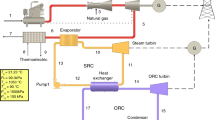
Abstract
In this paper, a typical combined cycle power generation unit in Iran is simulated by a mathematical method in order to perform sensitivity analysis on environmental emission and electricity price. The results of this study demonstrate that the efficiency of the power plant depends on both gas turbine design parameters such as gas turbine inlet temperature, compressor pressure ratio and steam cycle design parameters such as HRSG pinch point temperature, condenser pressure. The results demonstrate that an increase in TIT and compressor pressure ratio have a significant effect on exergy efficiency and destruction.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(c\) :
-
Cost per exergy unit ($ MJ−1)
- \(c_{\text{f}}\) :
-
Cost of fuel per energy unit ($ MJ−1)
- \(\dot{C}\) :
-
Cost flow rate ($ s−1)
- \(c_{\text{p}}\) :
-
Specific heat at constant pressure (kJ kg−1 K−1)
- \({\text{CRF}}\) :
-
Capital recovery factor
- \(E\) :
-
Exergy MJ kg−1
- f :
-
Exergoeconomic factor
- \(\dot{E}\) :
-
Exergy flow rate (MW)
- \(\dot{E}_{\text{D}}\) :
-
Exergy destruction rate (MW)
- \({\dot{\text{E}}}_{\text{W}}\) :
-
Exergy rate of work (MW)
- \(e\) :
-
Specific exergy (kJ kg−1)
- \({\text{e}}_{\text{f}}\) :
-
Chemical exergy of the fuel (kJ kg−1)
- \(i\) :
-
Annual interest rate (%)
- \(h\) :
-
Specific enthalpy (kJ kg−1)
- \(h_{0}\) :
-
Specific enthalpy at environmental state (kJ kg−1)
- LHV:
-
Lower heating value (kJ kg−1)
- \(\dot{m}\) :
-
Mass flow rate (kg s−1)
- \(n\) :
-
Number of years
- \(N\) :
-
Number of hours of plant operation per year
- \({\text{PP}}\) :
-
Pinch point
- \(\dot{Q}\) :
-
Heat transfer rate (kW)
- \(r_{\text{AC}}\) :
-
Compressor pressure ratio
- \(s\) :
-
Specific entropy (kJ kg−1 K−1)
- \(s_{0}\) :
-
Specific entropy at environmental state (kJ kg−1 K−1)
- \(T_{0}\) :
-
Absolute temperature (K)
- \(\dot{W}_{\text{net}}\) :
-
Net power output (MW)
- \(Z\) :
-
Capital cost of a component ($)
- \(\dot{Z}\) :
-
Capital cost rate ($ s−1)
- \(\eta\) :
-
Isentropic efficiency
- \(\xi\) :
-
Coefficient of fuel chemical exergy
- \(\sigma\) :
-
Standard deviation
- \(\varPhi\) :
-
Maintenance factor
- π :
-
Dimensionless pressure values
- θ :
-
Dimensionless temperature values
- a:
-
Air
- AC:
-
Air compressor
- CC:
-
Combustion chamber
- ch:
-
Chemical
- Cond:
-
Condenser
- D:
-
Exergy destruction
- f:
-
Fuel
- GT:
-
Gas turbine
- HP:
-
High pressure
- HRSG:
-
Heat recovery steam generator
- i:
-
ith trial vector
- k:
-
kth component
- LP:
-
Low pressure
- ph:
-
Physical
- tot:
-
Total
- ST:
-
Steam turbine
- sys:
-
System
- w:
-
Water
References
Hoseinzadeh S, Hadi Zakeri M, Shirkhani A, Chamkha AJ. Analysis of energy consumption improvements of a zero-energy building in a humid mountainous area. J Renew Sustain Energy. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5046512.
Hoseinzadeh S, Azadi R. Simulation and optimization of a solar-assisted heating and cooling system for a house in Northern of Iran. J Renew Sustain Energy. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5000288.
Yousef Nezhad ME, Hoseinzadeh S. Mathematical modelling and simulation of a solar water heater for an aviculture unit using MATLAB/SIMULINK. J Renew Sustain Energy. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5010828.
Hoseinzadeh S, Heyns PS, Chamkha AJ, Shirkhani A. Thermal analysis of porous fins enclosure with the comparison of analytical and numerical methods. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08203-x.
Hoseinzadeh S, Ghasemiasl R, Havaei D, Chamkha AJ. Numerical investigation of rectangular thermal energy storage units with multiple phase change materials. J Mol Liq. 2018;271:655–60.
Hoseinzadeh S, Moafi A, Shirkhani A, Chamkha AJ. Numerical validation heat transfer of rectangular cross-section porous fins. J Thermophys Heat Transf 1–7 (2019).
Yari A, Hosseinzadeh S, Golneshan AA, Ghasemiasl R. Numerical simulation for thermal design of a gas water heater with turbulent combined convection. In: ASME/JSME/KSME 2015 joint fluids engineering conference, AJKFluids 2015 (2015), vol. 1.
Ghasemiasl R, Hoseinzadeh S, Javadi MA. Numerical analysis of energy storage systems using two phase-change materials with nanoparticles. J Thermophys Heat Transf. 2018;32:440–8.
Ahmadi P, Dincer I. (2018). Exergoeconomics. In Comprehensive Energy Systems (Vol. 1–5, pp. 340–376). Elsevier Inc. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-809597-3.00107-3.
