFEM approach for EHD flow of nanofluid through porous medium within a wavy chamber under the impacts of radiation and moving walls. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08235-3.
Sheikholeslami M. Influence of Coulomb forces on Fe3O4–H2O nanofluid thermal improvement. Int J Hydrogen Energy. 2017;42:821–9.
Sheikholeslami M. New computational approach for exergy and entropy analysis of nanofluid under the impact of Lorentz force through a porous media. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng. 2019;344:319–33.
Farshad SA, Sheikholeslami M. Simulation of exergy loss of nanomaterial through a solar heat exchanger with insertion of multi-channel twisted tape. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;138:795–804. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08156-1.
Gao W, Wang WF. Second atom-bond connectivity index of special chemical molecular structures. J Chem 2014, Article ID 906254, 8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/906254.
Sheikholeslami M, Rokni HB. Numerical modeling of nanofluid natural convection in a semi annulus in existence of Lorentz force. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng. 2017;317:419–30.
Hwang KS, Jang SP. Choi S (2009) Flow and convective heat transfer characteristics of water-based Al2O3 nanofluids in fully developed laminar flow regime. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2009;52(1):193–9.
Qi C, Tang J, Ding Z, Yan Y, Guo L, Ma Y. Effects of rotation angle and metal foam on natural convection of nanofluids in a cavity under an adjustable magnetic field. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2019;109:104349.
Sheikholeslami M, Zeeshan A. Analysis of flow and heat transfer in water based nanofluid due to magnetic field in a porous enclosure with constant heat flux using CVFEM. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng. 2017;320:68–81.
Sheikholeslami M, Shehzad SA, Abbasi FM, Li Z. Nanofluid flow and forced convection heat transfer due to Lorentz forces in a porous lid driven cubic enclosure with hot obstacle. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng. 2018;338:491–505.
Yang L, Du K. A comprehensive review on the natural, forced and mixed convection of non-Newtonian fluids (nanofluids) inside different cavities. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08987-y.
Sheikholeslami M, Jafaryar M, Shafee A, Li Z. Nanofluid heat transfer and entropy generation through a heat exchanger considering a new turbulator and CuO nanoparticles. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7866-7.
Yang L, Ji W, Huang JN, Xu G. An updated review on the influential parameters on thermal conductivity of nano-fluids. J Mol Liq. 2019;296:111780.
Qin Y, Zhao Y, Chen X, Wang L, Li F, Bao T. Moist curing increases the solar reflectance of concrete. Constr Build Mater. 2019;215:114–8.
Sheikholeslami M, Shehzad SA. Magnetohydrodynamic nanofluid convection in a porous enclosure considering heat flux boundary condition. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;106:1261–9.
Sheikholeslami M, Gerdroodbary MB, Moradi R, Shafee A, Li Z. Application of neural network for estimation of heat transfer treatment of Al2O3–H2O nanofluid through a channel. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng. 2019;344:1–12.
Vo DD, Hedayat M, Ambreen T, Shehzad SA, Sheikholeslami M, Shafee A, Nguyen TK. Effectiveness of various shapes of Al2O3 nanoparticles on the MHD convective heat transportation in porous medium: CVFEM modeling. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08501-4.
Qin Y. A review on the development of cool pavements to mitigate urban heat island effect. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2015;52:445–59.
Sheikholeslami M, Vajravelu K, Rashidi MM. Forced convection heat transfer in a semi annulus under the influence of a variable magnetic field. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2016;92:339–48.
Sheikholeslami M, Ellahi R. Three dimensional mesoscopic simulation of magnetic field effect on natural convection of nanofluid. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2015;89:799–808.
Aly AM, Raizah ZAS, Sheikholeslami M. Analysis of mixed convection in a sloshing porous cavity filled with a nanofluid using ISPH method. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08575-0.
Qin Y, He Y, Hiller JE, Mei G. A new water-retaining paver block for reducing runoff and cooling pavement. J Clean Prod. 2018;199:948–56.
Nguyen TK, Sheikholeslami M, Jafaryar M, Shafee A, Li Z, Mouli KVVC, Tlili I. Design of heat exchanger with combined turbulator. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08401-7.
Qin Y, Hiller JE, Meng D. Linearity between pavement thermophysical properties and surface temperatures. J Mater Civ Eng. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0002890.
Sheikholeslami M, Shehzad SA. Thermal radiation of ferrofluid in existence of Lorentz forces considering variable viscosity. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;109:82–92.
Sheikholeslami M, Rokni HB. Nanofluid two phase model analysis in existence of induced magnetic field. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;107:288–99.
Li Z, Sheikholeslami M, Jafaryar M, Shafee A. Time dependent heat transfer simulation for NEPCM solidification inside a channel. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08140-9.