Ahmadi P, Dincer I. Thermodynamic and exergoenvironmental analyses, and multi-objective optimization of a gas turbine power plant. Appl Therm Eng. 2011;31:2529–40.
Ahmadi P, Dincer I. Thermodynamic analysis and thermoeconomic optimization of a dual pressure combined cycle power plant with a supplementary firing unit. Energy Convers Manag. 2011;52:2296–308.
Khalilarya S, Jafarmadar S, Abadi A. Exegetic modeling and second law based optimization of cogeneration heat and power system using evolutionary algorithm (genetic algorithm) (pp. 17–25). ASME International; (2011). https://doi.org/10.1115/ihtc14-22113.
Sahoo PK. Exergoeconomic analysis and optimization of a cogeneration system using evolutionary programming. Appl Therm Eng. 2008;28:1580–8.
Boyaghchi FA, Heidarnejad P. Thermoeconomic assessment and multi objective optimization of a solar micro CCHP based on organic rankine cycle for domestic application. Energy Convers Manag. 2015;97:224–34.
Boyaghchi FA, Molaie H. Sensitivity analysis of exergy destruction in a real combined cycle power plant based on advanced exergy method. Energy Convers Manag. 2015;99:374–86.
Kwak HY, Kim DJ, Jeon JS. Exergetic and thermoeconomic analyses of power plants. Energy. 2003;28:343–60.
Surendhar A, Sivasubramanian V, Vidhyeswari D, Deepanraj B. Energy and exergy analysis, drying kinetics, modeling and quality parameters of microwave-dried turmeric slices. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;136:185–97.
Matheswaran MM, Arjunan TV, Somasundaram D. Energetic, exergetic and enviro-economic analysis of parallel pass jet plate solar air heater with artificial roughness. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;136:5–19.
Anand S, Tyagi SK. Exergy analysis and experimental study of a vapor compression refrigeration cycle: a technical note. J Therm Anal Calorime. 2012;110:961–71. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-011-1904-z.
Govin OV, Diky VV, Kabo GJ, Blokhin AV. Evaluation of the chemical exergy of fuels and petroleum fractions. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2000;62:123–33.
Murugapoopathi S, Vasudevan D. Energy and exergy analysis on variable compression ratio multi-fuel engine. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;136:255–66.
Singh G, Singh PJ, Tyagi VV, Pandey AK. Thermal and exergoeconomic analysis of a dairy food processing plant. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;136:1365–82.
Saleh S, Pirouzfar V, Alihosseini A. Performance analysis and development of a refrigeration cycle through various environmentally friendly refrigerants. J Thermal Anal Calorim. 2018;136:1817–30.
Si Ningning, Zhao Zhigang, Sheng Su, Han Pengshuai, Sun Zhijun, Jun Xu, Cui Xiaoning, Song Hu, Wang Yi, Jiang Long, Zhou Yingbiao, Chen Gang, Xiang Jun. Exergy analysis of a 1000 MW double reheat ultra-supercritical power plant. Energy Convers Manag. 2017;147:155–65.
Abuelnuor AAA, Saqr KM, Mohieldein SAA, Dafallah KA, Abdullah MM, Nogoud YAM. Exergy analysis of Garri“2”180 MW combined cycle power plant. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2017;79:960–9.
Javadi MA, Hoseinzadeh S, Khalaji M, Ghasemiasl R. Optimization and analysis of exergy, economic, and environmental of a combined cycle power plant. Sādhanā. 2019;44:121.
Lamas WDQ. Exergoeconomic methodology applied to energy efficiency analysis of industrial power transformers. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst. 2013;53:348–56.
Sahraie H, Mirani MR, Ahmadi MH, Ashouri M. Thermo-economic and thermodynamic analysis and optimization of a two-stage irreversible heat pump. Energy Convers Manag. 2015;99:81–91.
Javadi MA, Ghomashi H. Thermodynamics analysis and optimization of abadan combined cycle power plant. Indian J Sci Technol. 2016. https://doi.org/10.17485/ijst/2016/v9i7/87770.
Sahin AZ, Al-Sharafi A, Yilbas BS, Khaliq A. Overall performance assessment of a combined cycle power plant: an exergo-economic analysis. Energy Convers Manag. 2016;116:91–100.
Hoseinzadeh S, Sahebi SAR, Ghasemiasl R, Majidian AR. Experimental analysis to improving thermosyphon (TPCT) thermal efficiency using nanoparticles/based fluids (water). Eur Phys J Plus. 2017;132:197. https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2017-11455-3.
Hosseinzadeh S, Galogahi MR, Bahrami A. Performance prediction of a turboshaft engine by using of one dimensional analysis. Int J Recent Adv Mech Eng. 2014;3:99–108.
Hosseinzadeh S, Bahrami A, Abbasi E, Absalan F. Performance prediction of a turboshaft engine through the use of losses models. Int J Recent Adv Mech Eng. 2014;3:35–45.
Rosen MA, Dincer I, Kanoglu M. Role of exergy in increasing efficiency and sustainability and reducing environmental impact. Energy Policy. 2008;36:128–37.
Ahmadi P, Dincer I, Rosen MA. Exergy, exergoeconomic and environmental analyses and evolutionary algorithm based multi-objective optimization of combined cycle power plants. Energy. 2011;36:5886–98.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Javadi, M.A., Hoseinzadeh, S., Ghasemiasl, R. et al. Sensitivity analysis of combined cycle parameters on exergy, economic, and environmental of a power plant. J Therm Anal Calorim 139, 519–525 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08399-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08399-y