Qin Y, Luo J, Chen Z, Mei G, Yan L-E. Measuring the albedo of limited-extent targets without the aid of known-albedo masks. Sol Energy. 2018;171:971–6.
Sheikholeslami M, Hayat T, Alsaedi A. Numerical study for external magnetic source influence on water based nanofluid convective heat transfer. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;106:745–55.
Sheikholeslami M, Hayat T, Alsaedi A. MHD free convection of Al2O3–water nanofluid considering thermal radiation: a numerical study. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2016;96:513–24.
Jafaryar M, Sheikholeslami M, Li Z, Moradi R. Nanofluid turbulent flow in a pipe under the effect of twisted tape with alternate axis. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;135(1):305–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7093-2.
Qin Y, He H, Ou X, Bao T. Experimental study on darkening water-rich mud tailings for accelerating desiccation. J Clean Prod. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118235.
Sheikholeslami M, Sadoughi M. Mesoscopic method for MHD nanofluid flow inside a porous cavity considering various shapes of nanoparticles. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;113:106–14.
Sheikholeslami M, Bhatti MM. Forced convection of nanofluid in presence of constant magnetic field considering shape effects of nanoparticles. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;111:1039–49.
Sheikholeslami M, Rokni HB. Melting heat transfer influence on nanofluid flow inside a cavity in existence of magnetic field. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;114:517–26.
Sheikholeslami M, Shehzad SA. CVFEM for influence of external magnetic source on Fe3O4–H2O nanofluid behavior in a permeable cavity considering shape effect. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;115:180–91.
Sheikholeslami M, Bhatti MM. Active method for nanofluid heat transfer enhancement by means of EHD Int J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017;109:115–22.
Alkanhal TA, Sheikholeslami M, Usman M, Haq R, Shafee A, Al-Ahmadi AS, Tlili I. Thermal management of MHD nanofluid within the porous medium enclosed in a Wavy Shaped cavity with square obstacle in the presence of radiation heat source. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2019;139:87–94.
Sheikholeslami M, Sadoughi MK. Simulation of CuO- water nanofluid heat transfer enhancement in presence of melting surface. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;116:909–19.
Sheikholeslami M, Rokni HB. Simulation of nanofluid heat transfer in presence of magnetic field: a review. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;115:1203–33.
Sheikholeslami M, Hayat T, Alsaedi A. On simulation of nanofluid radiation and natural convection in an enclosure with elliptical cylinders. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;115:981–91.
Sheikholeslami M. Numerical approach for MHD Al2O3-water nanofluid transportation inside a permeable medium using innovative computer method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng. 2018;344:306–18.
Sheikholeslami M. Application of Darcy law for nanofluid flow in a porous cavity under the impact of Lorentz forces. J Mol Liq. 2018;266:495–503.
Sheikholeslami M, Rokni HB. Numerical simulation for impact of Coulomb force on nanofluid heat transfer in a porous enclosure in presence of thermal radiation. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;118:823–31.
Sheikholeslami M. Magnetic source impact on nanofluid heat transfer using CVFEM. Neural Comput Appl. 2018;30(4):1055–64.
Sheikholeslami M, Shehzad SA. Numerical analysis of Fe3O4–H2O nanofluid flow in permeable media under the effect of external magnetic source. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;118:182–92.
Oueslati FS, Bennacer R, ElGanaoui M, ElCafsi A. Competition between the lid driven and the natural convection of nanofluids taking into consideration the Soret effect. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;114:1341–9.
Nithyadevi N, Begum AS, Oztop HF, Abu-Hamdeh N. Mixed convection analysis in heat transfer enhancement of a nanofluid filled porous enclosure with various wall speed ratios. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;113:716–29.
Khanafer K, Vafai K, Lightstone M. Buoyancy-driven heat transfer enhancement in a two-dimensional enclosure utilizing nanofluids. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2003;446:3639–53.
Sheikholeslami M, Seyednezhad M. Simulation of nanofluid flow and natural convection in a porous media under the influence of electric field using CVFEM. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;120:772–81.
Sheikholeslami M, Hayat T, Alsaedi A, Abelman S. Numerical analysis of EHD nanofluid force convective heat transfer considering electric field dependent viscosity. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;108:2558–65.
Sheikholeslami M. Numerical investigation of nanofluid free convection under the influence of electric field in a porous enclosure. J Mol Liq. 2018;249:1212–21.
Sheikholeslami M. Application of control volume based finite element method (CVFEM) for nanofluid flow and heat transfer. Elsevier; 2019. ISBN: 9780128141526.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, G., Shafee, A., Nam, N.D. et al. Coulomb forces impacts on nanomaterial transportation within porous tank with lid walls. J Therm Anal Calorim 143, 4249–4260 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09407-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09407-2